Surface treatment method after nitride material laser lift-off
A laser lift-off and surface treatment technology, used in electrical components, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as cracking, impact on device performance and stability, hinder industrial development and promotion, and reduce cracks or chipping. The probability of cracking, the improvement of composition and roughness, the effect of good market application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] S11. Using MOCVD technology to grow a 10um-thick GaN epitaxial film on a 2-inch 430um-thick sapphire substrate to prepare a sapphire-based GaN composite substrate.
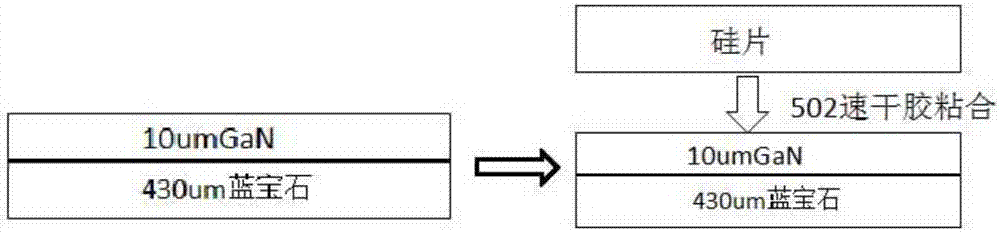
[0048] S12. Use 502 quick-drying adhesive to bond the GaN surface of the silicon wafer and the GaN composite substrate, as attached Figure 3-1 shown.
[0049] S13, using a 248nm wavelength laser to lift off the sapphire substrate, exposing the surface after laser lift off, and obtaining a GaN composite substrate.
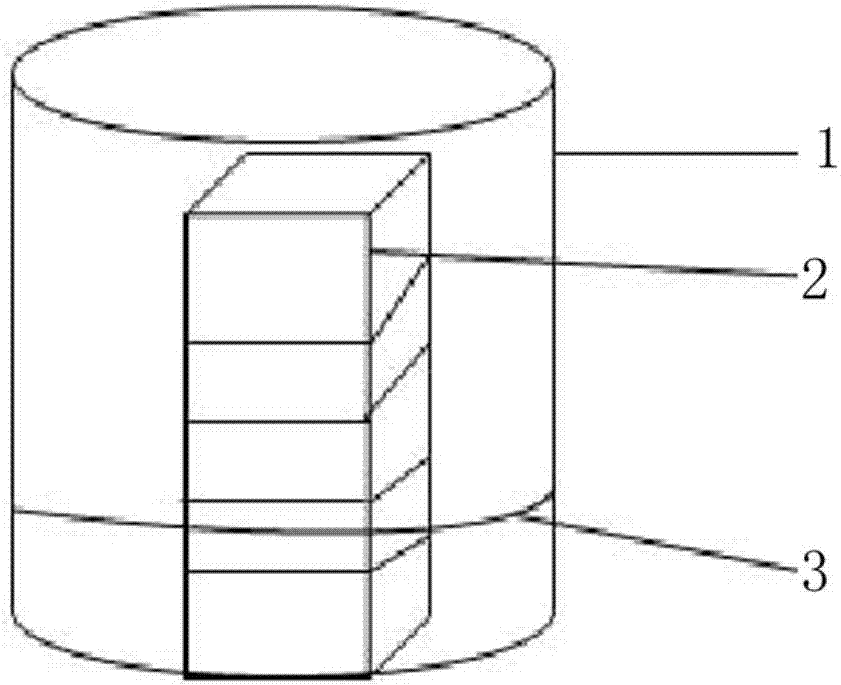
[0050] S14, choose as attached figure 1 For the chamber structure shown, put 300ml of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 37% into the beaker, place the laser-stripped GaN composite substrate 2cm above the liquid surface at the height of the slot, and seal the opening of the beaker with tin foil. After standing still for 40 minutes, use isopropanol, acetone and ultrapure water to perform ultrasonic cleaning, and blow dry with nitrogen gas to complete the atmosphere corrosion treatment of...
Embodiment 2
[0052] S21. Using PVD to grow 25nm AlN as a buffer layer on a 2-inch 430um-thick sapphire substrate, and then using MOCVD epitaxy technology combined with HVPE epitaxy technology to prepare a 20um-thick GaN composite substrate.
[0053] S22, using 502 quick-drying adhesive to bond the quartz glass sheet and the GaN surface of the GaN composite substrate.
[0054] S23. Use a 193nm wavelength laser to lift off the sapphire substrate to expose the surface after laser lift off to obtain a GaN composite substrate, as shown in the attached Pic 4-1 shown.
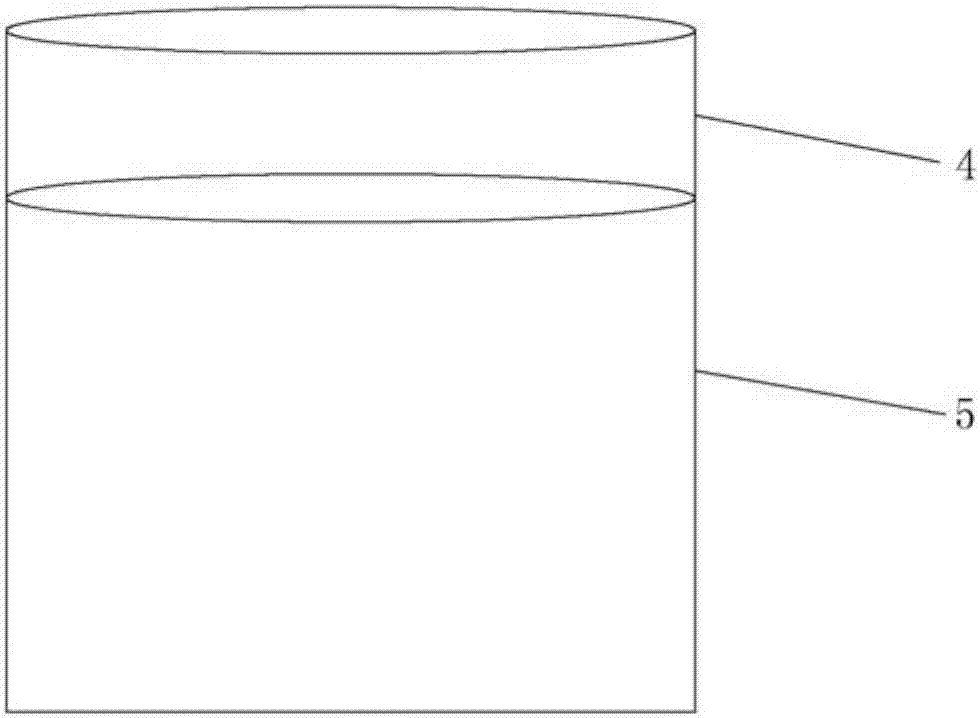
[0055] S24 option attached figure 2 In the chamber structure shown, put the GaN composite substrate into the sealed chamber, close the chamber door, let hydrochloric acid gas flow in, let it stand for 30 minutes, use isopropanol, acetone and ultrapure water to perform ultrasonic cleaning, and blow dry with nitrogen gas. That is, the atmosphere etching treatment on the laser peeled surface is completed. as attached Figure 5-...
Embodiment 3
[0057] S31. Using MOCVD technology to grow a 10um-thick GaN epitaxial film on a 2-inch 430um-thick sapphire substrate to prepare a sapphire-based GaN composite substrate.
[0058] S32. Evaporate an Au film with a thickness of 1 micron on the GaN epitaxial layer and the tungsten-copper (WCu) substrate respectively, and then bond the WCu substrate and the GaN epitaxial layer together at 300°C and a pressure of 10 tons for 120 minutes .
[0059] S33. Using the 248nm wavelength laser lift-off technology to remove the sapphire substrate to expose the surface after laser lift-off. as attached Figure 5-1 shown.
[0060] S34, choose as attached figure 2 Chamber structure shown. Place the laser-stripped GaN composite substrate in the upper and lower fixtures, and fix the fixtures. Put it into a sealed cavity, close the cavity door, let hydrochloric acid gas flow in, let it stand for 20 minutes, use isopropanol, acetone and ultrapure water to perform ultrasonic cleaning, and blow...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com