Fluorescent probe for detecting bivalent copper ions, and preparation method and application of fluorescent probe
A technology of diethylamino and reflux reaction, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, chemical instruments and methods, luminescent materials, etc., can solve the problems of low detection sensitivity, poor selectivity, sensitivity to pH value, etc., and achieve high sensitivity and low detection limit , the effect of fewer synthesis steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
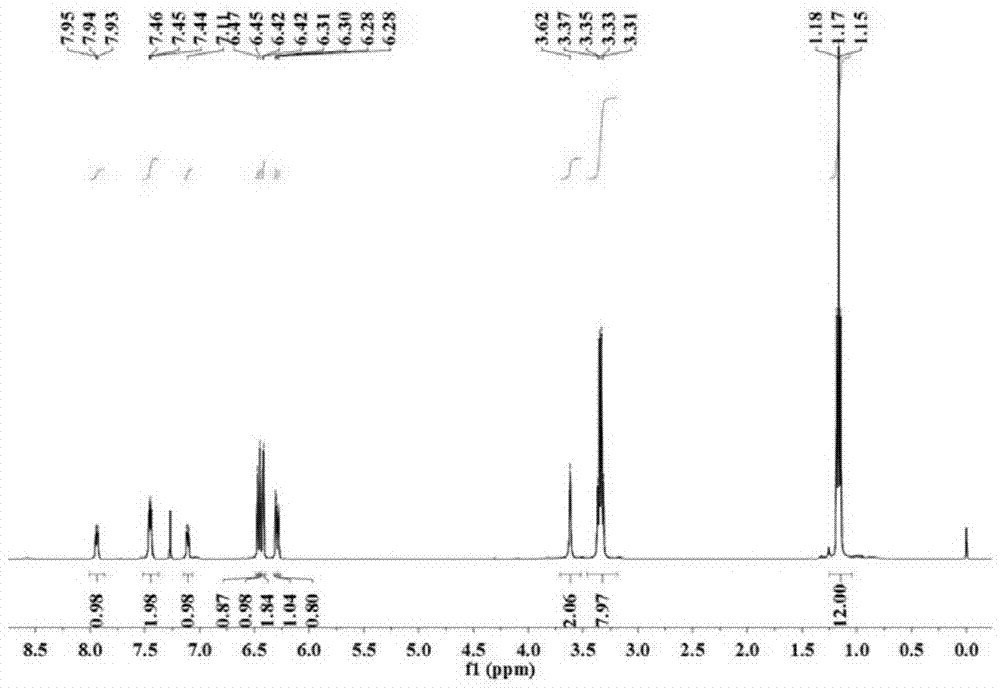
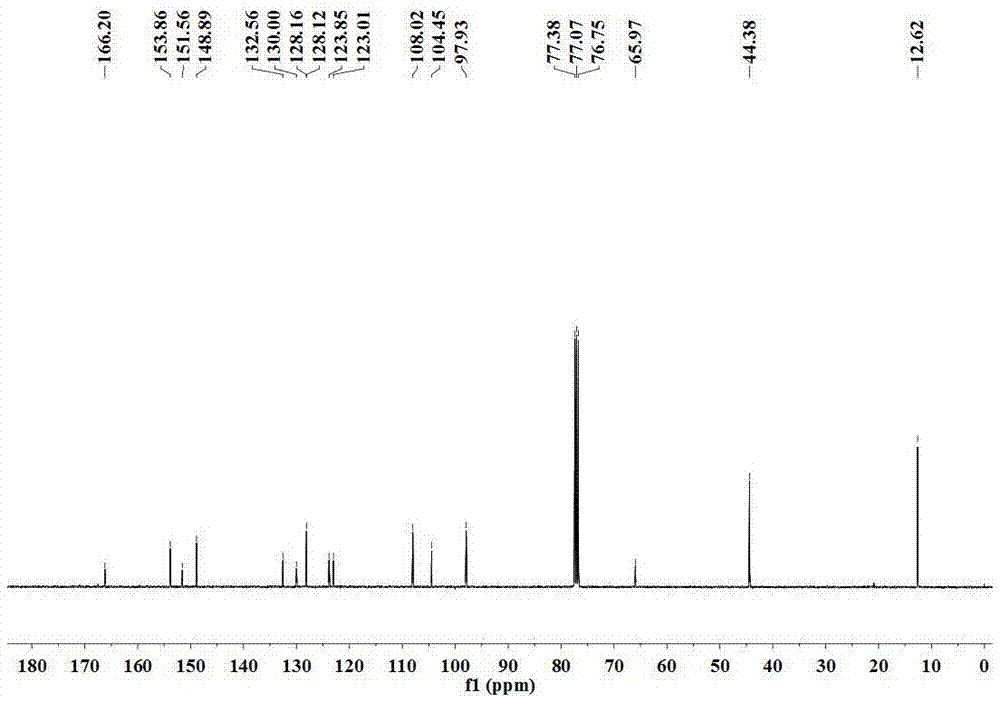
[0044] Embodiment 1: the preparation of fluorescent probe I
[0045] Step 1: Compound II was synthesized according to the literature Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2013, 23, 2916–2919.
[0046] Step 2: Add 300.0 mg of compound II to 20 mL of absolute ethanol, then add 2.0 mL (1.7 g) of 85% hydrazine hydrate, and then reflux the reaction under the protection of nitrogen; after the reaction, cool the solution to room temperature and rotate Remove ethanol by evaporation, then add 50 parts of dichloromethane and 150 parts of saturated sodium chloride solution; separate with a separatory funnel, dry the organic phase with anhydrous sodium sulfate, and spin to dry the solvent; use petroleum ether (bp 60-90 °C ) / ethyl acetate (v:v)=5:1 as the developing solvent, separated by silica gel column chromatography, and dried in vacuo to obtain 273.1 mg of compound Ⅰ as a yellow solid. Yield: 89.2%.
[0047] Since the compound II synthesized in step 1 has some impurities, it is ...
Embodiment 2
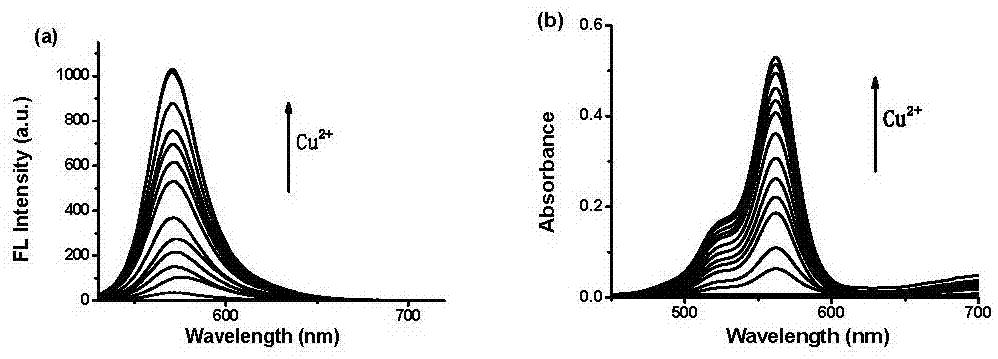
[0052] Embodiment 2: compound I and different concentration Cu 2+ Spectral changes after action
[0053] Compound I was added to acetonitrile / water solution at a concentration of 10 μM, and then the concentration of copper ions was gradually increased (0-70 μM), and the corresponding UV and fluorescence spectra were recorded. The test results are shown in image 3 In a and 3b, it can be seen from the figure that with the increase of the concentration of copper ions, the ultraviolet absorption intensity at 562 nm and the fluorescence emission intensity at 571 nm gradually increase. 2+ When it reaches 60 μM, the UV absorption and fluorescence intensity are saturated, and then increase Cu 2+ concentration, the intensity of both will no longer increase.
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3: the selectivity of compound I to common cation
[0055] The selectivity to copper ions was evaluated using compound I, which was added at a concentration of 10 μM to acetonitrile aqueous solution containing 50 μM divalent copper ions and various common cations (respectively, compound I and divalent copper ions in acetonitrile aqueous solution, compound I and any common cation in acetonitrile aqueous solution), the test results are shown in Figure 4 Medium (UV and fluorescence spectra). It can be seen from the figure that compound I (probe) has a high selectivity for divalent copper ions, and the addition of copper ions significantly enhances the fluorescence intensity of compound I, while the addition of other common cations has no significant change.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com