Viscose Serratia marcescens strain
A technology of Serratia marcescens and bacterial strains is applied in the field of microorganisms, which can solve the problems of citrus psyllid control and the like, and achieve the effects of not easily producing drug resistance, strong pathogenicity and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1: Isolation and Screening of Entomopathogenic Bacteria
[0020] (1) Separation and purification of bacterial strains:
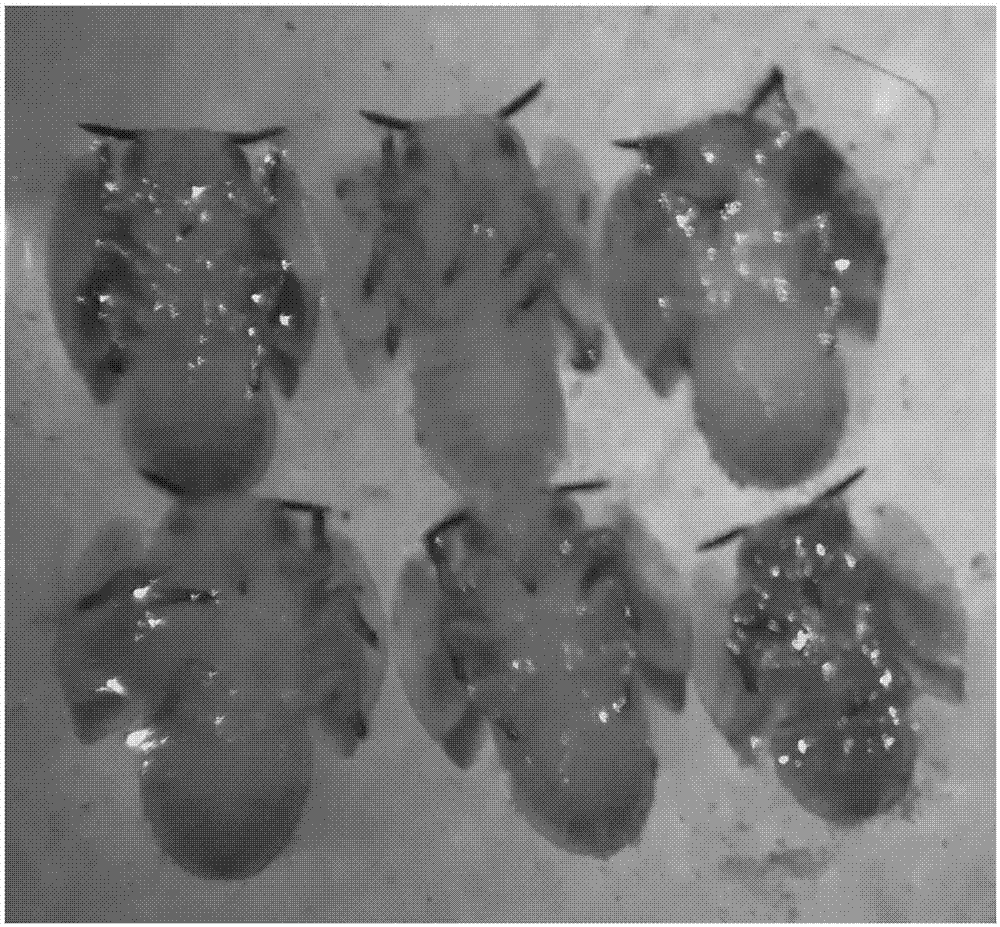
[0021] From the natural pathogenic body of the citrus psyllid raised in the Pest Laboratory of Gannan Normal University, Ganzhou City, Jiangxi Province, the body color of the citrus psyllid was completely red, and after surface disinfection with 75% ethanol aqueous solution for 5 minutes, it was cleaned with sterile water in the ultra-clean workbench. Rinse with water for 3 times, dry the water on the worm body with sterile filter paper, then place it on LB solid medium, cultivate it in a 28°C incubator for 24 hours, pick the red colony, and carry out isolation and purification culture . A single colony selected for isolation and purification was stored on LB medium and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C.
[0022] LB solid medium preparation method: Add 10g of peptone, 5g of yeast extract powder, and 10g of sodium chloride to 1000mL of distille...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Embodiment 2: the identification of bacterial strain
[0027] (1) Physiological and biochemical identification of strains
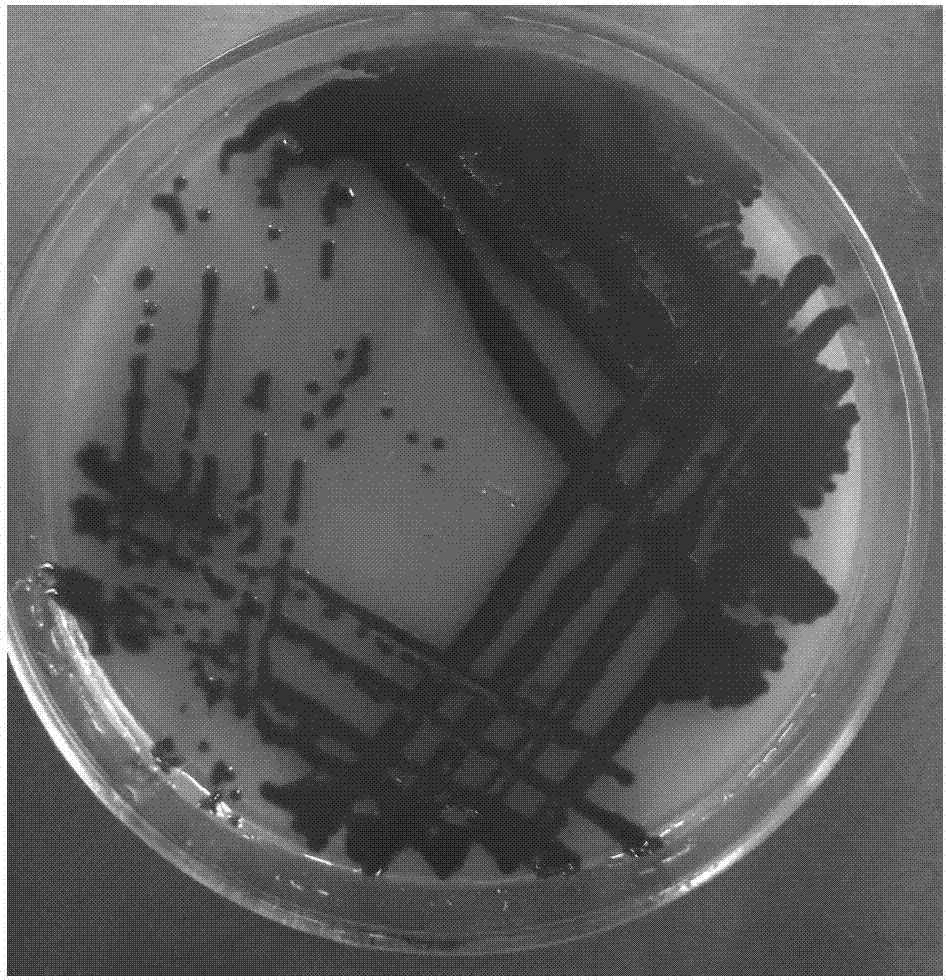
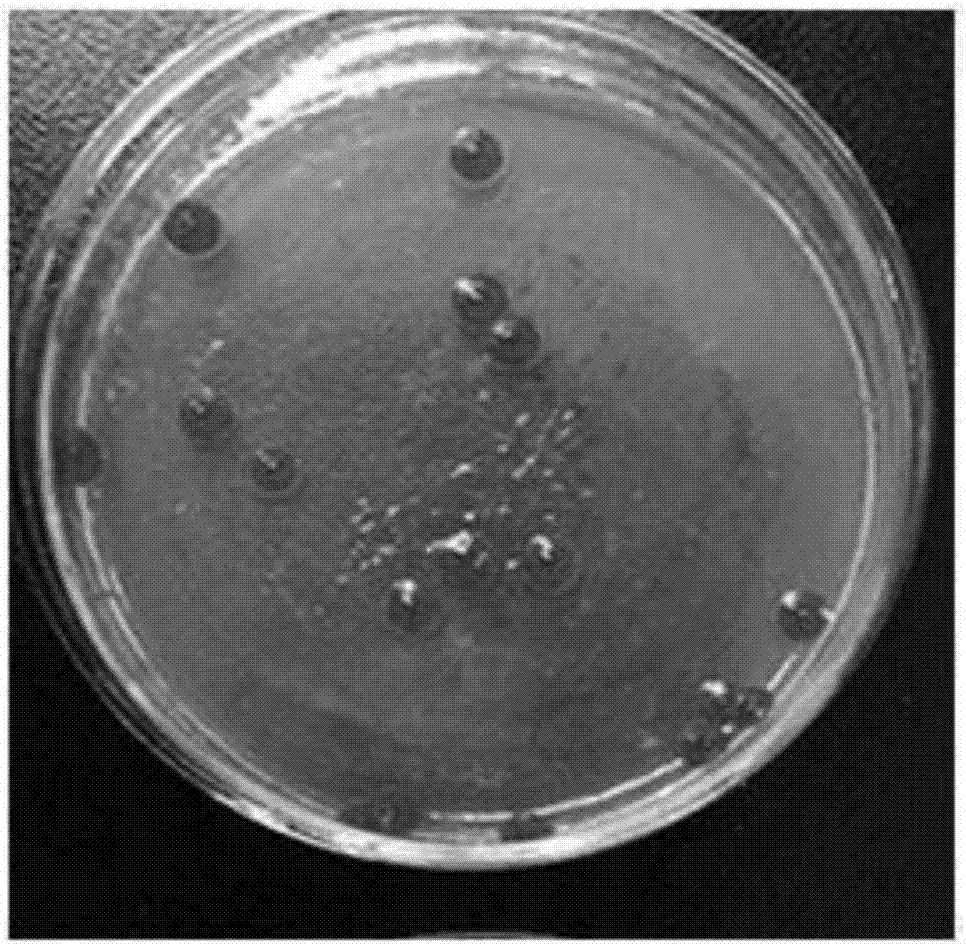
[0028] Spread the bacterial strain obtained in Example 1 on the LB solid medium, and cultivate it at a constant temperature of 28°C for 24h. See the plate growth of the bacterial strain figure 1 . The colonies of this strain are basically raised, with an opaque center and irregular edges, with a size of 1-2.5mm, all of which can produce red pigment. The strain was cultured on LB solid medium at 37°C, and the colony of the strain was white.
[0029] (2) Sequence analysis of strains
[0030] Pick a single colony of the bacterial strain obtained in Example 1 and inoculate it in 5ml of LB liquid medium, culture overnight at 28°C, 180rpm for 12h, take fresh bacterial liquid, centrifuge at 12000rpm, 4°C for 10min, and collect the wet cells. According to the extraction method of the TIANamp Bacteria DNAKit Bacterial Genomic DNA Extraction Kit, the abo...
Embodiment 3
[0035] The preparation of embodiment 3 bacterial suspension
[0036] (1) plate culture
[0037] The aforementioned Serratia marcescens strains were diluted and streaked onto LB solid medium, cultured at a constant temperature of 28°C for 24h, and then stored at 4°C.
[0038] (2) Seed liquid culture: Pick a single colony of the above-mentioned Serratia marcescens strain from the plate and inoculate it in 5 ml of LB liquid medium, shake and culture at 28° C. and 180 rpm for 6 hours to obtain a seed liquid.
[0039] (3) Fermentation culture: Take 500 μL of seed solution and inoculate it into 50 ml of LB liquid medium for expansion culture, shake culture at 28° C. and 180 rpm for 12 hours to obtain fermentation culture solution. Centrifuge the fermentation broth at 4°C and 12000 rpm, remove the supernatant, then resuspend with physiological saline, and resuspend twice according to the above steps. The bacterial suspension was serially diluted with 0.8% normal saline, and the dil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com