Lovastatin high-yield monascus and high-throughput screening method thereof
A screening method, lovastatin technology, applied in the field of microbiology, can solve the problems of low lovastatin yield, low screening efficiency, and complicated screening process of Monascus, achieving high accuracy, high throughput, and simple operation steps Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
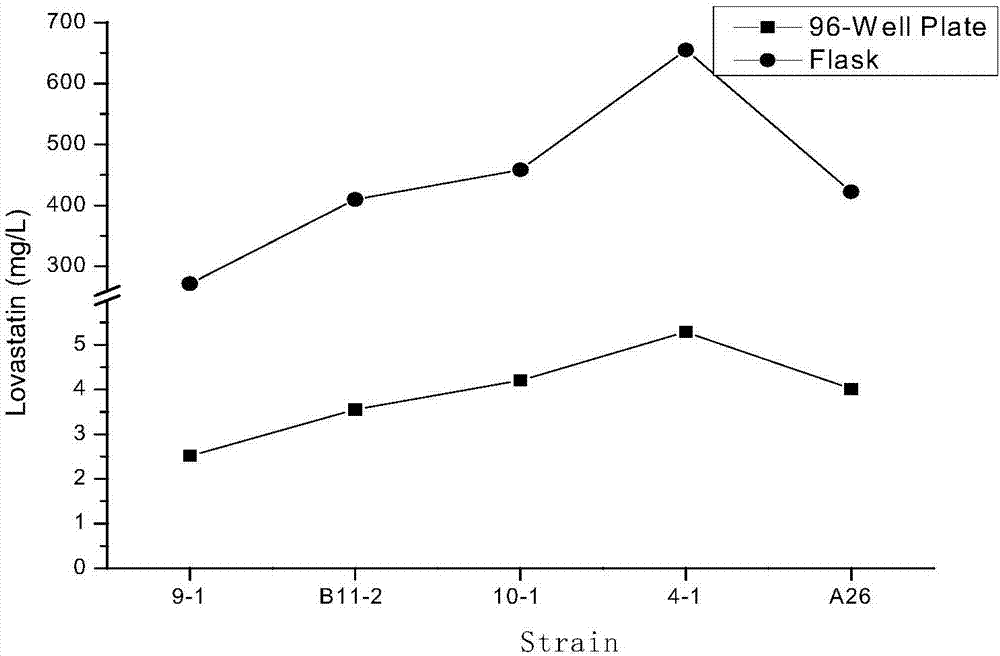
[0032] Example 1. High-throughput screening of high-yield lovastatin strains of Monascus mutated by space
[0033] Weigh an appropriate amount of Monascus lyophilized powder, dilute it with peptone sodium chloride activation solution 50 times, spread it on a malt extract agar medium, and cultivate it at 30°C for 5-7 days. After the activation of the strain, the colonies of Monascus in the plate were scraped with an inoculating spatula, and inserted into a 96-well deep-well plate containing 1 ml of the primary fermentation medium, and cultured on a shaker at 27° C. and 180 rpm for 7 days. The initial screening fermentation medium components are: 7% rice flour, 1.5% ammonium chloride, 0.15% dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.05% MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, pH is natural.
[0034] Centrifuge the 96-well plate with fermentation broth at 4000 rpm for 5 minutes, use a multi-channel pipette to take 0.2 ml of the supernatant, adjust the pH to about 3.0 with phosphoric acid, add an equal volume of ethyl...
Embodiment 2
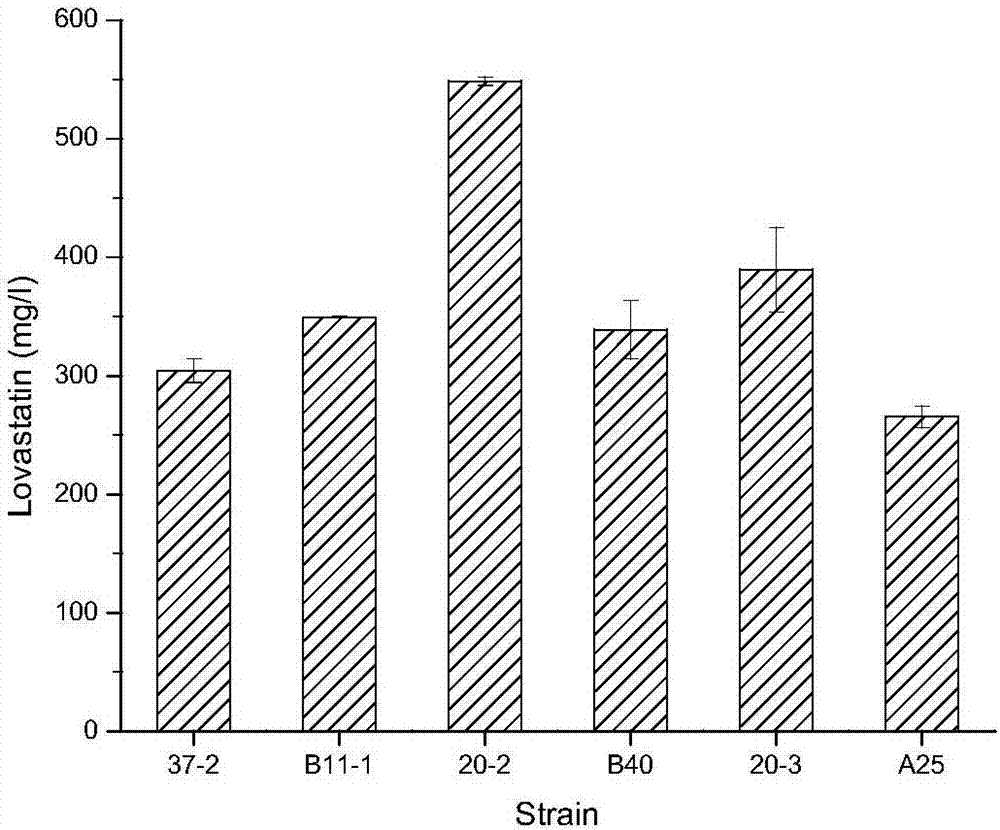
[0039] Example 2. Re-screening of high-yield lovastatin strain of Monascus 30192 carried by space
[0040] Six strains, including 37-2, B11-1, 20-3, 20-2, A25, and B40, were selected for shake flask re-screening. The seed solution of the above strain was inoculated into a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 40 mL of fermentation medium according to an inoculum amount of 7%, and cultured on a shaker at 27°C and 180 rpm. Fermentation medium components are 7% rice flour, 1.5% ammonium chloride, 0.15% dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.05% MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, pH is natural. After 7 days of fermentation, the production of lovastatin was measured.
[0041] The content of lovastatin was detected by liquid chromatography. The specific steps are as follows: centrifuge the fermentation broth at 4000 rpm for 5 minutes, take 4 mL of the supernatant, adjust the pH to 3 with phosphoric acid, add an equal volume of ethyl acetate, 50 ℃, 150 rpm water bath shaker Extraction for 2 hours, 3000rpm, centri...
Embodiment 3
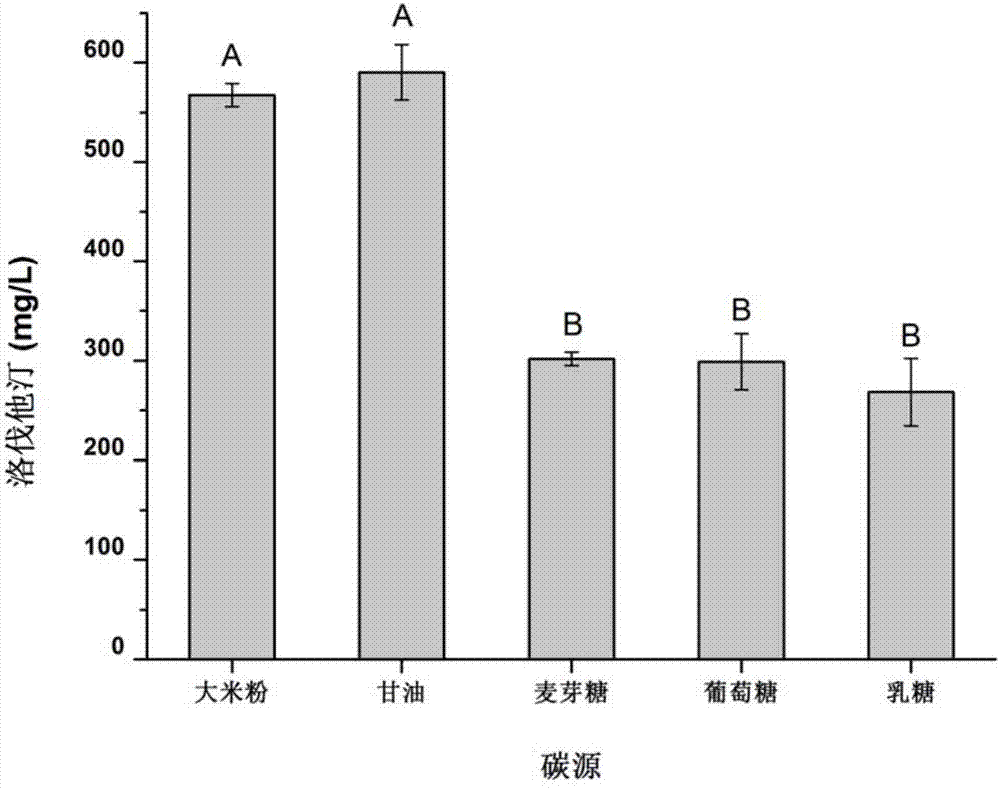
[0043] Example 3. The influence of carbon source and carbon source content on the production of lovastatin
[0044] 7% carbon source, 1.5% peptone, 0.2% ammonium chloride, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.05% and potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.15% are fermentation medium to detect the effects of glycerol, rice flour, lactose, glucose, and maltose as carbon sources on the production of lovastatin. The inoculum volume is 7%, and the liquid volume in a 250mL flask is 40mL After 7 days of fermentation in a shaker at 27°C and 180 rpm, the content of lovastatin in the fermentation broth was detected. The detection method is the same as in Example 2.
[0045] The result is image 3 As shown, when glycerol was used as the carbon source, the yield of lovastatin was the highest, followed by rice flour, with yields of 590 mg / L and 567.5 mg / L, respectively. Glycerol is not only used as a nutrient for monascus to absorb, but because of its molecular structure, it may be used as a precursor to promote the sy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com