3D printing based degradation-controllable bone tissue engineering scaffold and preparation method
A technology of bone tissue engineering and 3D printing, applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve the problems such as the inability to guarantee the precise design and manufacture of the microporous structure, the inability to achieve the degradation speed of the implant, and the inability to combine and assemble different materials, and achieve optimal material utilization. It is beneficial to the interaction of nutrients and the effect of good economic benefits.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] This embodiment provides the preparation of degradable and controllable bone tissue engineering scaffolds, specifically:
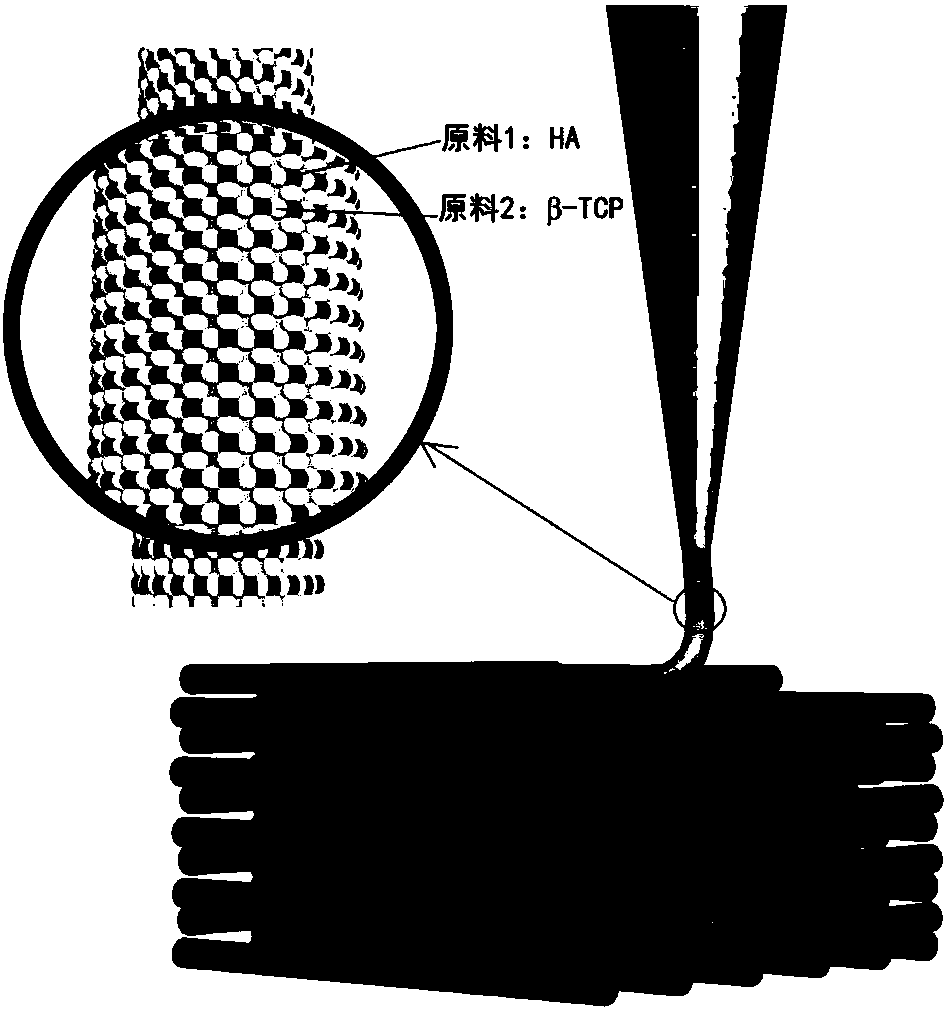
[0037]Take hydroxyapatite (HA) as raw material 1, tricalcium phosphate powder (β-TCP) as raw material 2, and mix raw material 1 and raw material 2 uniformly at a mass ratio of 60:40 to obtain a mixed powder. Take 10g of polyvinyl alcohol, add 90ml of water to dissolve, and prepare a polyvinyl alcohol solution. Mix 20ml of polyvinyl alcohol solution evenly into 32.5g of mixed powder, add 7ml of deionized water and 6ml of absolute ethanol while stirring, until the mixture is evenly stirred to obtain printing ink raw materials. Wherein, the powder particle diameters of hydroxyapatite and tricalcium phosphate are both 50 nm to 100 μm.
[0038] In the modeling software, a 10mm × 10mm × 3mm cube was established, and then combined with the layering software to perform layered slicing processing on the built model, setting the diameter of the printing mate...
Embodiment 2
[0041] This example provides the preparation of degradable and controllable bone tissue engineering scaffold. The modeling and sintering process of the bracket in this embodiment are the same as in Embodiment 1, the difference is that the configuration of 3D printing ink raw materials is carried out in a different batching method from that in Embodiment 1, specifically:
[0042] Take 10g of polyvinyl alcohol, add 90ml of water to dissolve, and prepare a polyvinyl alcohol solution. 20ml of polyvinyl alcohol solution was uniformly added to 32.5g of hydroxyapatite (HA), and while stirring, 7ml of deionized water and 6ml of absolute ethanol were added until the mixture was evenly stirred to obtain printing ink raw materials. Wherein, the particle size of the hydroxyapatite powder is 50 nm to 100 μm.
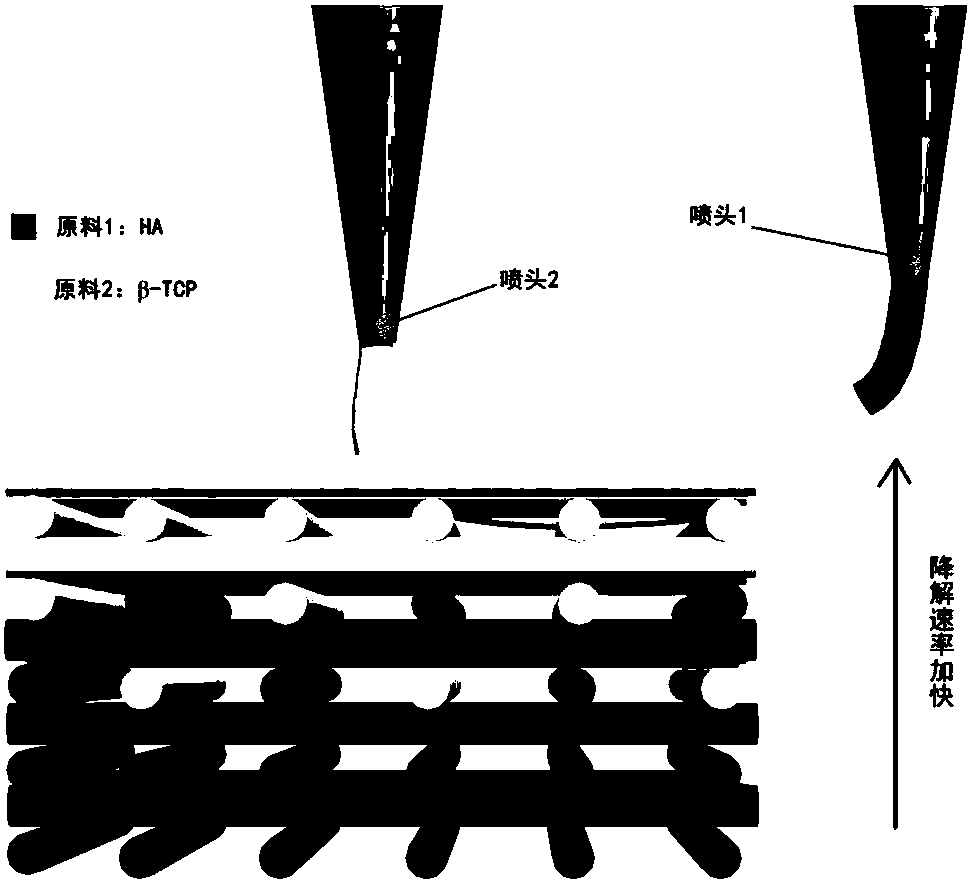
[0043] Then, the model in Example 1 was 3D printed and sintered into porcelain to obtain the HA ceramic bone tissue engineering scaffold. The degradation rate of the stent in this ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] This example provides the preparation of degradable and controllable bone tissue engineering scaffold. The modeling and sintering process of the bracket in this embodiment are the same as in Embodiment 1, the difference is that the configuration of 3D printing ink raw materials is carried out in a different batching method from that in Embodiment 1, specifically:
[0046] Take 10g of polyvinyl alcohol, add 90ml of water to dissolve, and prepare a polyvinyl alcohol solution. 20ml of polyvinyl alcohol solution was uniformly added to 32.5g of tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP), and while stirring, 7ml of deionized water and 6ml of absolute ethanol were added until the mixture was evenly stirred to obtain printing ink raw materials. The particle size of tricalcium phosphate powder is 50nm-100μm.
[0047] Then, the model in Example 1 was 3D printed and sintered into porcelain to obtain the β-TCP ceramic bone tissue engineering scaffold. The degradation rate of the scaffold in th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wire diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com