A method for preparing tissue engineering scaffold material by using degradable synthetic polymer material
A tissue engineering scaffold, a technology for synthesizing macromolecules, used in medical science, prostheses, etc., can solve problems such as poor connectivity, affecting cell activity, and being unsuitable for tissue engineering.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] A method for preparing a tissue engineering scaffold material by using a degradable synthetic polymer material, comprising the following steps:
[0040] (1) The raw material used is polyglycolide with a crystallinity of 48%, and the flakes are prepared by hot pressing, and then placed in a high-temperature and high-pressure reactor;
[0041] (2) Using supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO 2 ) to replace the gas in the high-temperature and high-pressure reactor;
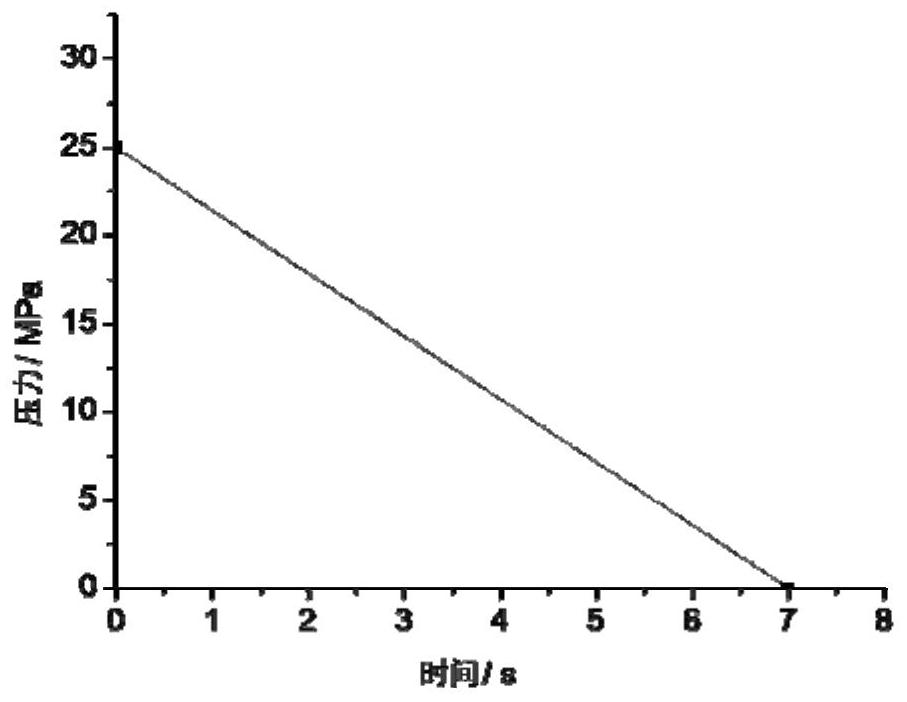
[0042] (3) Put the high-temperature and high-pressure reactor into an oil bath at 250°C, pressurize it to 25MPa, and saturate it for 1 hour;
[0043] (4) Rapidly cool down the oil bath to 220°C, and saturate the flakes in the reactor for 1 hour;
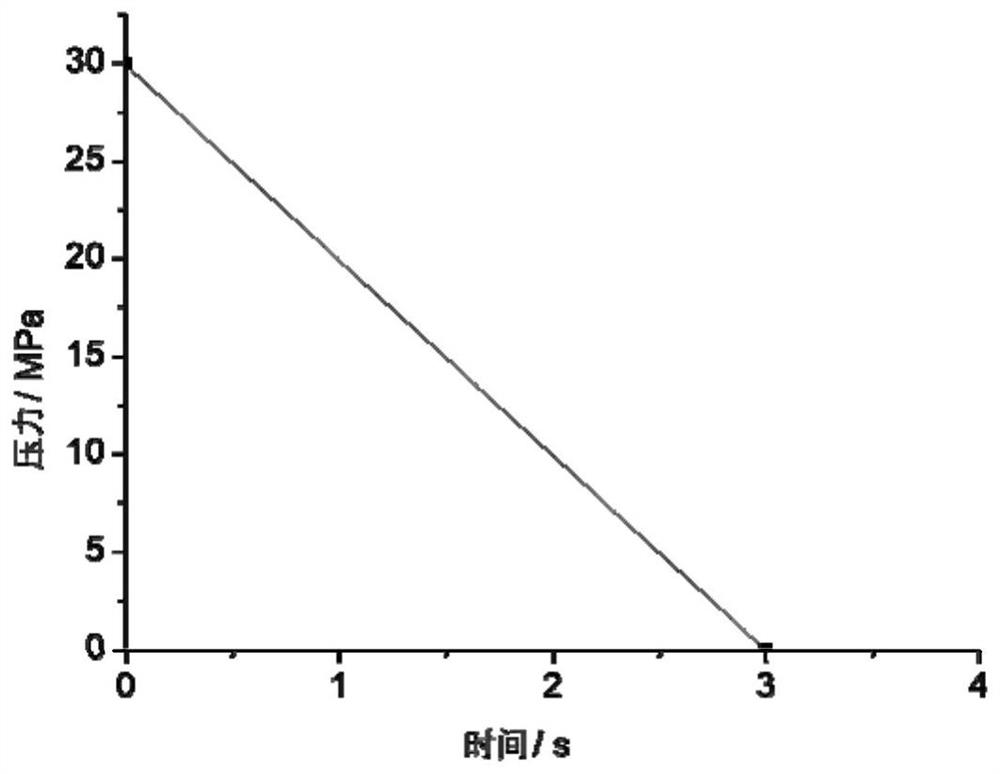
[0044] (5) According to the set pressure drop curve to release the pressure, the tissue engineering scaffold material can be obtained; the pressure drop curve of the pressure release is as follows: figure 1 shown.
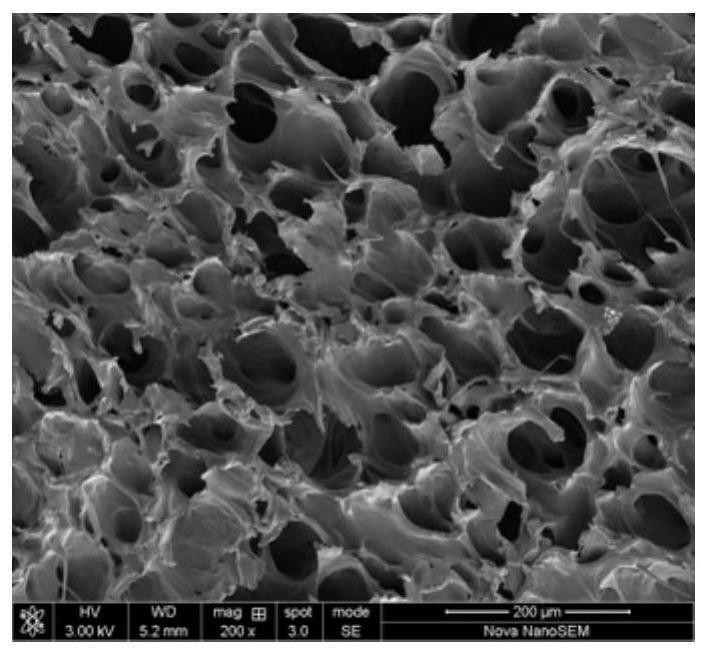
[0045] The SEM image of the internal cross-section ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] A method for preparing a tissue engineering scaffold material by using a degradable synthetic polymer material, comprising the following steps:
[0048] (1) The raw material used is polyglycolide with a crystallinity of 50%, and the flakes are prepared by hot pressing, and then placed in a high-temperature and high-pressure reactor;
[0049] (2) Using supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO 2 ) to replace the gas in the high-temperature and high-pressure reactor;
[0050] (3) Put the high-temperature and high-pressure reactor into an oil bath at 250°C, pressurize it to 30MPa, and saturate it for 1 hour;
[0051] (4) Rapidly cool down the oil bath to 220°C, and saturate the flakes in the reactor for 1 hour;
[0052] (5) According to the set pressure drop curve to release the pressure, the tissue engineering scaffold material can be obtained; the pressure drop curve of the pressure release is as follows: image 3 shown.
[0053] The SEM image of the internal cross-section ...
Embodiment 3
[0055] A method for preparing a tissue engineering scaffold material by using a degradable synthetic polymer material, comprising the following steps:
[0056] (1) The raw material used is polycaprolactone (PCL) powder with a crystallinity of 67%, and the flakes are prepared by hot pressing, and then placed in a high-temperature and high-pressure reactor;
[0057] (2) Using supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO 2 ) to replace the gas in the high-temperature and high-pressure reactor;
[0058] (3) Put the high-temperature and high-pressure reactor into a water bath at 90°C, pressurize it to 30MPa, and saturate it for 1 hour;
[0059] (4) Cool the oil bath to 30°C quickly, and saturate the flakes in the reactor for 1 hour;
[0060] (5) According to the set pressure drop curve to release the pressure, the tissue engineering scaffold material can be obtained; the pressure drop curve of the pressure release is as follows: Figure 5 shown.
[0061] The SEM image of the internal cro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com