Method for preparing self-support layered materials MXenes and application of self-support layered materials MXenes as Raman substrates
A layered material and self-supporting technology, which is applied in Raman scattering, material analysis, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of high price and complicated preparation process, and achieve the effect of low cost, simple preparation process and long application time limit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1—Self-supporting layered material Ti 3 C 2 T x preparation of
[0037] Step 1. At 25°C, take 200 mesh Ti 3 AlC 2 1.0 g of the powder was dissolved in 10 ml of HF aqueous solution with a concentration of 40 wt% (40% by mass), and magnetically stirred for 2 h. Dilute the stirred suspension with deionized water, put it into a centrifuge at 1800rpm and centrifuge for 15min to obtain Ti 3 C 2 T x powder, and then wash the powder with deionized water until the pH of the centrifuged supernatant is 6-7. Use a filter to suction-filter the washed powder on the filter membrane, dry it in a blast drying oven at 50°C for 12 hours, and save it for other use.
[0038] Step 2, "insertion method" layered Ti 3 C 2 T x : Take part of the powder in step 1 and disperse it into a dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) solution at a ratio of 1g / 10ml (that is, 1g powder corresponds to 10ml DMSO) at 25°C, and stir magnetically for 18h. Centrifuge at 1800rpm for 15min to obtain Ti after ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2, a kind of self-supporting layered material Ti 3 C 2 T x Compared with Example 1, the difference in the preparation method is that in step 1, magnetic stirring is performed for 4 hours, which corresponds to 2 hours of magnetic stirring in step 1.
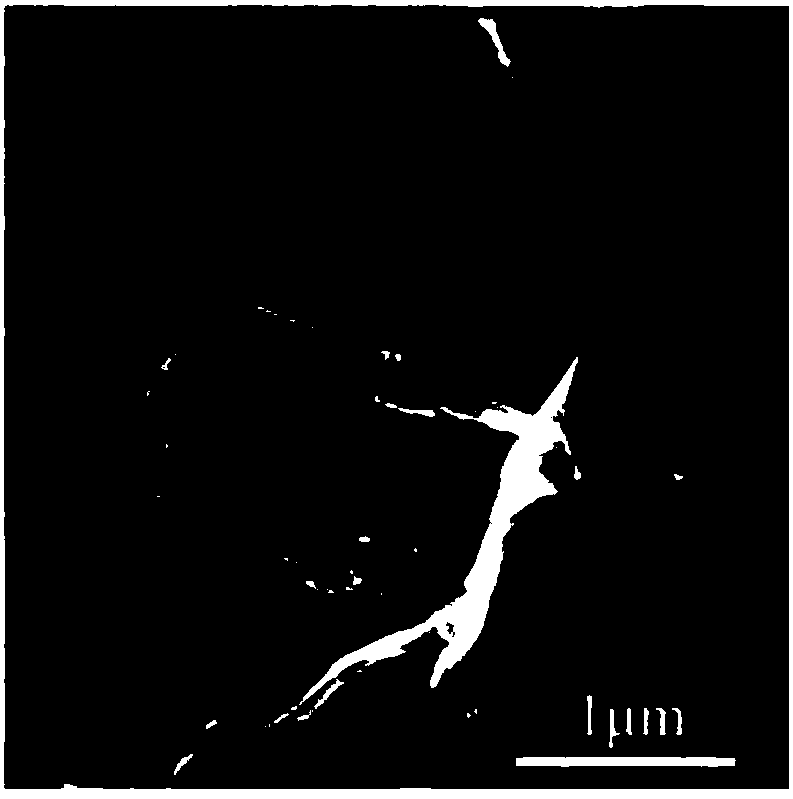
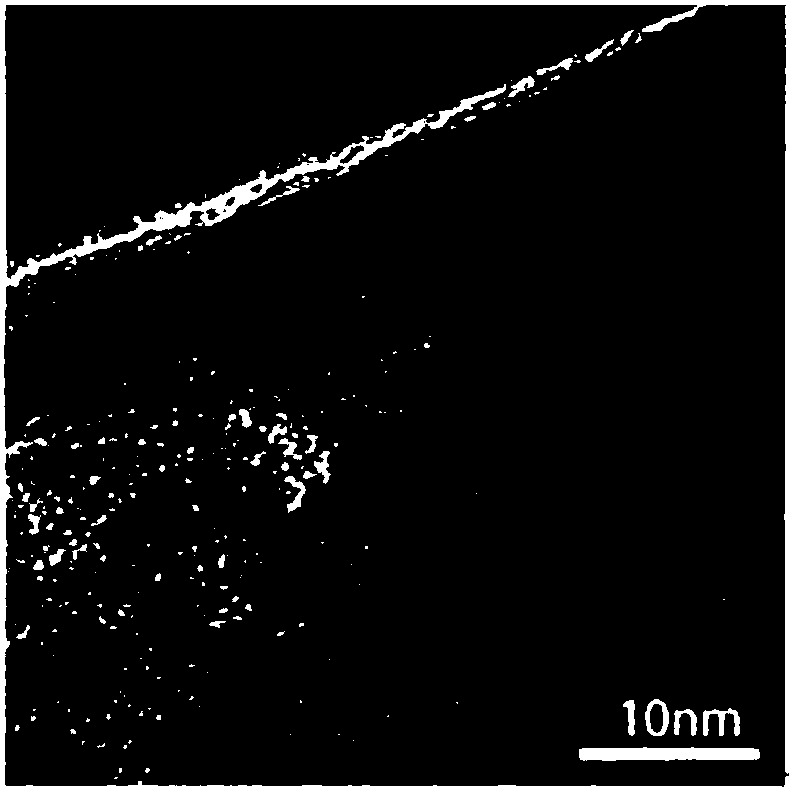
[0041] figure 1 It is the two-dimensional Ti obtained by etching in Example 2 3 C 2 T x SEM photographs of the sheets. figure 2 It is the two-dimensional Ti obtained by etching in Example 2 3 C 2 T x The TEM photo of the layer, the number of layers is less than 10 layers. The prepared material is macroscopically composed of sheet material Ti 3 C 2 T x Composition, and two-dimensional Ti 3 C 2 T x The sheets are nano-layers, which are layered and dispersed through solvent intercalation to form Ti 3 C 2 T x nanolayers, forming a self-supporting structure.
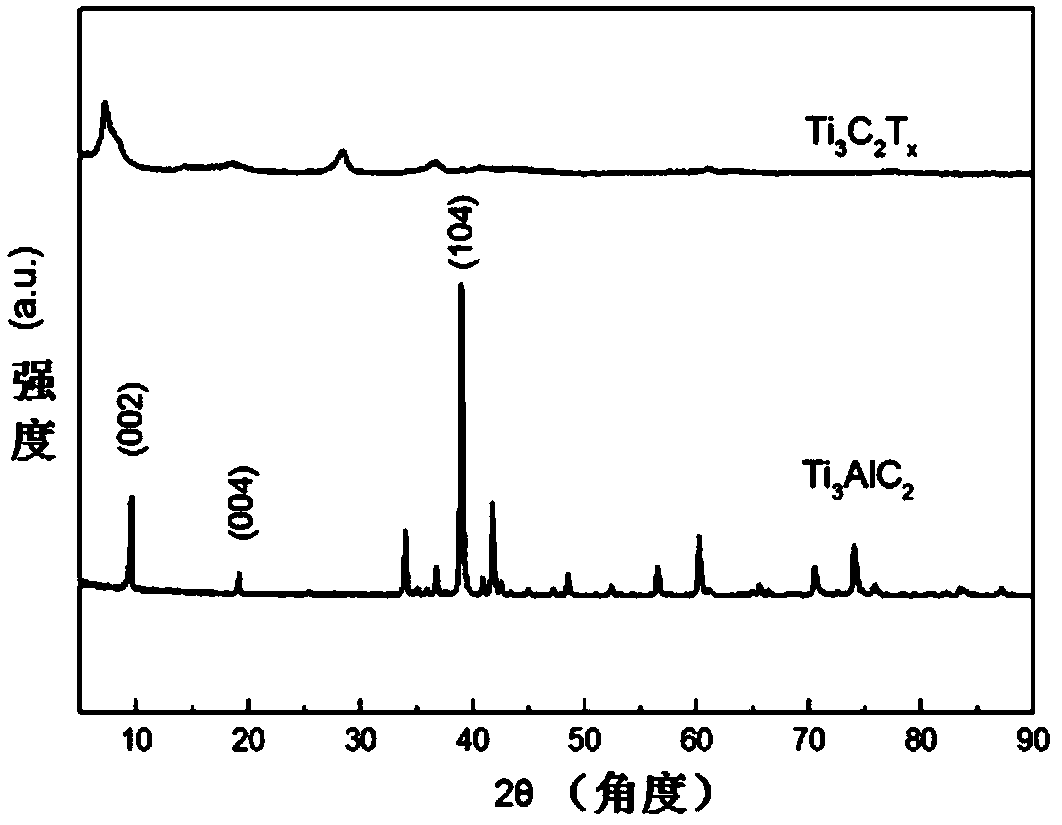
[0042] image 3 for Ti 3 AlC 2 In the XRD patterns before and after etching, the (104) phase disappears after etching, and the intensity ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3—Using the self-supporting layered material Ti prepared in embodiment 2 3 C 2 T x As a SERS substrate, rhodamine B is used as a Raman probe molecule, and the detection of rhodamine B molecular content includes the following steps:
[0044] Step 1. Use tweezers to take a small piece of the SERS substrate material and place it on a 1×1cm 2 On the silicon wafer, drop 6.5ul on the SERS substrate material with a concentration of 10 -5 The rhodamine B solution was volatilized in the air and dried to prepare a test sample for use.
[0045] Step 2. Place the detection sample prepared in step 1 in the Renishaw laser Raman spectrometer, wherein: the frequency range is 1710cm -1 —600cm -1 , the wavelength is 532nm, and the laser attenuation power is 0.01-0.05%. In the continuous mode, the Raman detection of Rhodamine B is completed with 2-5s exposure time and multiple acquisitions.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com