Microbial recovery of precious metals from spent lithium batteries
A lithium battery and microorganism technology, applied in the field of precious metal recovery, can solve the problems of staying, high equipment requirements, secondary pollution, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing cost and energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
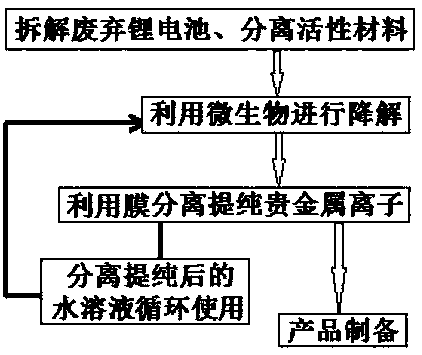
[0050]A kind of method that utilizes microorganism to reclaim precious metal from waste lithium battery, contains following steps (see figure 1 ):
[0051] (1) Disassemble waste lithium batteries and separate active materials
[0052] Disassemble the waste lithium battery, remove its metal shell and separator, and separate the positive and negative electrodes in the lithium battery from the separator: immerse the positive electrode material in the organic solvent 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), soak for 30min, control The temperature is 120°C, and then the active material is peeled off from the copper foil or aluminum foil by ultrasonic technology, and the obtained copper foil or aluminum foil can be directly used for the recovery of copper and aluminum; the obtained positive electrode active material is washed three times with distilled water, and then Dry at 80°C, crush the dried positive electrode active material with a pulverizer, and collect 100-300 mesh positive electrode...
Embodiment 2
[0074] A method for recovering precious metals from waste lithium batteries using microorganisms, comprising the following steps:
[0075] (1) Disassemble waste lithium batteries and separate active materials
[0076] Disassemble the waste lithium battery, remove its metal shell and diaphragm, and separate the positive and negative electrodes in the lithium battery from the diaphragm: immerse the positive electrode material in the organic solvent acetone or ethanol for 60 minutes, control the temperature at 50 ° C, and then use ultrasonic The process strips the active material (including lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese) from the copper foil or aluminum foil, and the obtained copper foil or aluminum foil can be directly used for the recovery of copper and aluminum; the positive active material obtained is washed three times with distilled water , and then dried at 25° C., crushed the dried positive electrode active material with a pulverizer, and collected 100-300 mesh posit...
Embodiment 3
[0092] A method for recovering precious metals from waste lithium batteries using microorganisms, comprising the following steps:
[0093] (1) Disassemble waste lithium batteries and separate active materials
[0094] Disassemble the waste ternary lithium battery, remove its metal shell and separator, and separate the positive and negative electrodes in the lithium battery from the separator: immerse the positive electrode material in the organic solvent 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidone for 20 minutes, and control the temperature At 200°C, the active material is peeled off from the copper foil or aluminum foil by an ultrasonic process, and the obtained copper foil or aluminum foil can be directly used for the recovery of copper and aluminum; the obtained positive electrode active material is washed three times with distilled water, and then Dry at 80° C., crush the dried positive electrode active material with a pulverizer, and collect 100-300 mesh positive electrode active material pow...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com