Molecularly imprinted microsphere for detecting teicoplanin and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of molecularly imprinted microspheres and teicoplanin, applied in separation methods, other chemical processes, solid adsorbent liquid separation, etc., achieving good application prospects, low detection limits, and high recovery rates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
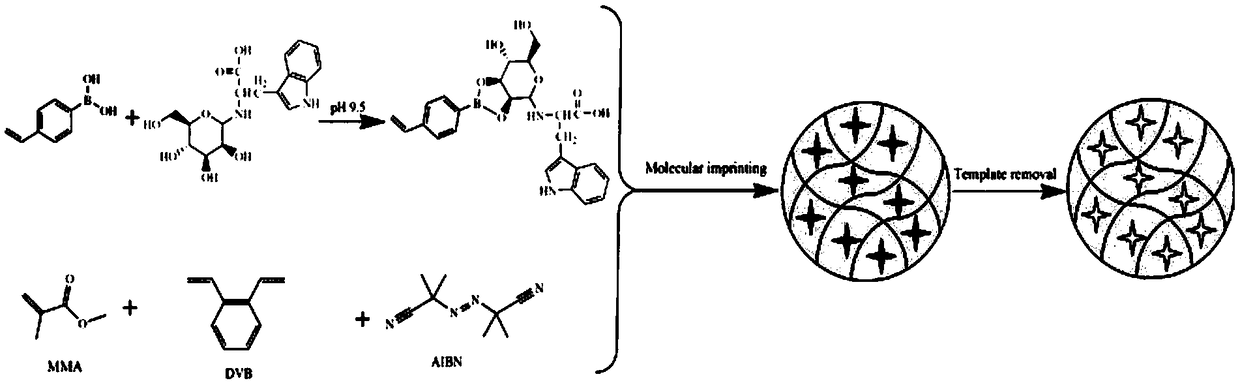
[0043] The reaction route of sugar-based molecularly imprinted microspheres is as follows: figure 1Shown, mainly comprise the following steps: in the round bottom flask of 250mL, 200mg methyl methacrylate, 700mg divinylbenzene and 100mg azobisisobutyronitrile are dissolved in the mixed solvent of 128mL acetonitrile and toluene (75 / 25, v / v). Stir at room temperature for 10 min under nitrogen blowing. 100 μg of template molecules and 0.242 g of 4-vinylphenylboronic acid were dissolved in 5.0 mL of phosphate buffer solution (0.01 mol / L, pH 9.5), and added dropwise to the above solution. Then ultrasonic degassing for 5 minutes, followed by nitrogen purging for 10 minutes. Then the obtained mixed solution was sealed and stirred with an electromagnetic stirrer, and then the temperature was raised to 60° C., and the polymerization reaction was carried out for 24 hours. The resulting MIMs were centrifuged at 9000 rpm for 10 min. Subsequently, the above MIMs were repeatedly washed...
Embodiment 2
[0047] MIMs and NIMs microspheres were prepared by the method of Example 1. 10 mg of MIMs (NIMs) was added to 2 mL of buffer solutions with different pH values containing 100 μg / L teicoplanin, shaken horizontally at room temperature for 2 h, and then centrifuged. The concentration of teicoplanin in the supernatant was detected by UPLC-MS / MS.
[0048] Figure 6 is the adsorption capacity of MIMs and NIMs for teicoplanin at different pH values. Boric acid can covalently react with cis-diol in alkaline aqueous solution to form cyclic ester, and when the medium becomes acidic, the cyclic ester is free. Therefore, pH will affect the adsorption amount of MIMs. When the pH is 9.0, the adsorption capacity of MIMs is the largest.
Embodiment 3
[0050] MIMs microspheres were prepared by the method in Example 1. A 3 mL empty column was directly filled with 60 mg of dry MIMs, and both ends of the filler were sealed by sieve plates. The resulting column was a MISPE column. Then use 3mL methanol and 3mL 0.05mol / L phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) to activate the column, then load the sample, then wash with 2.0mL deionized water, and use the eluent to rinse the loaded MISPE column . The obtained eluate was collected, blown with nitrogen at 40° C., and then dissolved in 0.1% formic acid solution, and detected by UPLC-MS / MS.
[0051] By changing the type and volume of the eluent, the extraction conditions of the solid-phase extraction column are optimized to obtain the best eluent and elution volume.
[0052] Figure 7 and Figure 8 Respectively represent the pH value of the eluent and the impact of its volume on the recovery rate of teicoplanin, the best eluent is pH=4.0 buffer solution+methanol (1 / 1), and the best elution volum...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com