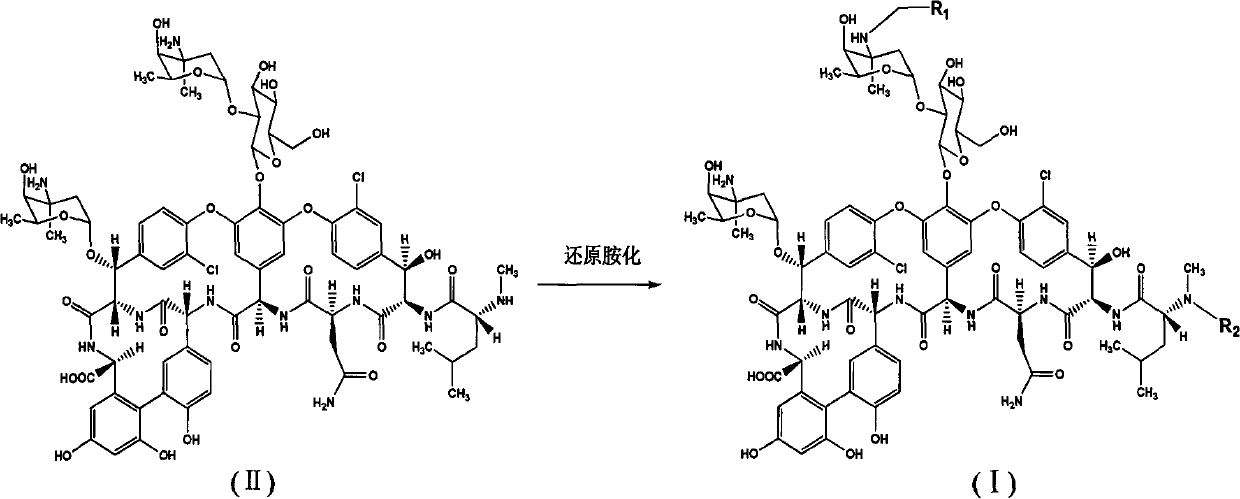
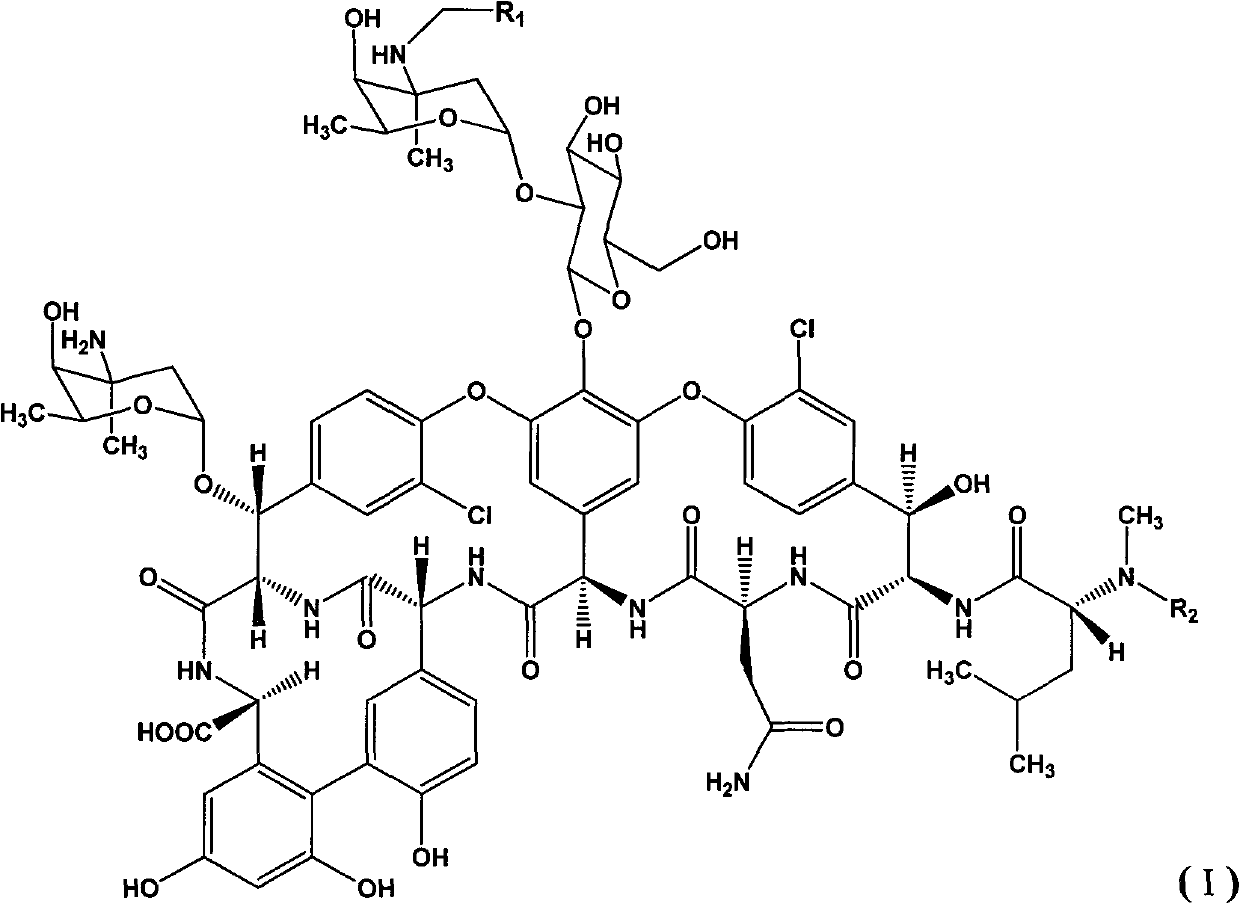
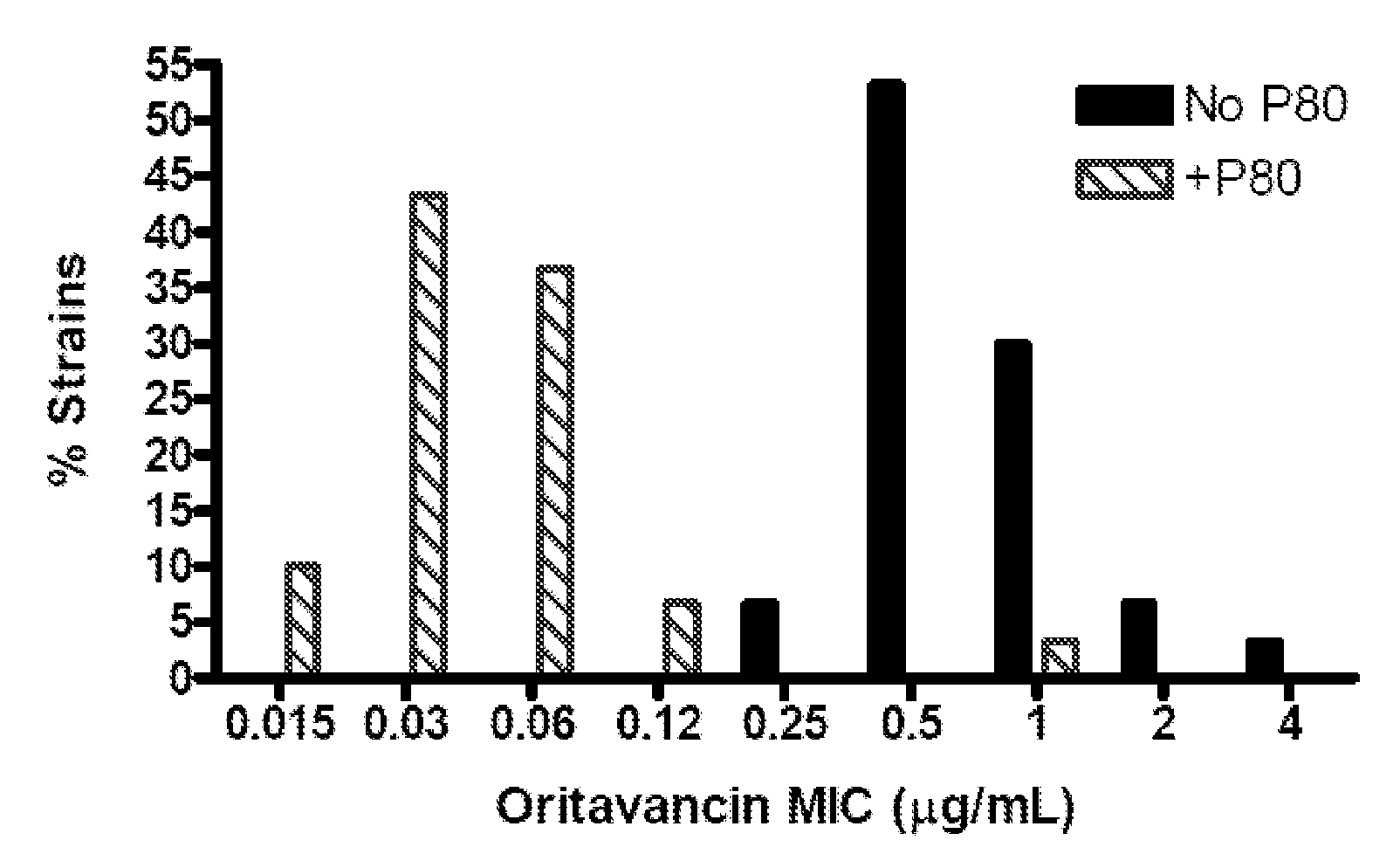
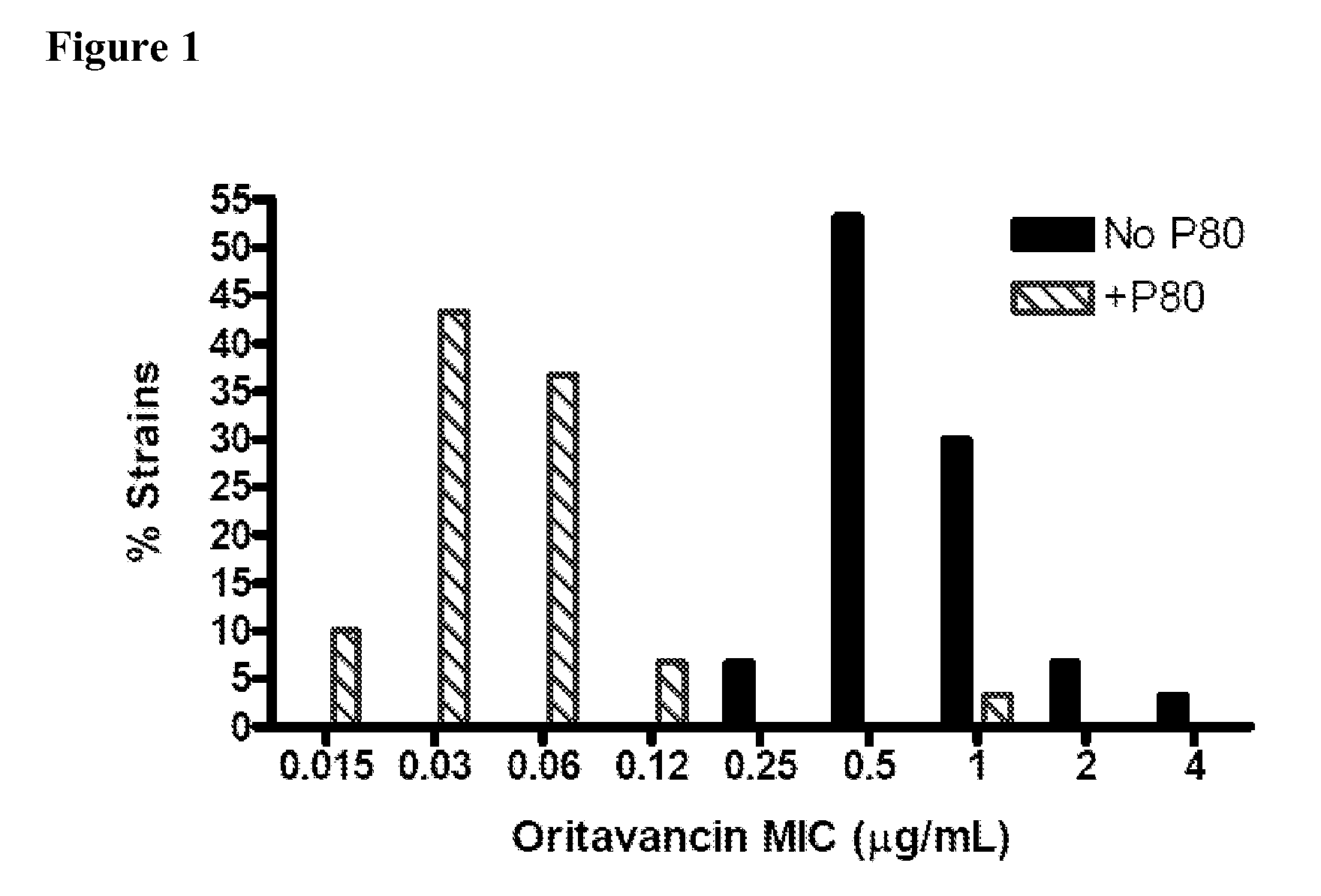
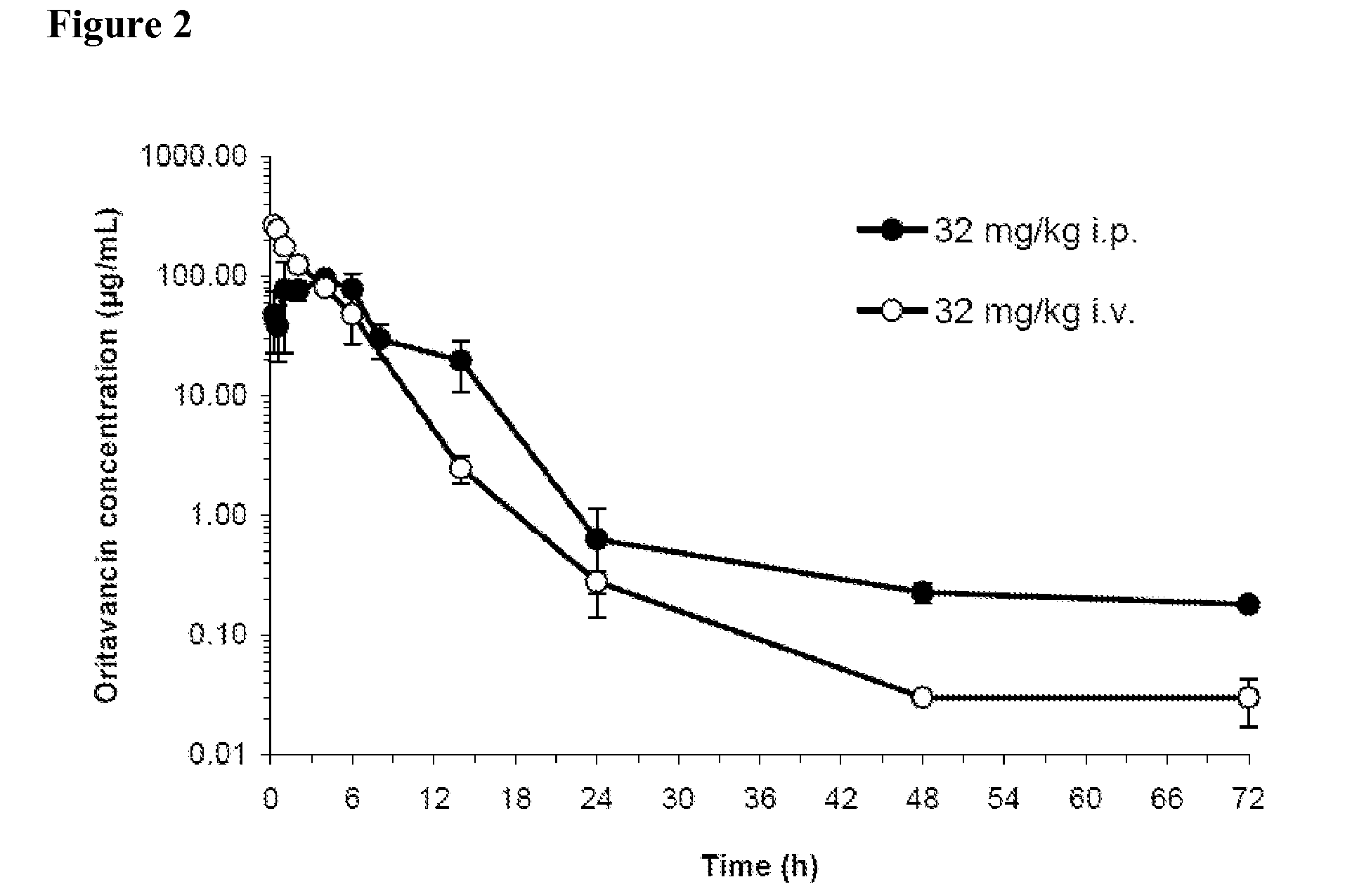
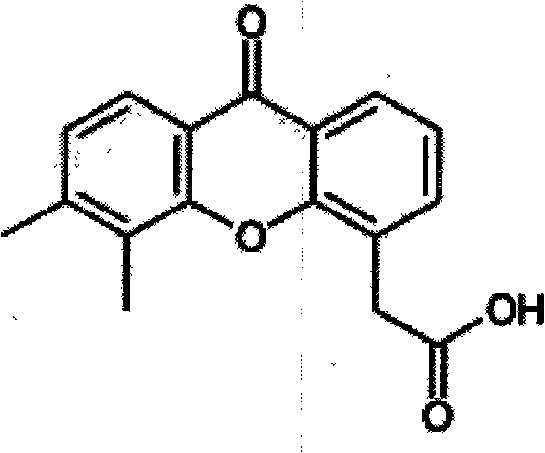
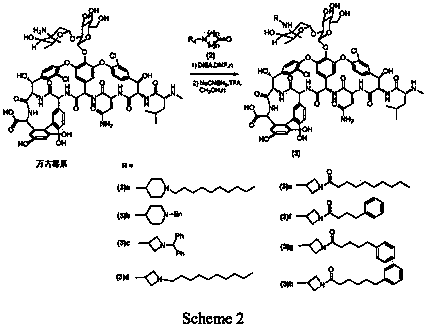
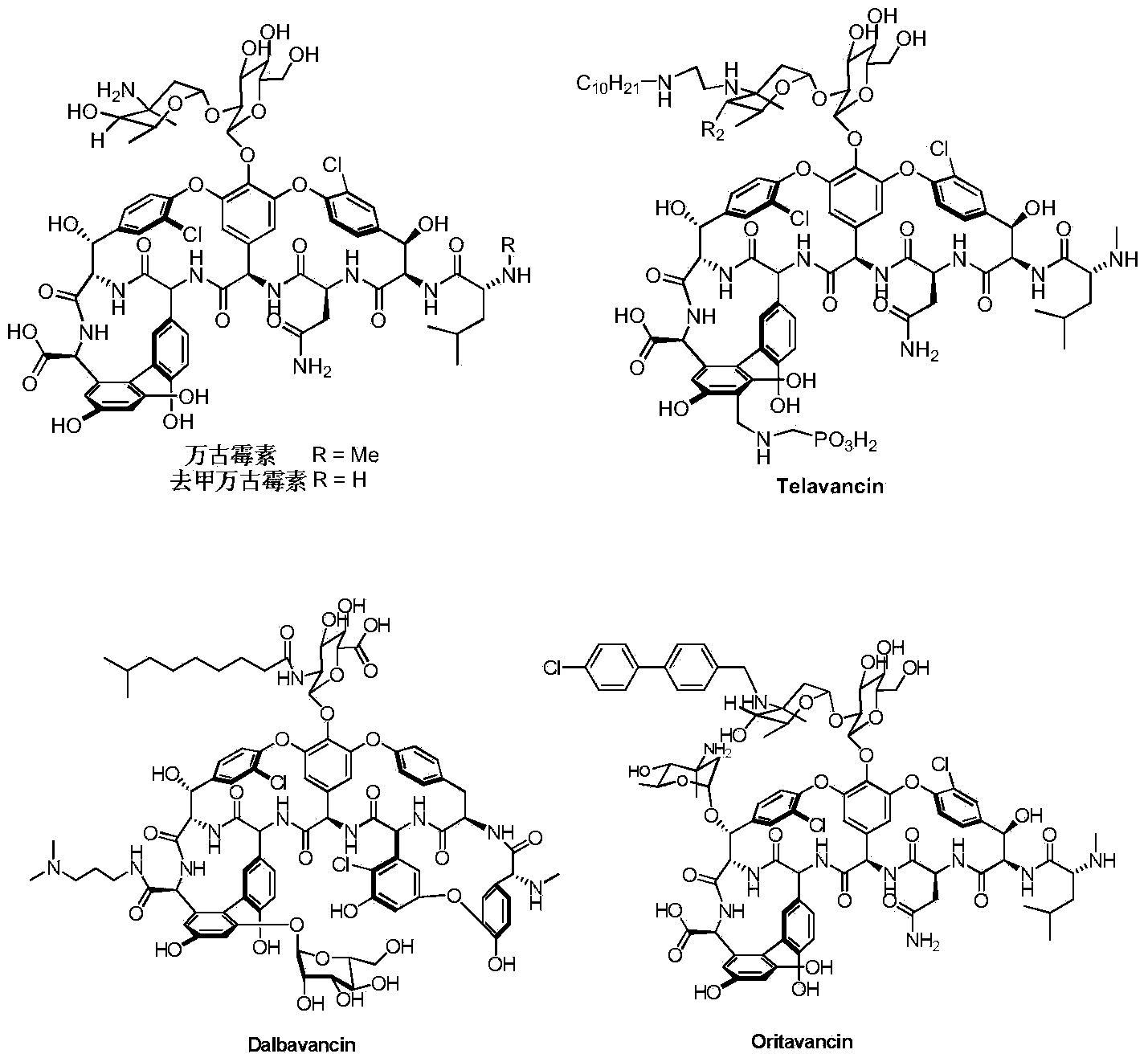
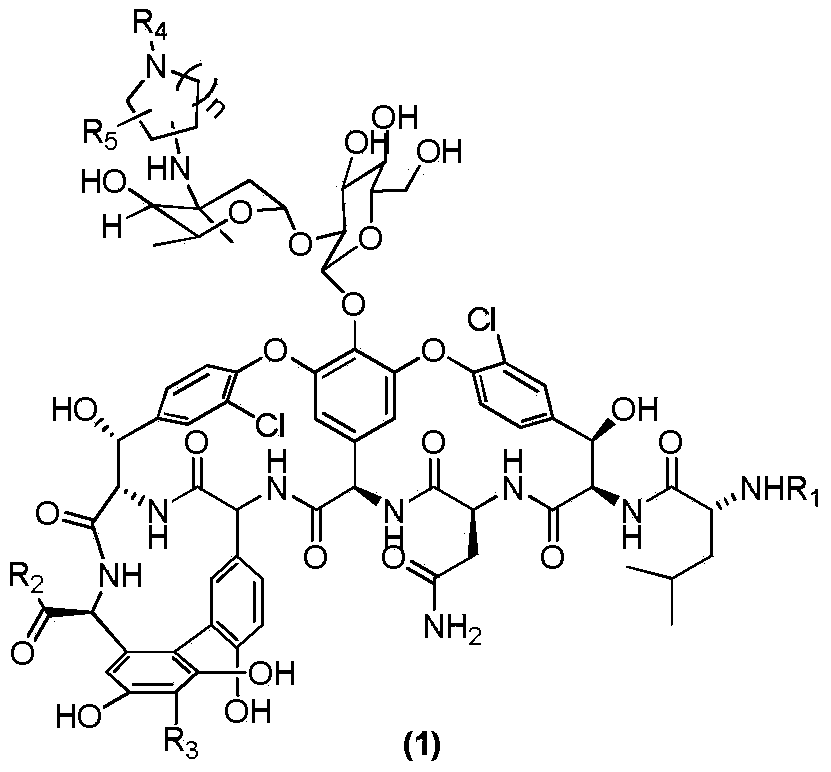
Patents
Literature
78 results about "Glycopeptide antibiotic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
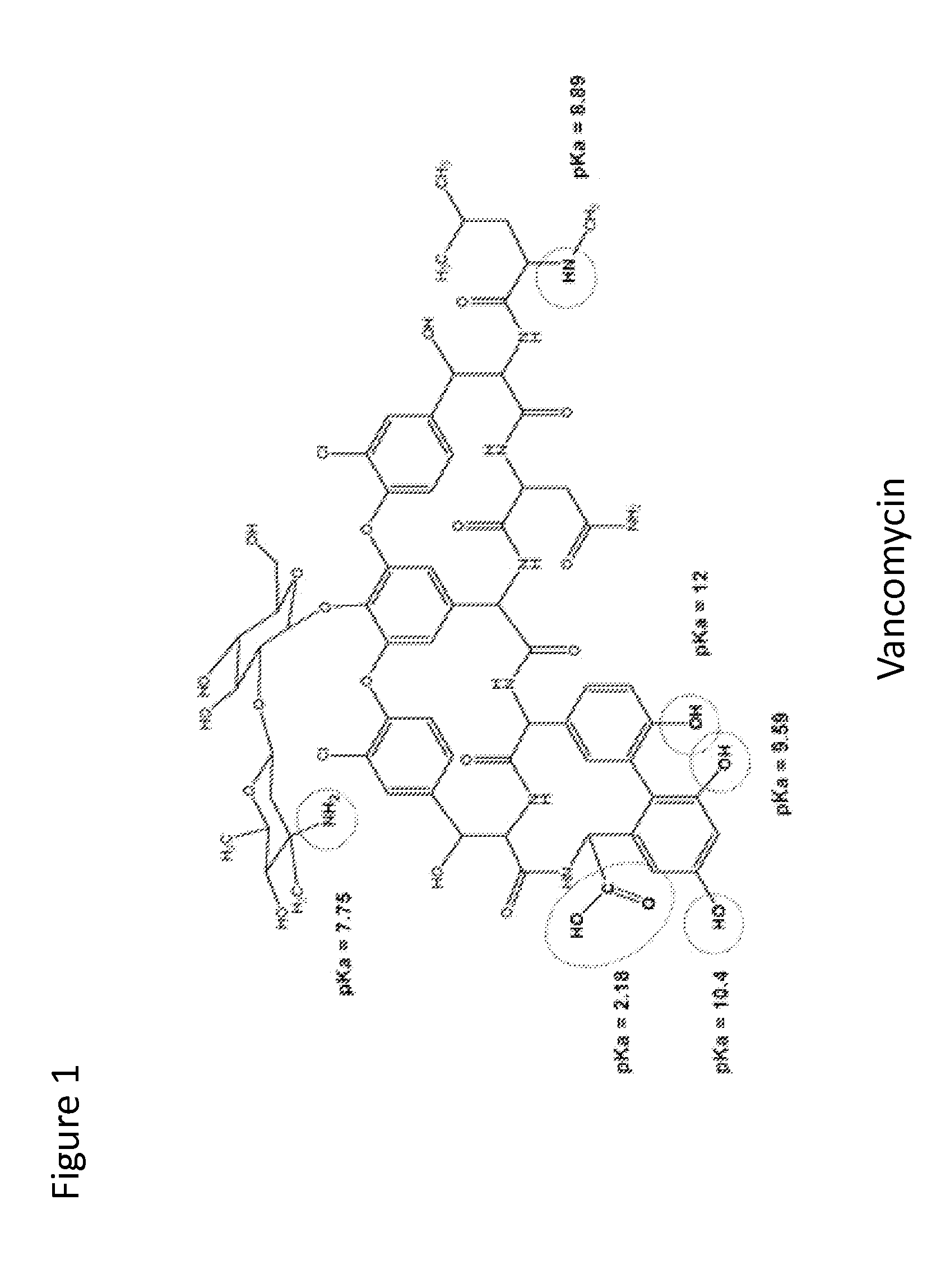
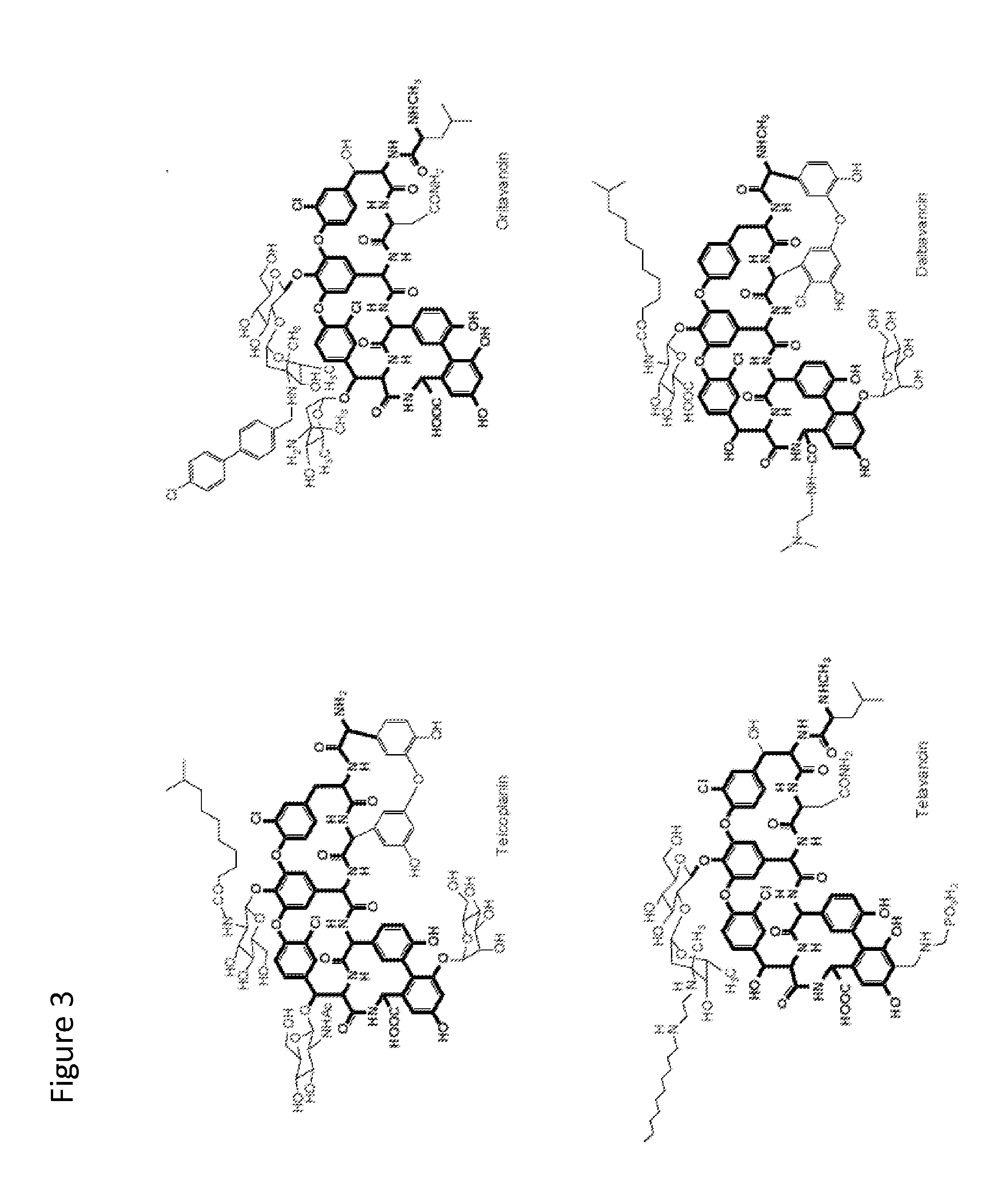
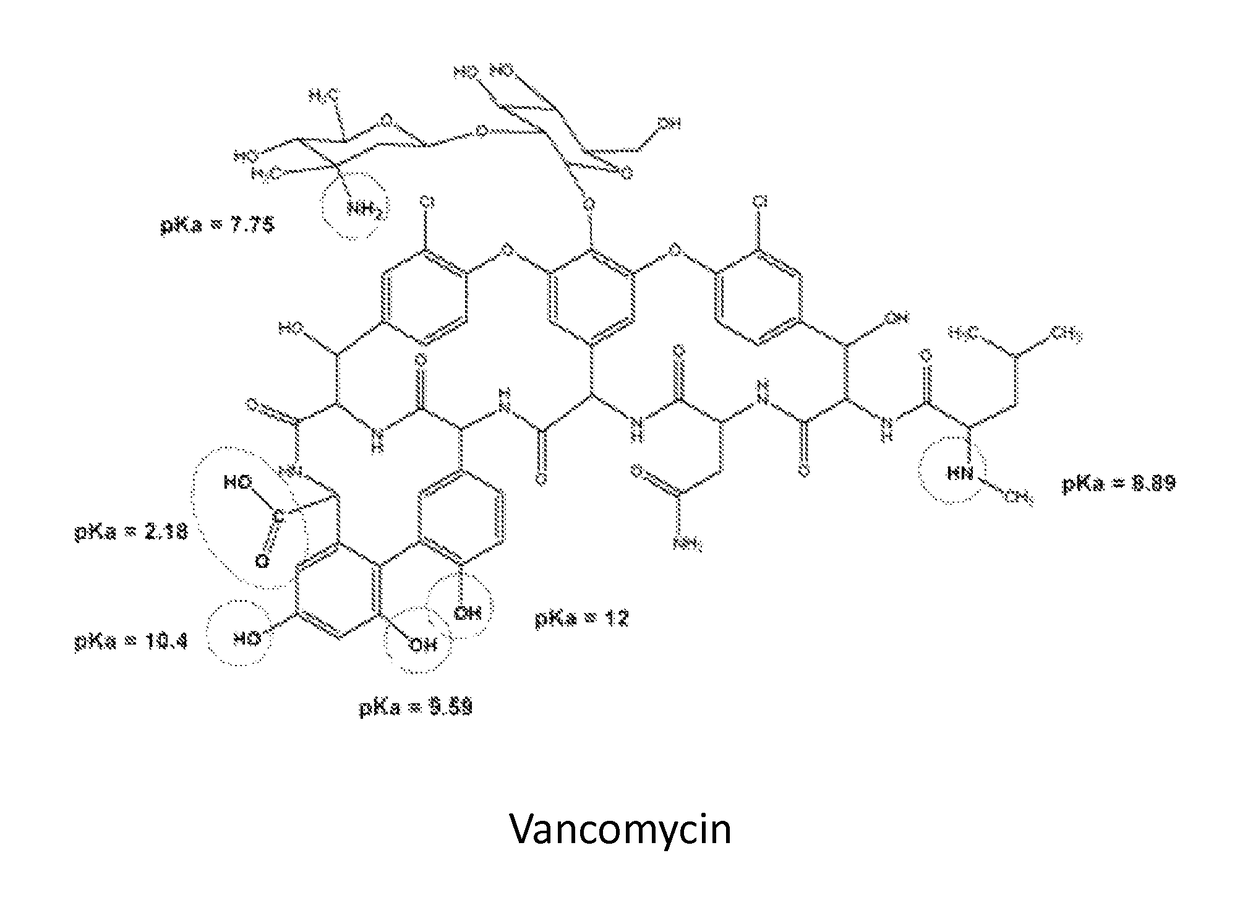
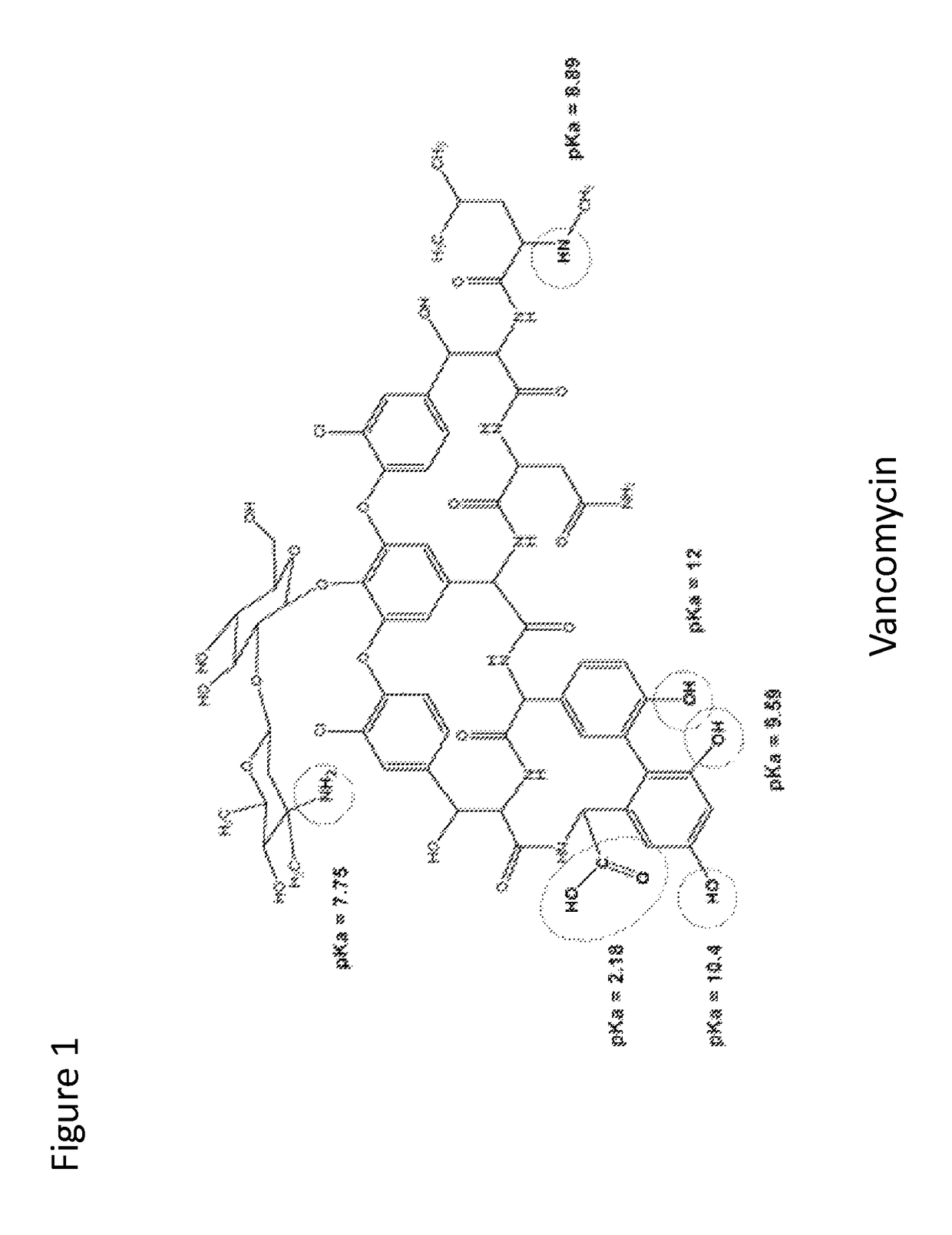
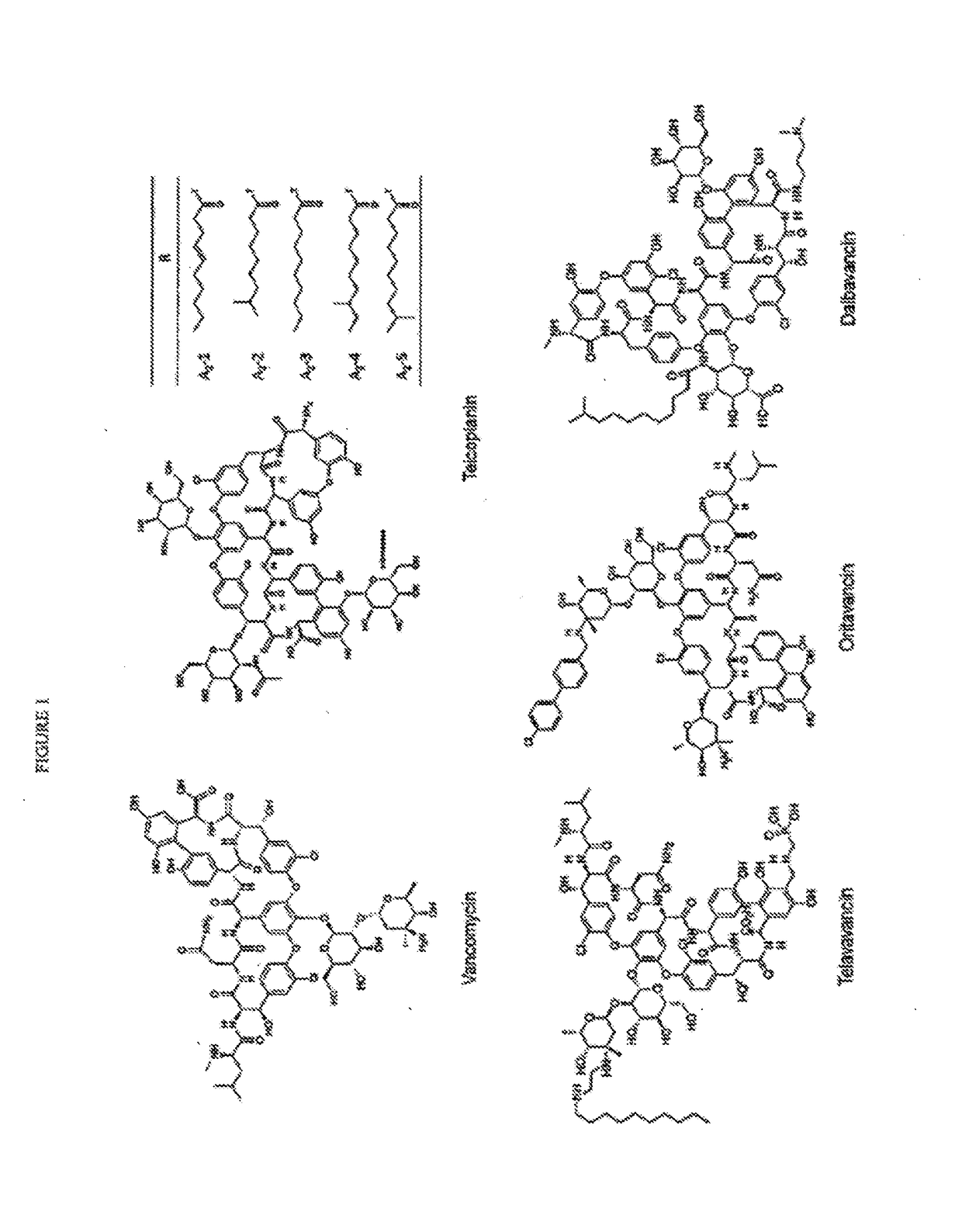
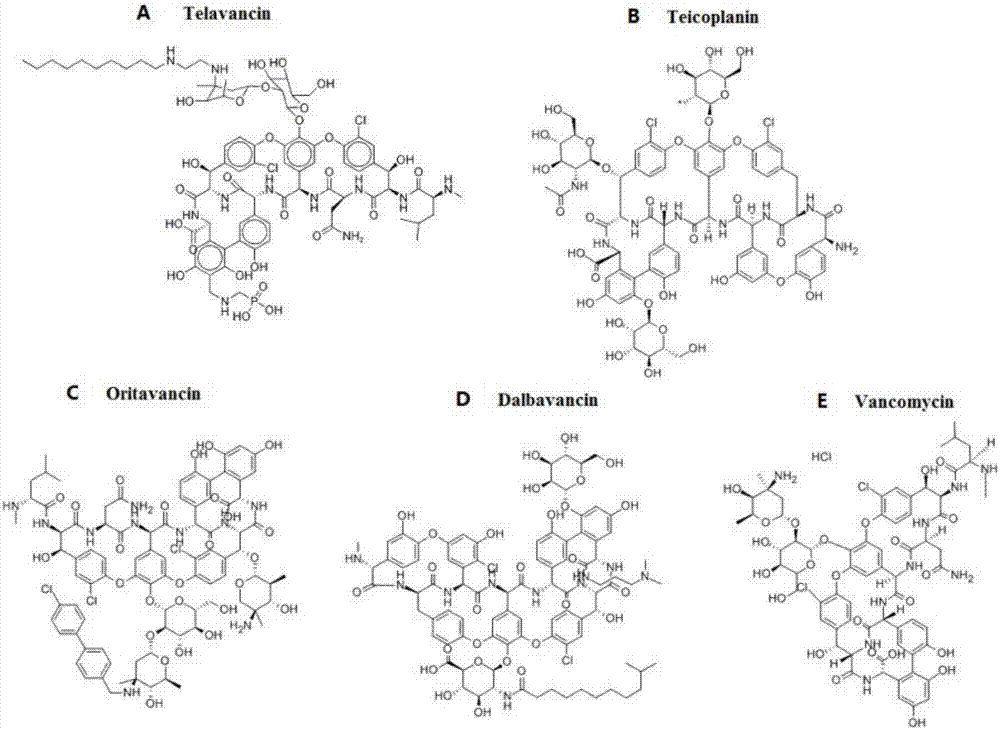
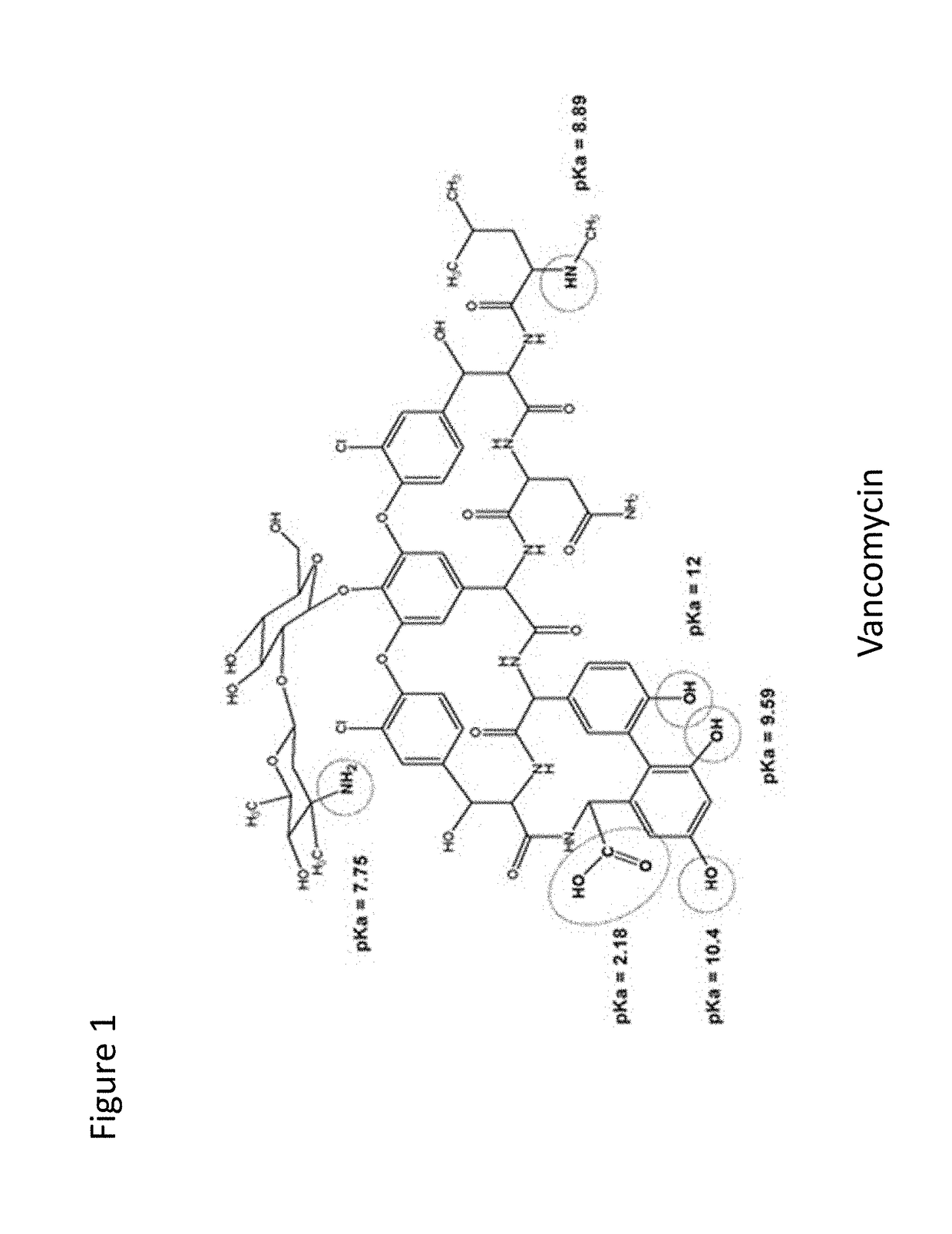
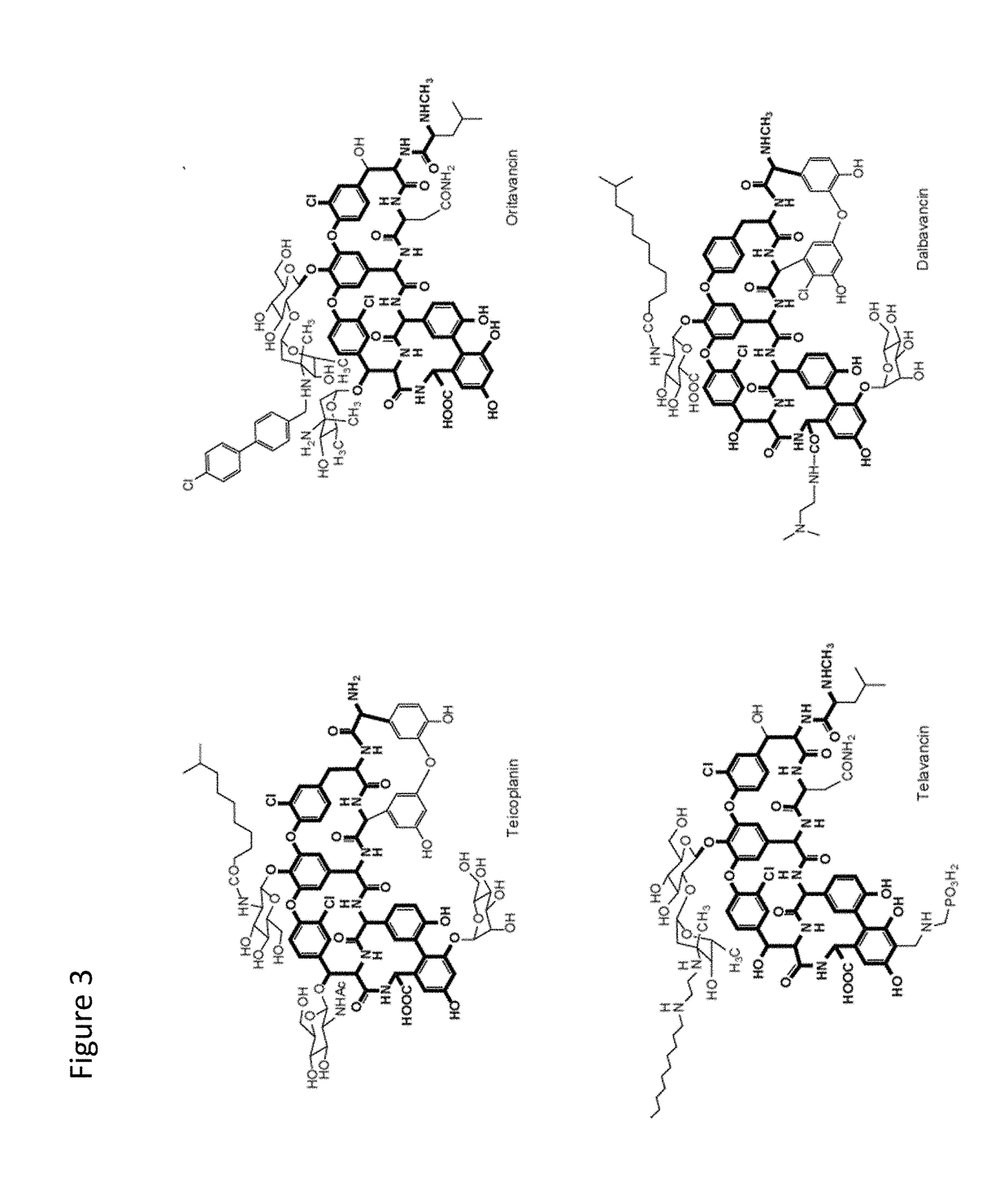
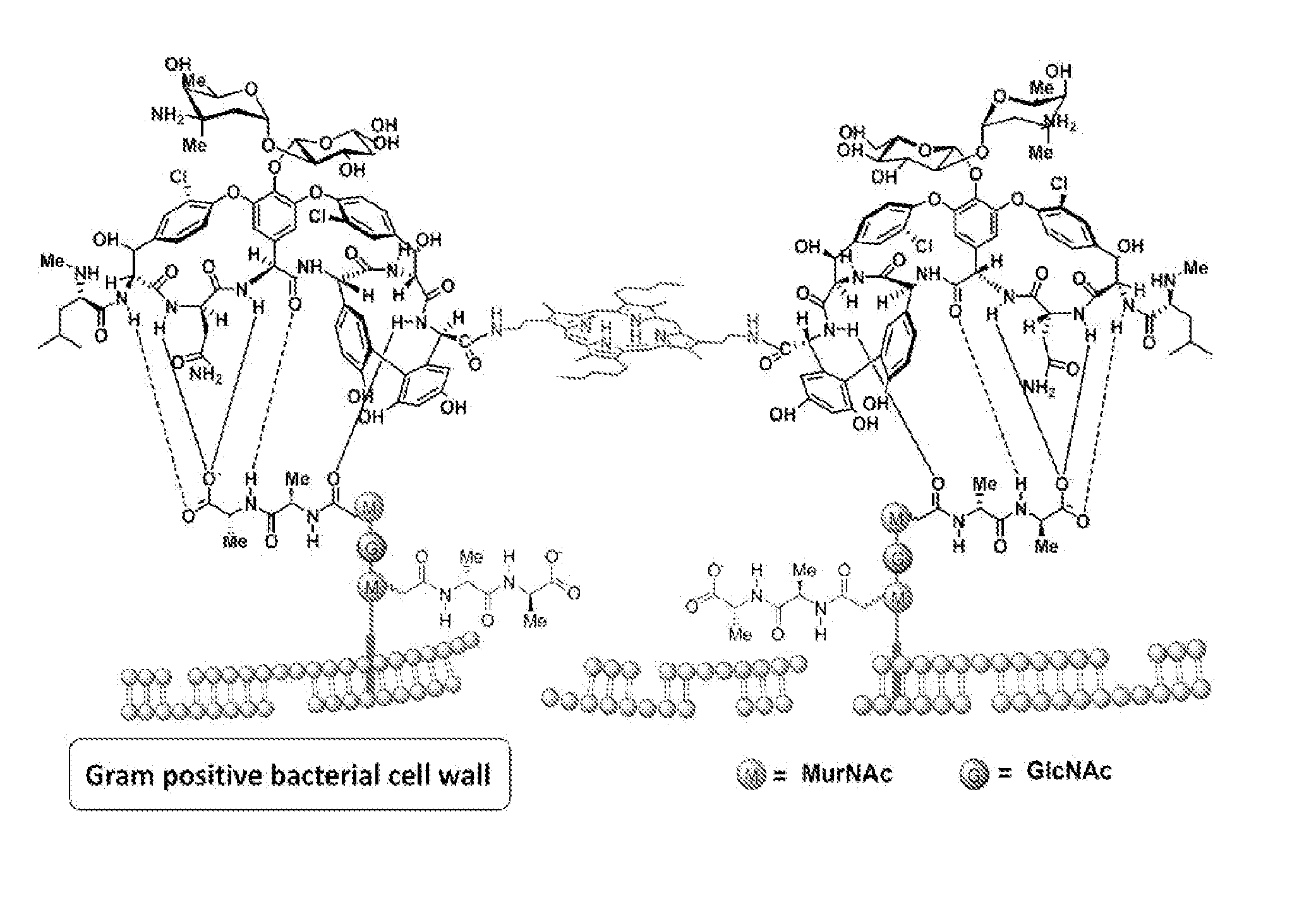
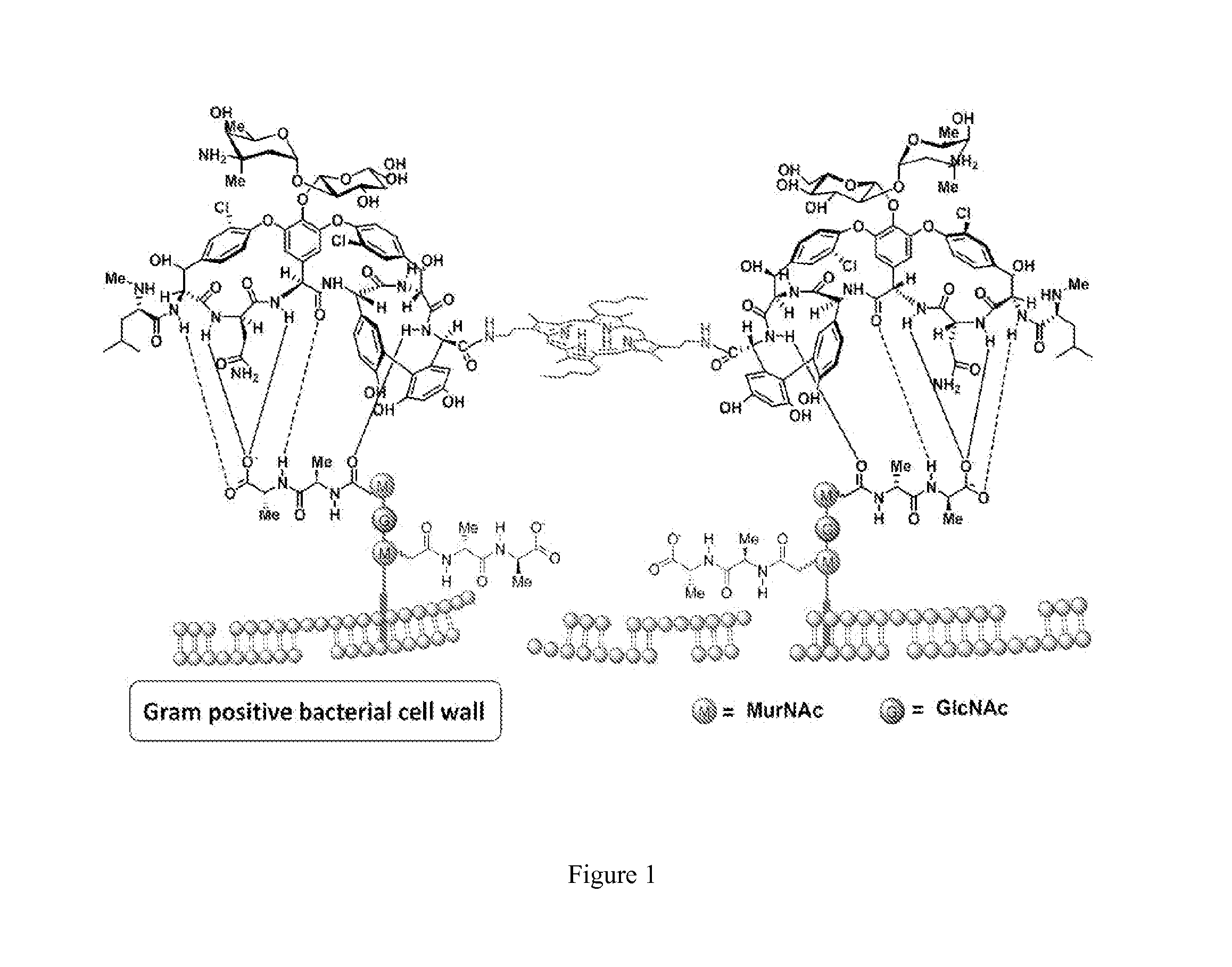
Glycopeptide antibiotics are a class of drugs of microbial origin that are composed of glycosylated cyclic or polycyclic nonribosomal peptides. Significant glycopeptide antibiotics include the anti-infective antibiotics vancomycin, teicoplanin, telavancin, ramoplanin and decaplanin, and the antitumor antibiotic bleomycin. Vancomycin is used if infection with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is suspected.
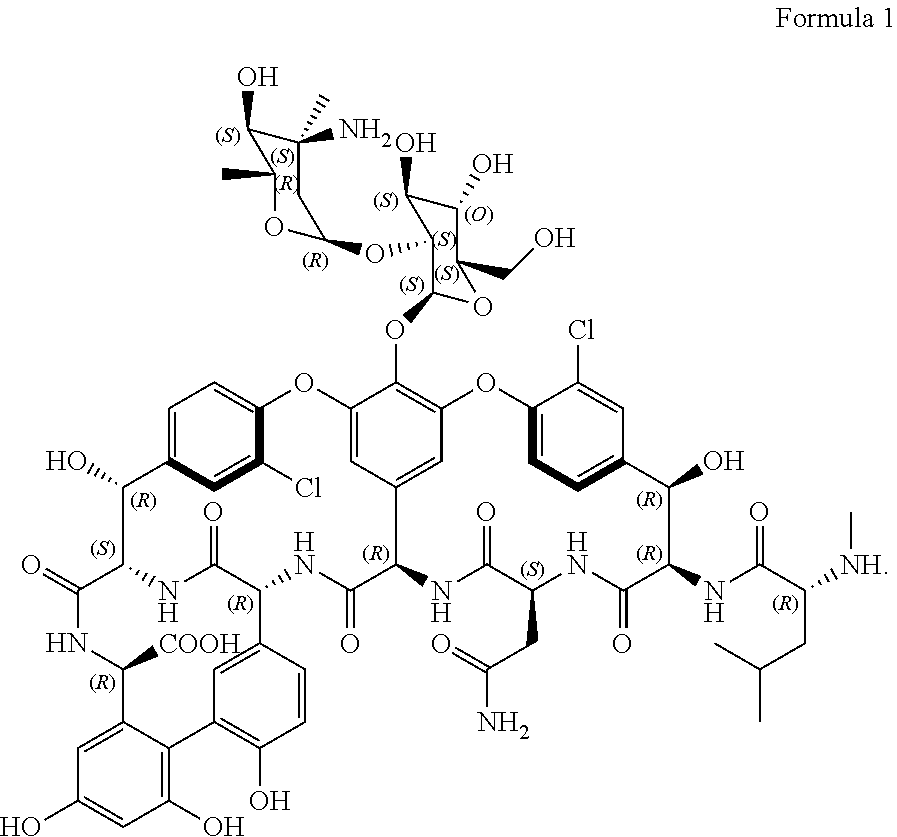
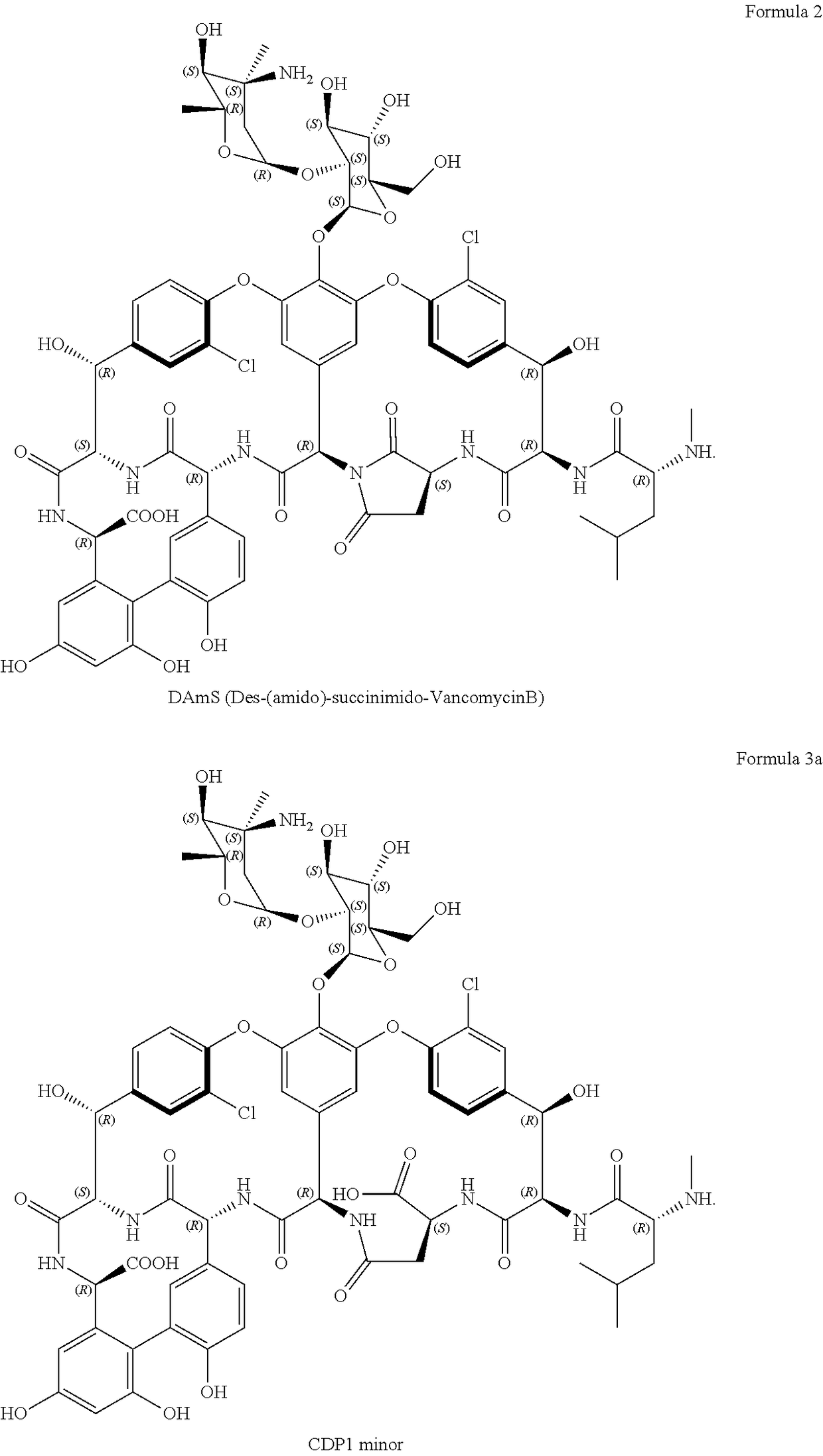
Stabilized vancomycin formulations
InactiveUS20150314002A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPulmonary infectionLipid formation
In one aspect, the invention provides a stabilized lipid-based glycopeptide antibiotic composition and a process for producing the same. In another aspect, the invention provides methods for treating a bacterial pulmonary infection by administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of the stabilized lipid-based glycopeptide antibiotic composition.
Owner:INSMED INC
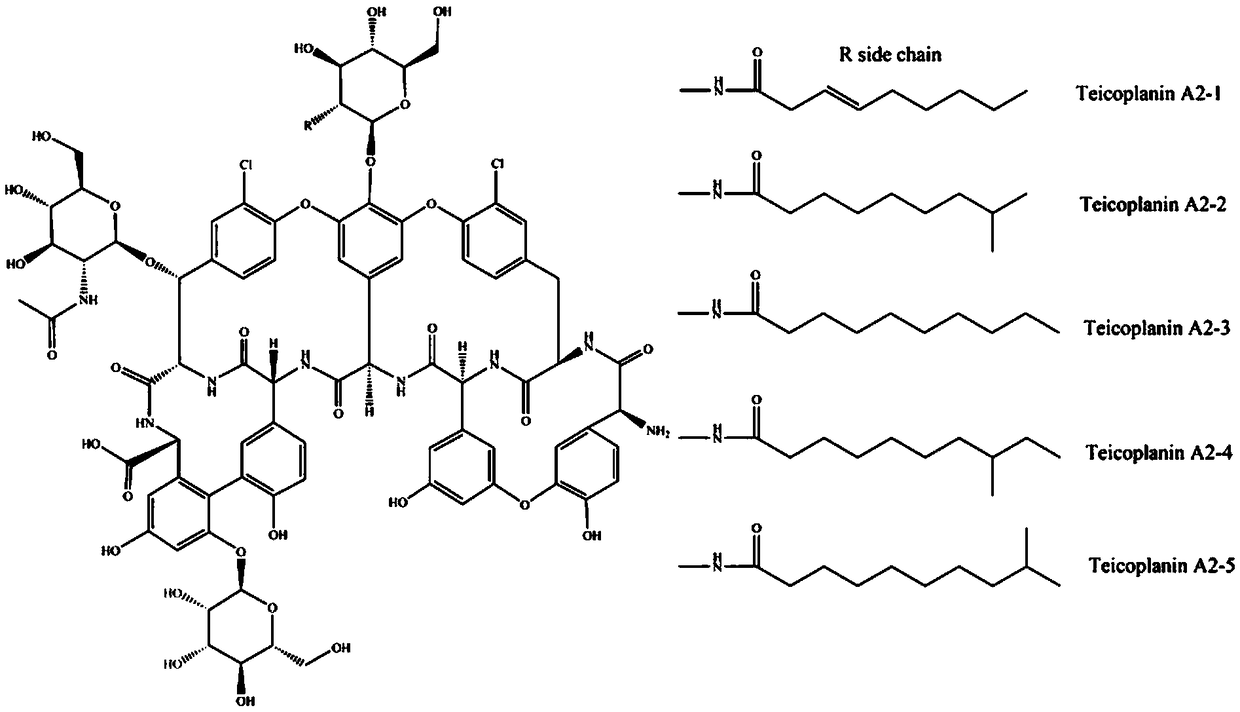
Purification method of teicoplanin
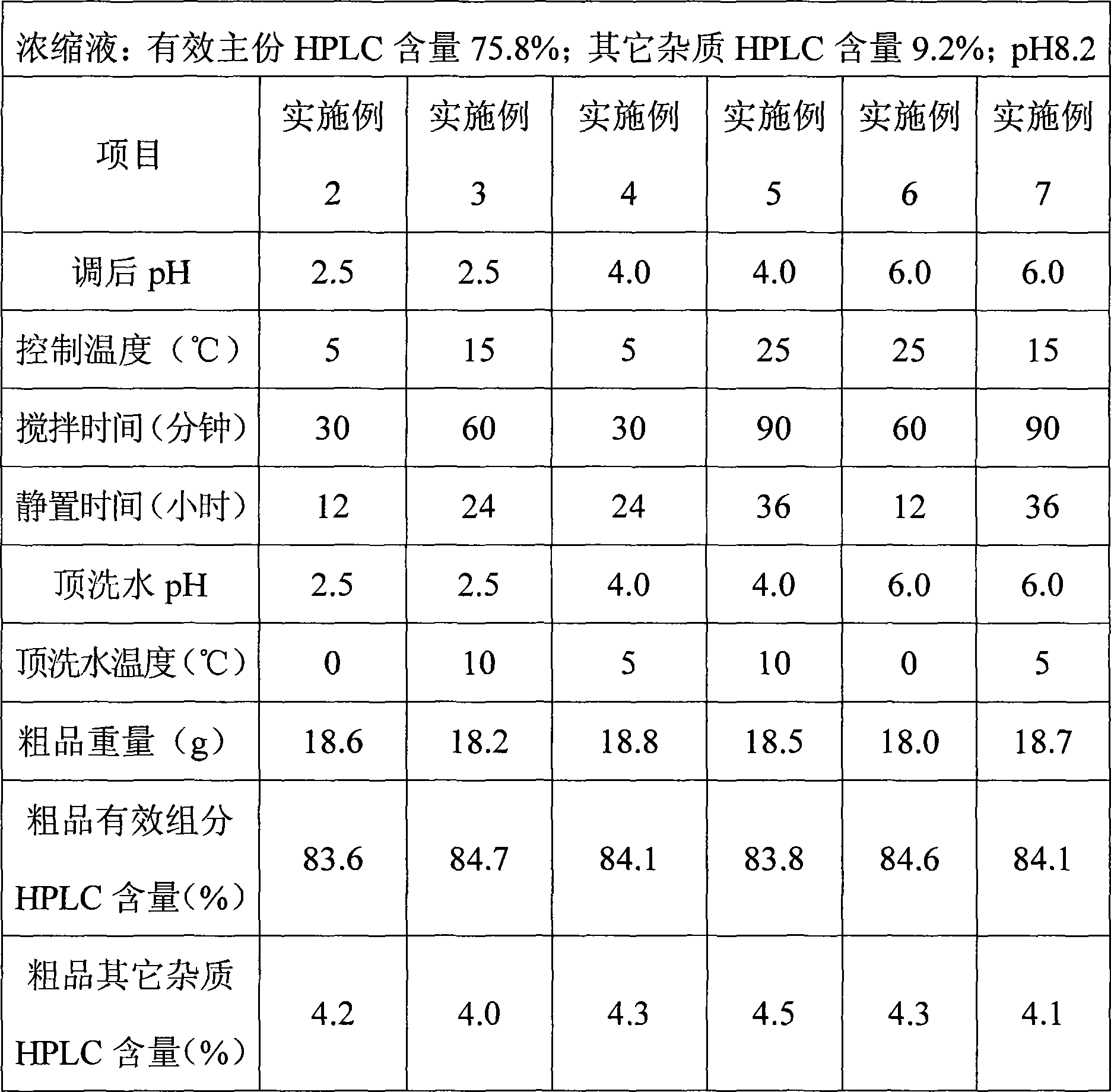
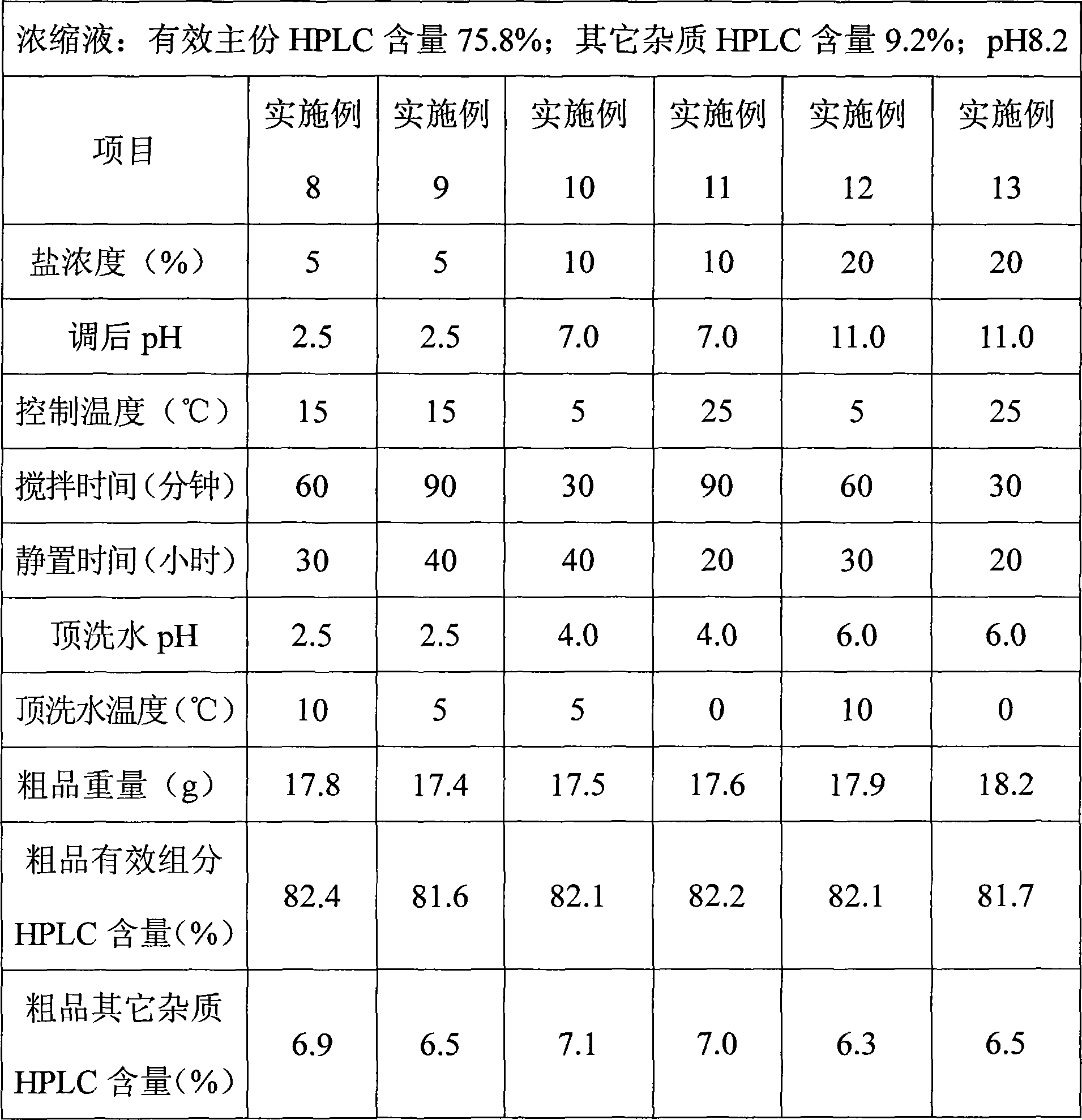
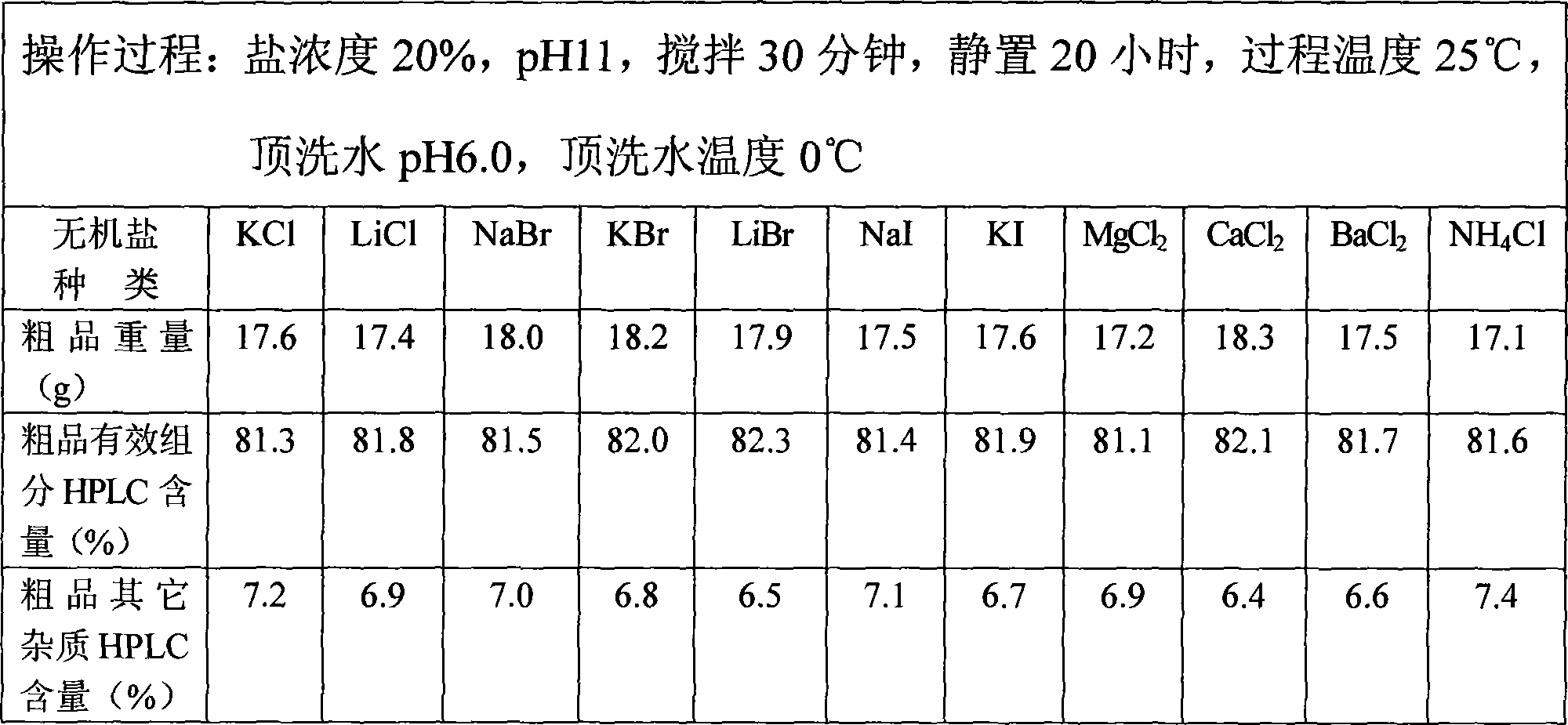
ActiveCN101423547AEffective components increaseLess impuritiesPeptide preparation methodsHigh concentrationPurification methods
The invention relates to a method for preparing glycopeptides antibiotic teicoplanin, which comprises the following steps: after teicoplanin fermented solution is subjected to filtration, adsorption by macroporous resin and decoloring by active carbon, the decoloring solution is concentrated and desolventizing by nanofilteration or hyperfiltration to obtain the teicoplanin water solution with high concentration, and then the teicoplanin is deposited from the solution by adjusting pH, adding salt or adjusting pH and adding salt simultaneously, and the mixture is filtered to obtain teicoplanin. The effective ingredients of the teicoplanin obtained through deposition are obviously improved, and other impurities are reduced. Meanwhile, the appearance color of the product is improved obviously.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEDICINE CO LTD XINCHANG PHAMACEUTICAL FACTORY
Pharmaceutical compositions containing a glycopeptide antibiotic and a cyclodextrin
InactiveUS20020077280A1Reduce adverse effectsExpanding Therapeutic WindowAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryCyclodextrinBacterial Disorder
Disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions containing a cyclodextrin and a therapeutically effective amount of a glycopeptide antibiotic or a salt thereof. Also disclosed are methods of treating a bacterial disease in a mammal by administering such pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:CUMBERLAND PHARM INC
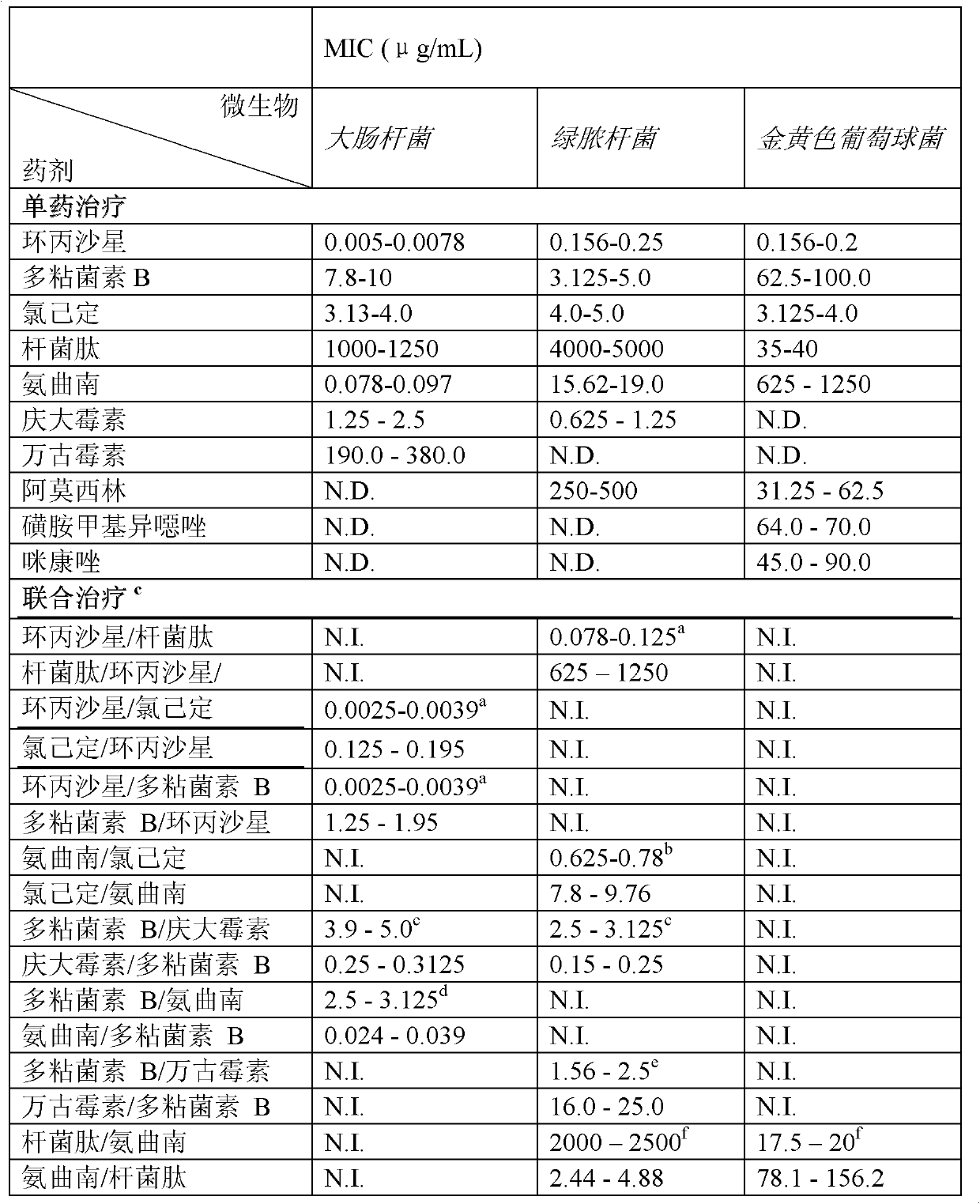
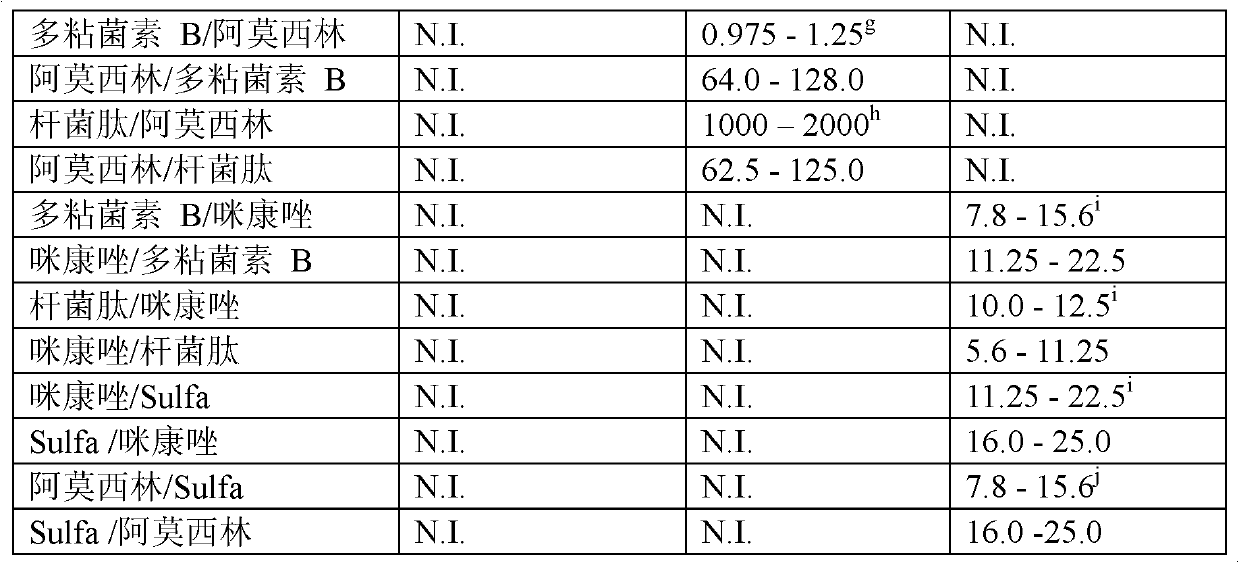
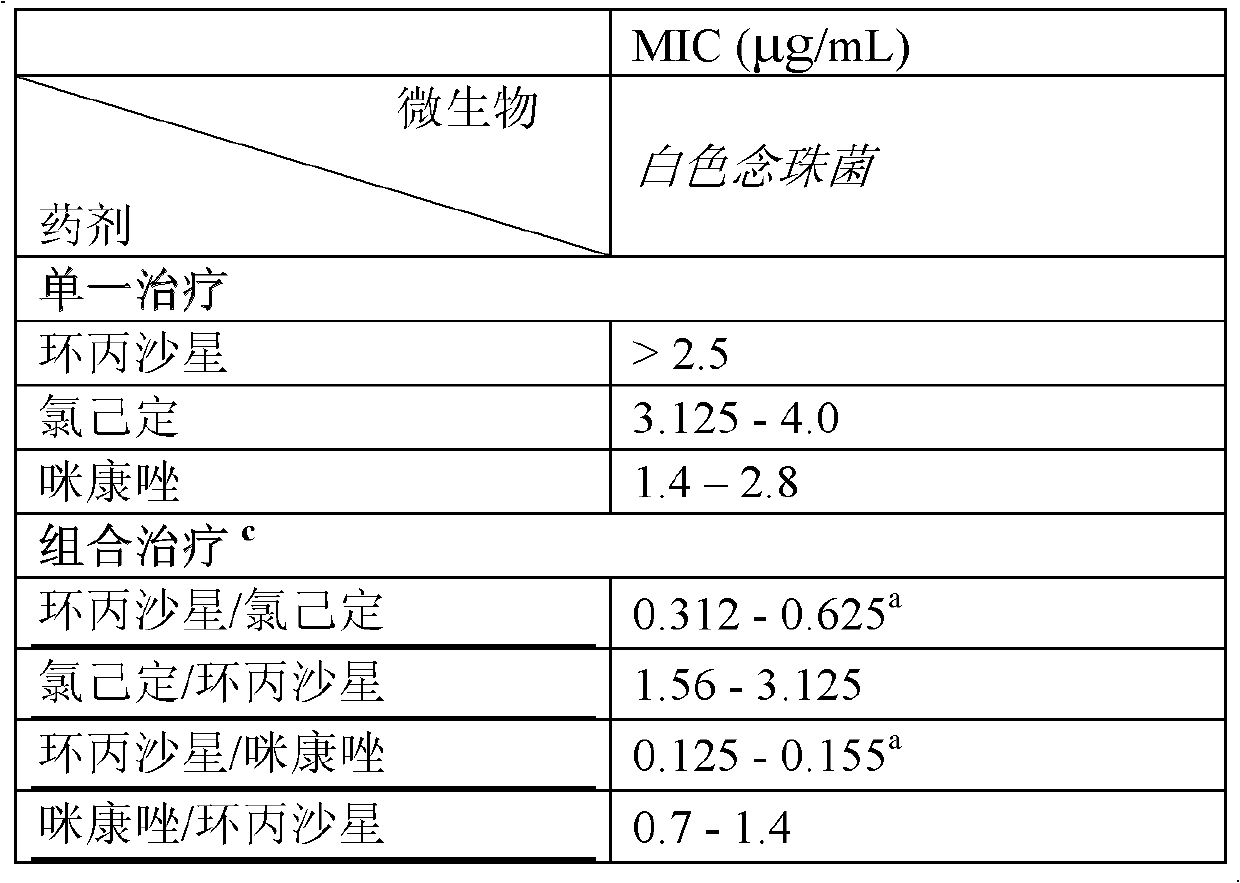
Combination therapy for the treatment of bacterial infections
Compositions comprising the combination of a membrane active biocide and a second agent selected from fluoroquinolones, ammoglycodies, ss-lactams, glycopeptide antibiotics, sufonamides and antifungal azoles and their use in the treatment or prevention of bacterial or fungal infections Preferred membrane active biocides are selected from chlorohexidme, polymyxin B-nonapeptide, bacitracin, aztreonam, benzlakomum salts and metal chelators The active ingredients can be in either monomer or polymeric form.
Owner:INTERFACE BIOLOGICS INC
Glycosylated glycopeptide antibiotic derivative
InactiveCN101959900AGood water solubilityGood body dynamicsAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsVancomycinumSimple aromatic ring
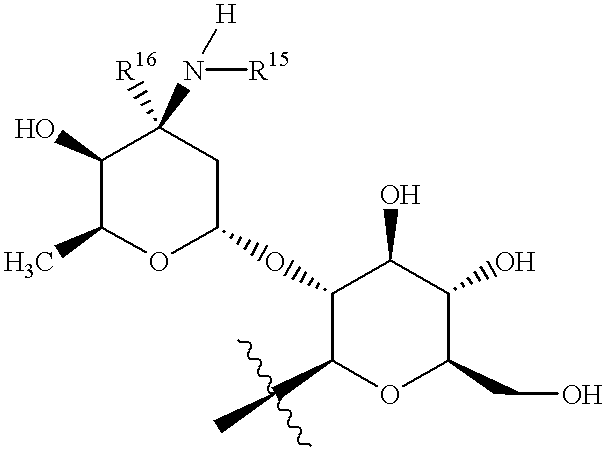
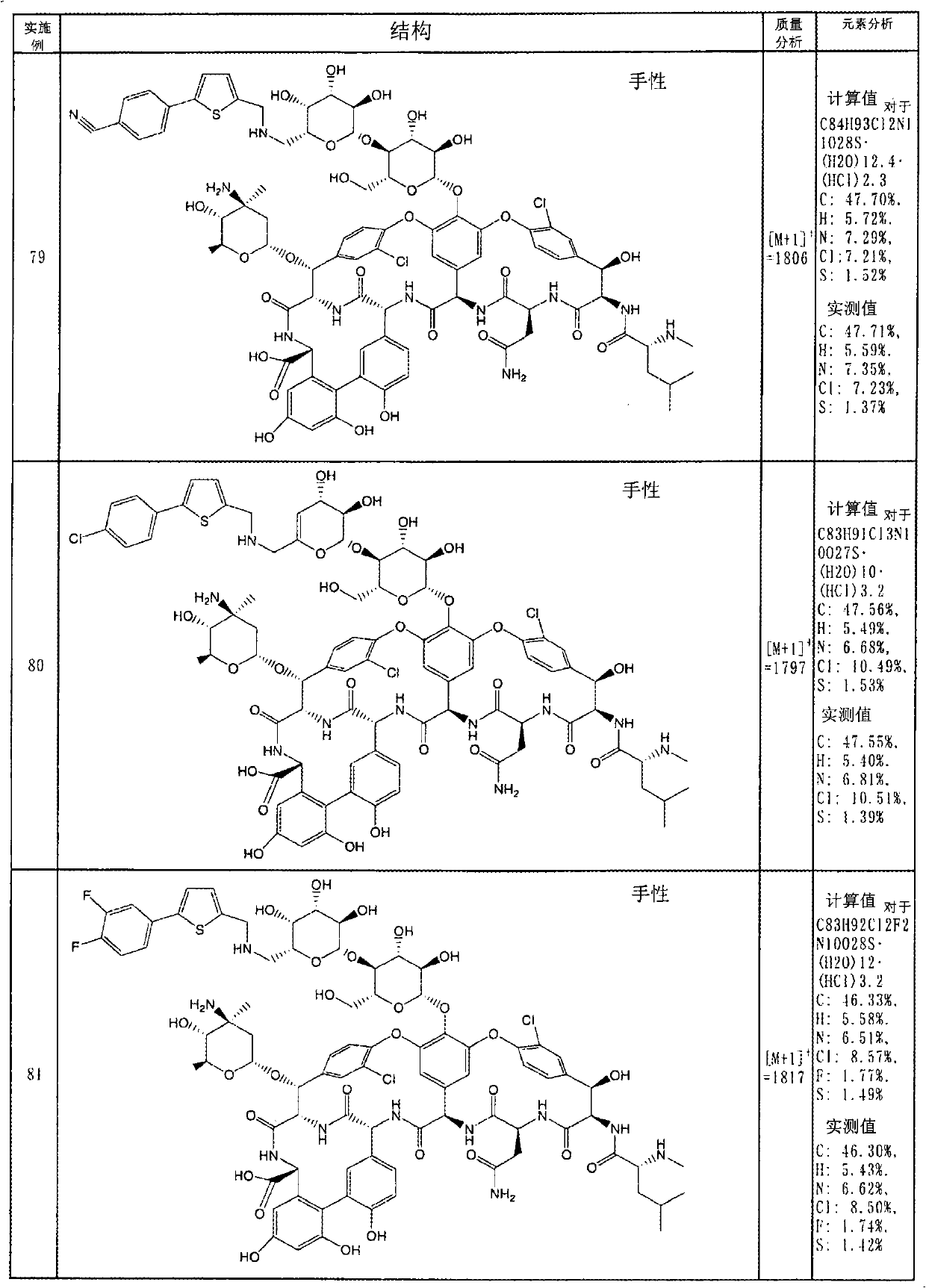
Disclosed is a novel glycopeptide antibiotic derivative. The glycopeptide antibiotic derivative is characterized by having a sugar residue (I) represented by formula (I) [wherein n represents an integer of 1 to 5; Sug's independently represent a monosaccharide, and (Sug)n represents a bivalent sugar residue formed by binding 1 to 5 monosaccharides which are the same as or different from each other; RA1 represents a lower alkyl which may be substituted, a lower alkenyl which may be substituted, or a cycloalkyl which may be substituted; and RE represents OH or NHAc (wherein Ac represents an acetyl)] bound to an aromatic ring in the 4th amino acid residue located in a glycopeptide skeleton. The derivative has an antibacterial activity against a vancomycin-resistant bacterium.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
Stabilized vancomycin formulations
InactiveUS10124066B2Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationPulmonary infection
In one aspect, the invention provides a stabilized lipid-based glycopeptide antibiotic composition and a process for producing the same. In another aspect, the invention provides methods for treating a bacterial pulmonary infection by administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of the stabilized lipid-based glycopeptide antibiotic composition.
Owner:INSMED INC
Glycopeptide antibiotic derivatives
InactiveUS20050250677A1Decreasing and removing antibacterial activityMaintain antiviral activityBiocideDigestive systemHerpes zoster virusGlycopeptide
Novel glycopeptide antibiotic derivatives, processes for their preparation, their use as a medicine, their use to treat or prevent viral infections and their use to manufacture a medicine to treat or prevent viral infections are provided. The present invention relates to the use of glycopeptide antibiotics and their semisynthetic derivatives to treat or prevent viral infections and their use to manufacture a medicine to treat or prevent viral infections of subjects, more in particular infections with viruses belonging to Retroviridae, Herpes viridae, Flaviviridae and the Coronaviridae, like HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), HCV (hepatitis C virus), BVDV (bovine viral diarrhoea virus), SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) causing virus, FCV (feline coronavirus), HSV (herpes simplex virus), VZV (varicella zoster virus) and CMV (cytomegalovirus).
Owner:BALZARINI JAN +2
Novel formulation of pegylated-liposome encapsulated glycopeptide antibiotics
This invention is directed to a novel method of treating an individual suffering from a bacterial infection, such as bacterial infections of various tissues or organs of an individual. In general, the method of treatment involves administering to an individual a pharmaceutical formulation that comprises a liposome-encapsulated antimicrobial agent, wherein polyethylene glycol (PEG) molecules are covalently attached to the surface of the liposomes.
Owner:WESTERN UNIV OF HEALTH SCI
Glycopeptide compositions
Solutions comprising a glycopeptide antibiotic, for example Vancomycin, and an amino acid or amino acid derivative such as N-acetyl-Glycine or N-acetyl-D-Alanine are provided. These solutions are stable or stabilized for long-term periods at conditions of normal use and storage, and can be formulated as pharmaceutical solutions for use in subjects. Methods of manufacturing and using these solutions are also provided, as are methods of stabilizing a glycopeptide antibiotic, for example Vancomycin, using amino acids or amino acid derivatives such as N-acetyl-Glycine or N-acetyl-D-Alanine.
Owner:AXELLIA PHARMA APS
Novel glycopeptide antibiotic derivative and pharmaceutical composition, and preparation method and purpose thereof
ActiveCN102690332AImprove antibacterial propertiesAntibacterial agentsSaccharide peptide ingredientsAntibiosisHalogen
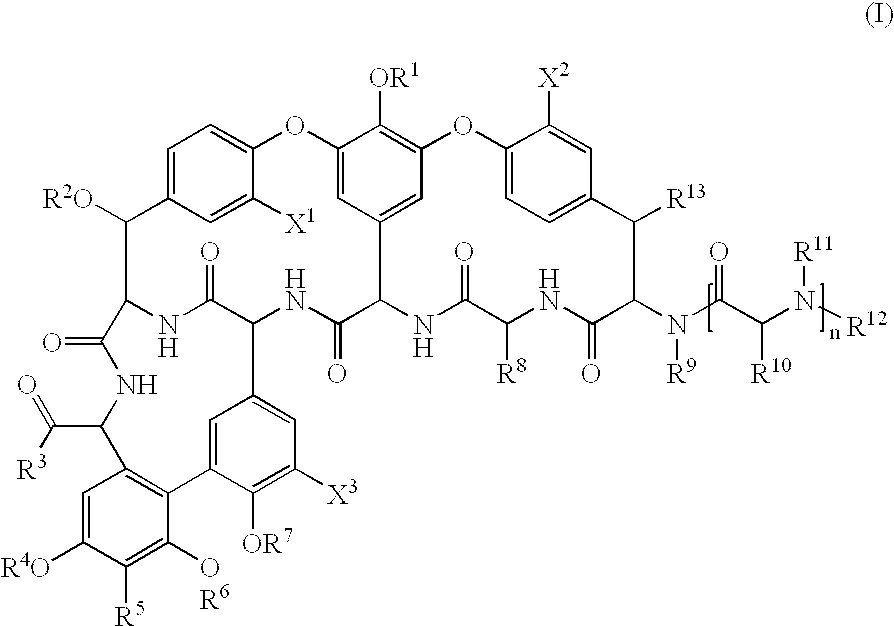
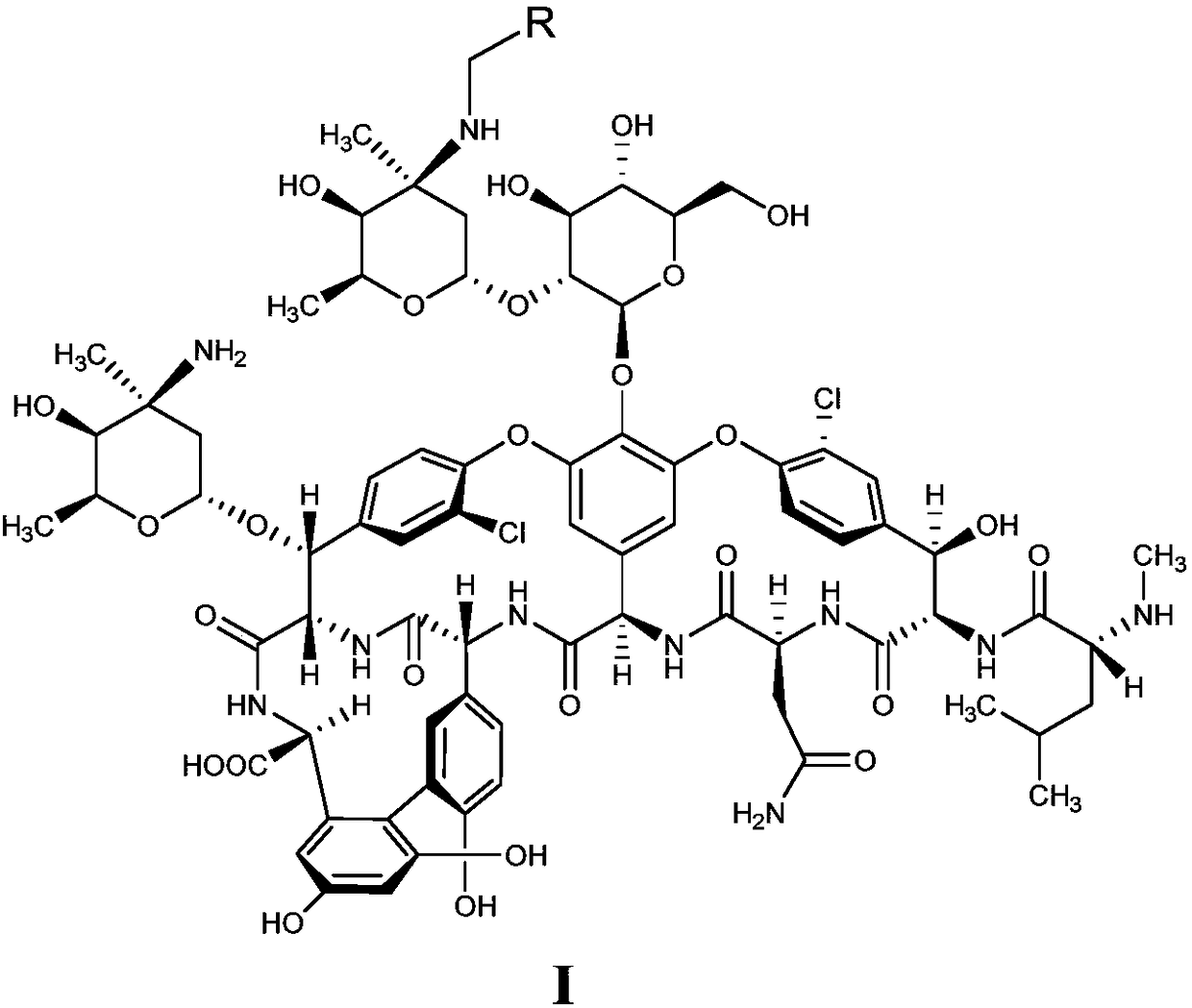
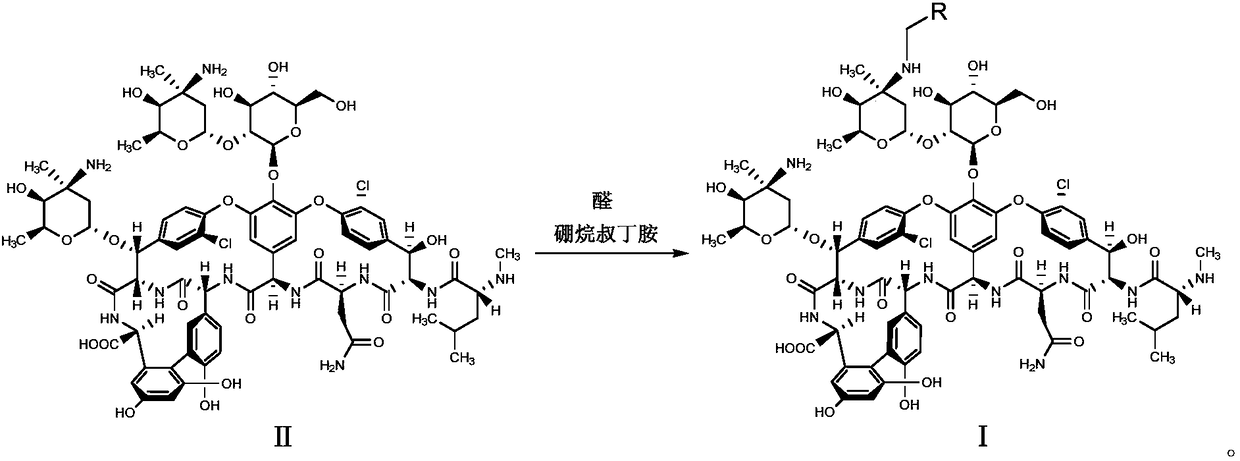
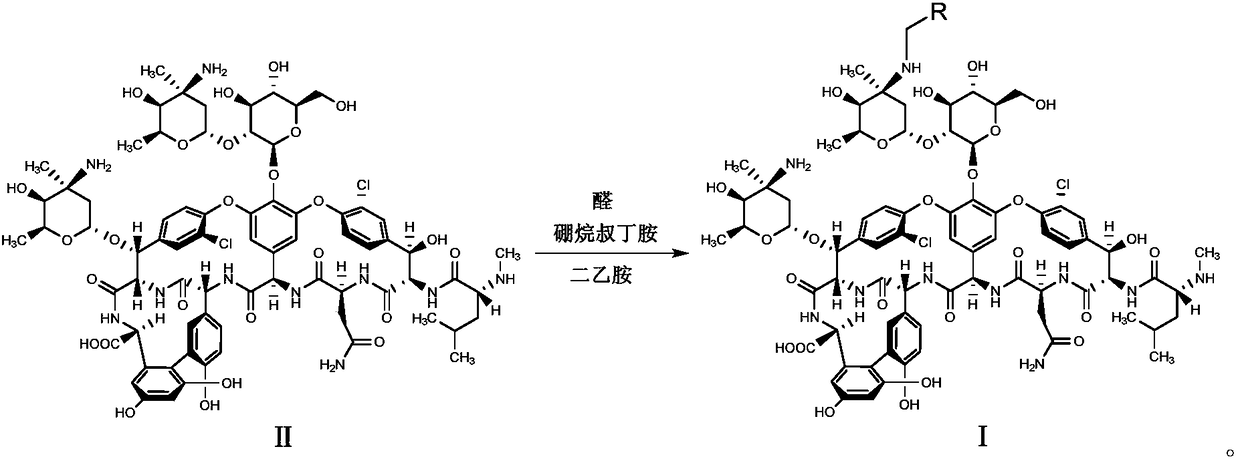
The invention discloses a glycopeptide antibiotic derivative shown as a general formula (I) and pharmaceutically accepted salt thereof, and a preparation method thereof. R1 represents C3-9 saturated fatty alkyl, decylamine methyl or an aromatic group, which is unsubstituted or substituted phenyl ring, biphenyl ring or naphthalene ring; and a substituent of the phenyl ring, biphenyl ring or naphthalene ring is one or more selected from the group of halogen, hydroxy, amino, C1-9 alkyloxy, nitro and isopropyl. R2 represents H or CH2-R3. R3 represents C3-9 saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon group. In addition, the invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition containing the glycopeptide antibiotic derivative and pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof as active components, and application thereof. The compound and pharmaceutical composition provided by the invention have good antibiosis activity and great significance for development of novel antibacterial medicament.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEDICINE CO LTD XINCHANG PHAMACEUTICAL FACTORY +1
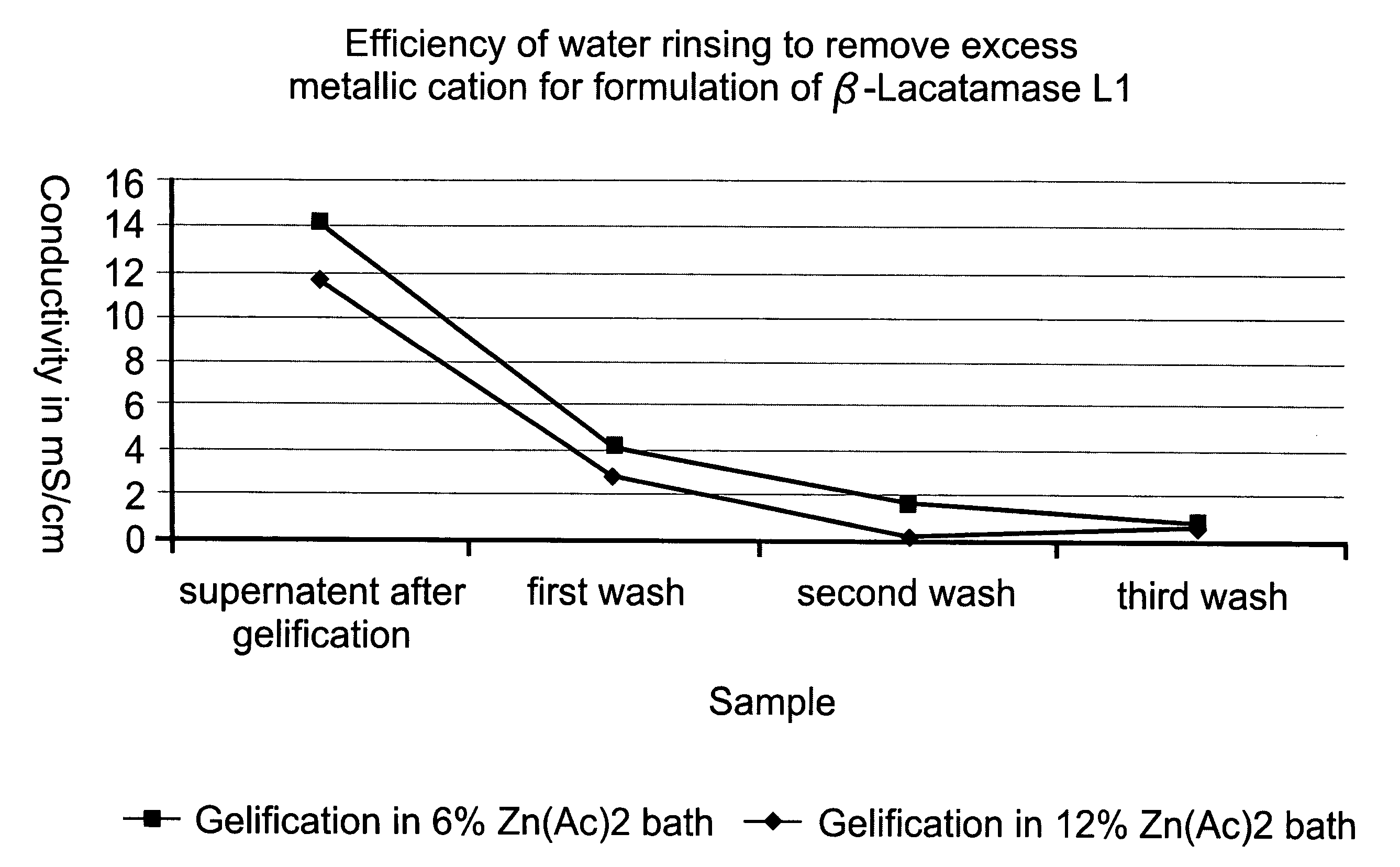
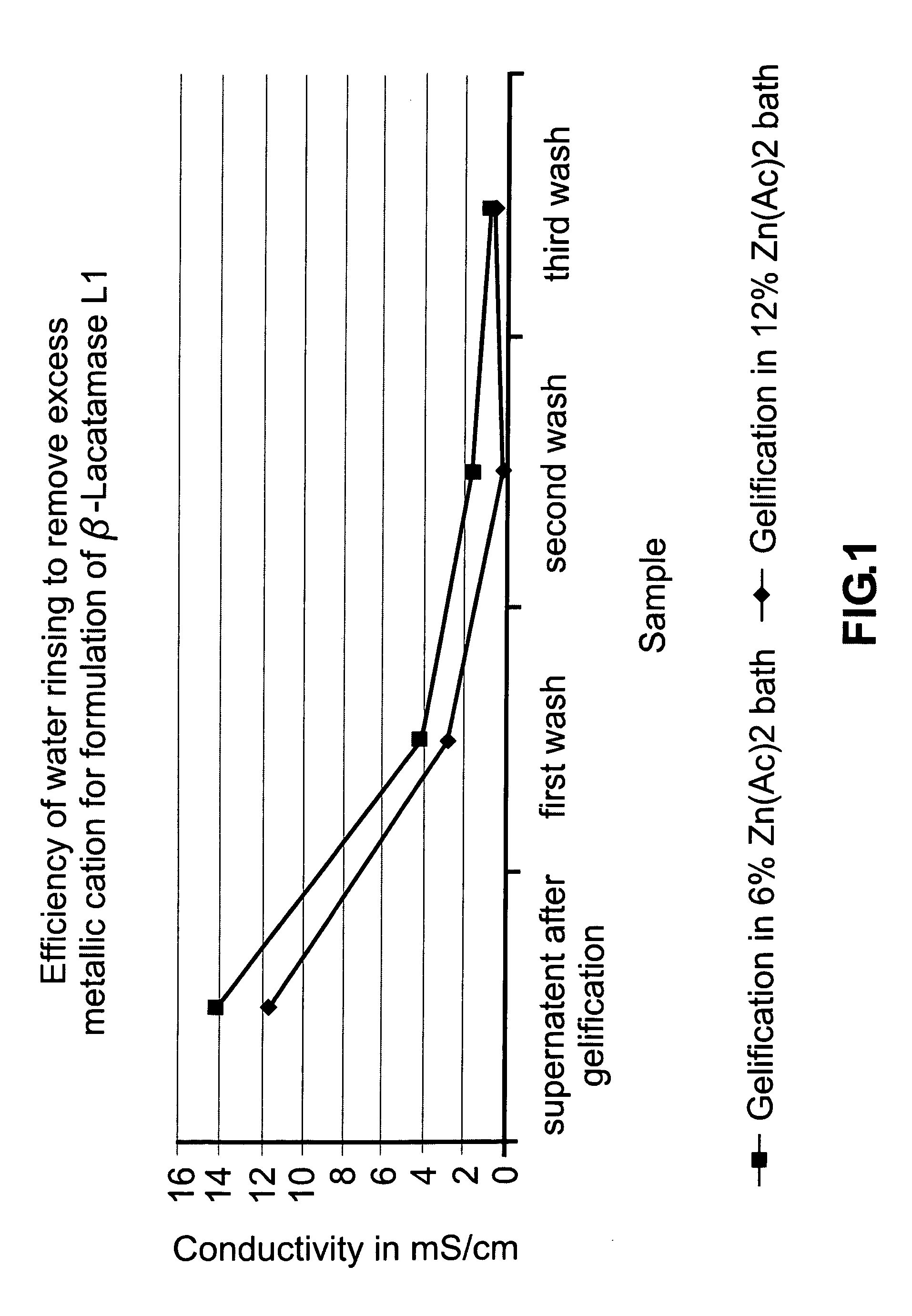
Colonic delivery of metallo-dependent enzymes
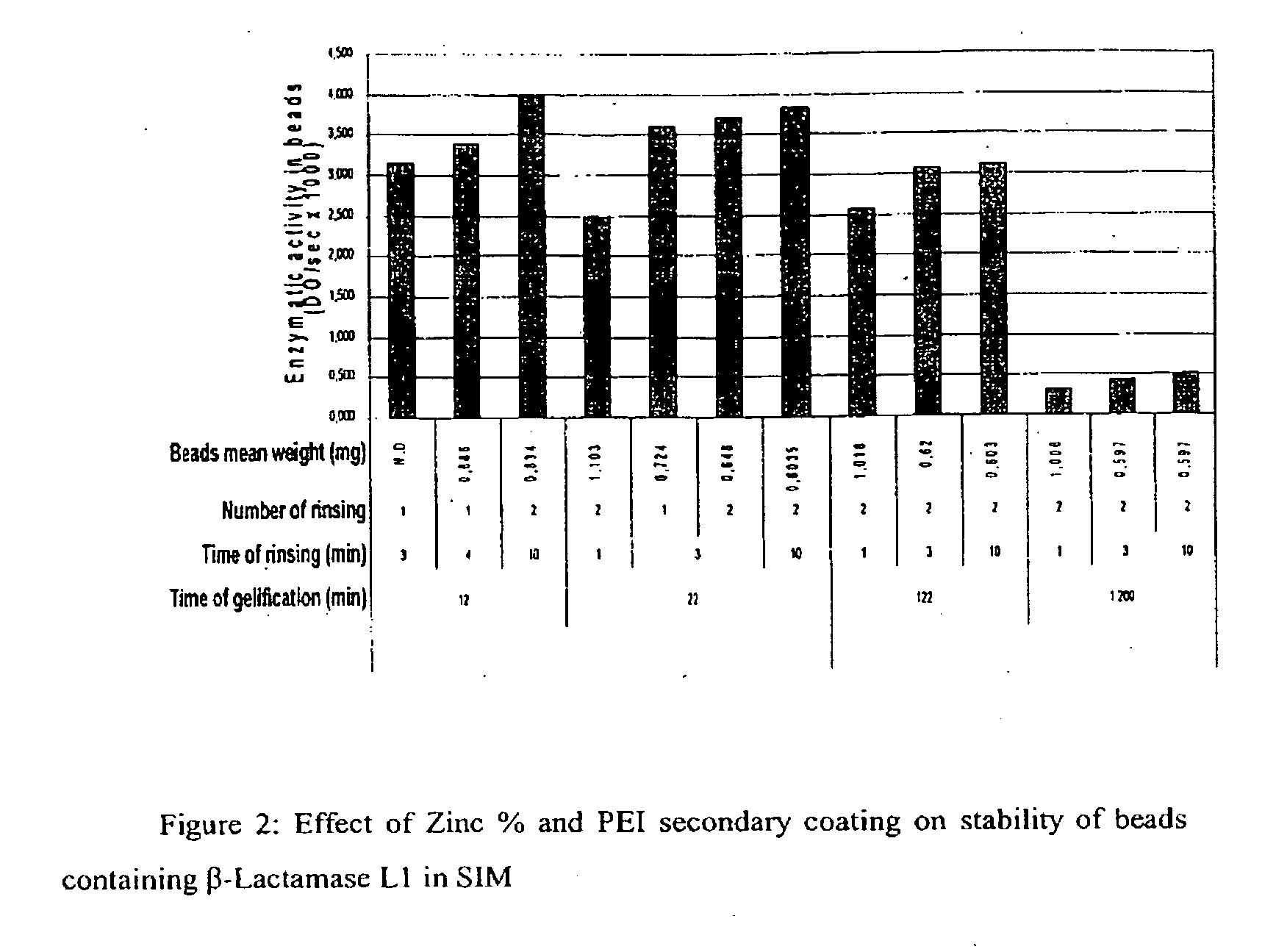
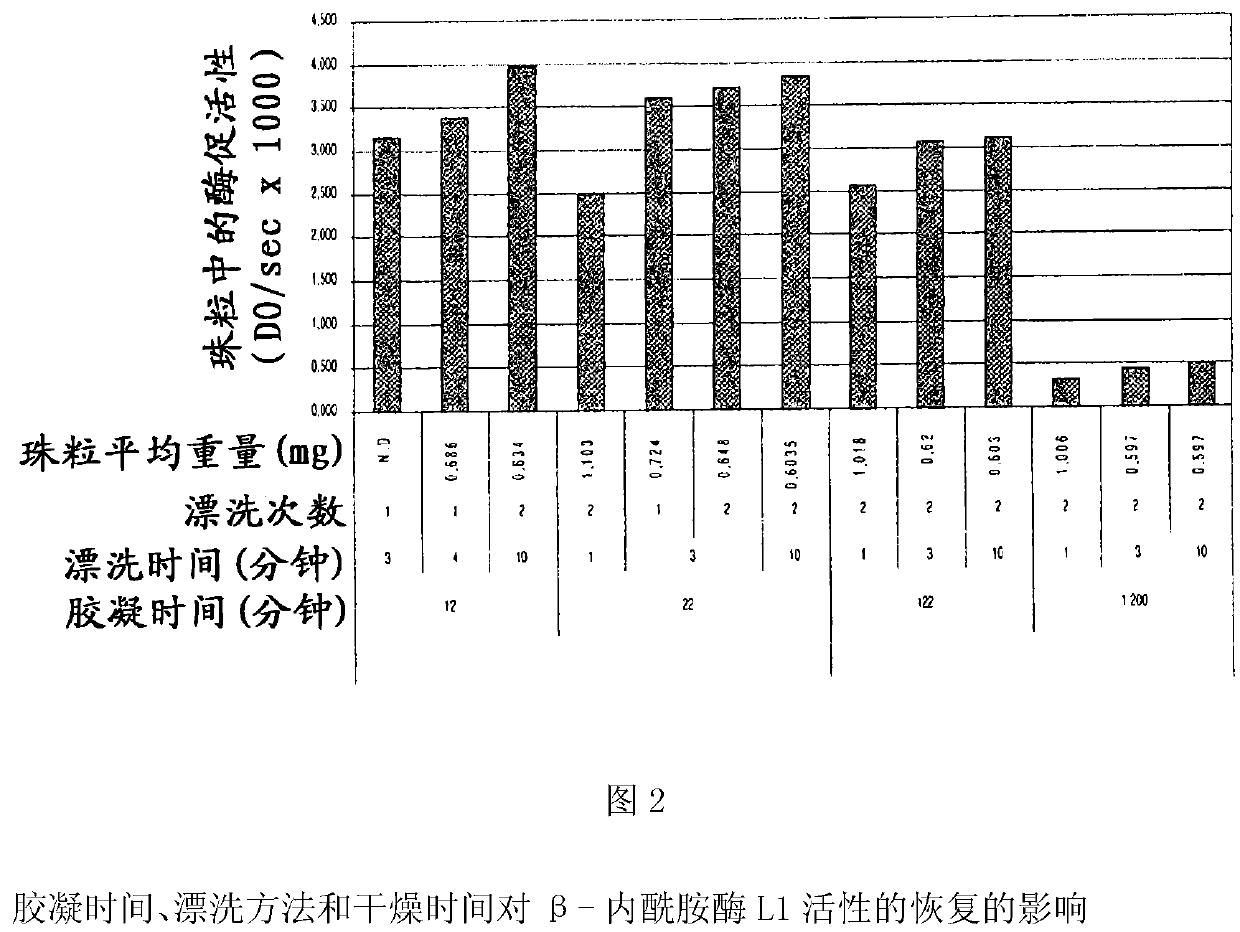
Drug delivery systems for delivering agents capable of reducing the quantity of residual antibiotics reaching the colon following oral or parenteral antibiotic therapy, and for delivering metallo-dependent enzymes, and methods of using the drug delivery systems, are disclosed. The drug delivery systems include pectin beads that encapsulate the active agent (which can be a metallo-dependent enzyme), where the pectin is crosslinked with zinc or any divalent cation of interest and the pectin beads are coated with Eudragit®-type polymers. The drug delivery systems are orally administrable, but can deliver the active agents to the colon. In some embodiments, they can administer the agents to various positions in the gastro-intestinal tract, including the colon. One metallo-dependent enzyme is the β-lactamase L1 from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, and agents that inactivate macrolide, quinolone, fluoroquinolone or glycopeptide antibiotics can also be used. The delivery of the active agent can be modulated to occur at various pre-selected sites of delivery within the intestinal tract by gelling / crosslinking a mixture of the active agent, such as a metallo-dependent enzyme, and pectin, with divalent metallic cations such as Ca+2 or Zn+2. A stable metallo-dependent enzyme formulation can be delivered to the lower intestine or colon. The use of zinc cations to crosslink the pectin is particularly preferred when specific metallo-dependent enzymes, which are Zn2+ dependent, could interact with other cationic species if they were used to gel the pectin beads and thus adversely affect the activity of such metallo-dependent enzymes.
Owner:ASSISTANCE PUBLIQUE HOPITAUX DE PARIS +2
Method for simultaneously detecting various glycopeptides antibiotics in animal derived food
ActiveCN107957464AHigh recovery rateThe detection method is sensitive, accurate and fastComponent separationDalbavancinTelavancin
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously detecting various glycopeptides antibiotics in animal derived food. The method mainly comprises the following steps: carrying out solution extraction on a sample; carrying out series purification and enrichment by using HLB solid-phase extraction columns and strong cation (MCX) solid-phase extraction columns; separating the sample by using reversed phase columns, and then detecting the sample by using an ultra-efficient liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry in a multi-reaction monitoring mode; and carrying out qualitative and quantitative analysis. Five glycopeptides antibiotics including telavancin, teicoplanin, oritavancin, dalbavancin and vancomycin in the sample animal derived food such as milk, eggs and chicken can be detected simultaneously. The detecting method is sensitive, accurate and rapid; and the five glycopeptides antibiotics can be qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed by six minutes displayed on an instrument. Moreover, the detecting method also has certain reference value for detection of other glycopeptides antibiotics.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION (GUANGZHOU HYGIENE INSPECTION CENT GUANGZHOU CENT FOR FOOD SAFETY RISK SURVEILLANCE & ASSESSMENT INST OF PUBLIC HEALTH OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV)
Antibiotic-/ antibiotic-polymer compound
An antibiotic polymer combination / antibiotics polymer combination that ensures the continuous release of antibiotics over a period of several days under physiological conditions, and that can be used in human and veterinary medicine. Surprisingly, one or more antibiotic salts, which are sparingly soluble in water, from the groups comprising aminoglycoside antibiotics, lincosamide antibiotics, tetracycline antibiotics, glycopeptide antibiotics, quinolone antibiotics and chlorhexidine, are suspended in homogeneous polymer mixtures, which comprise one or more hydrophobic, nonionic polymers from the groups comprising poly(vinyl, chloride), post-chlorinated poly(vinyl chloride), poly(vinylidene chloride), poly(vinyl fluoride), poly(vinylidene fluoride) and copolymers comprising vinyl chloride and one or more nonionic monomers, and which comprise one or more hydrophilic polymers from the groups comprising polyethers, and this suspension forms composites that exhibit the release of an active ingredient over a period of days in an aqueous medium.
Owner:HERAEUS KULZER
Colonic delivery using Zn/pectin beads with a Eudragit coating
Drug delivery systems that can deliver therapeutic and / or diagnostic agents to the colon are disclosed. The systems include pectin beads crosslinked with zinc or any divalent cation of interest, which beads are then coated with Eudragit TM -type polymers. The drug delivery systems are orally administrable, but can deliver the active agents to the colon, or, in some embodiments, to various other positions in the gastro-intestinal tract. The agents can be used to diagnose, treat, prevent, or investigate a variety of conditions, including infectious diseases, inflammatory diseases, cancers and the like. Certain agents, such as metallo-dependent enzymes, for example, ss-lactamase Ll from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, as well as agents that inactivate macrolide, quinolone, fluoroquinolone or glycopeptide antibiotics, can reduce the quantity of residual antibiotics reaching the colon following antibiotic therapy.
Owner:DA VOLTERRA
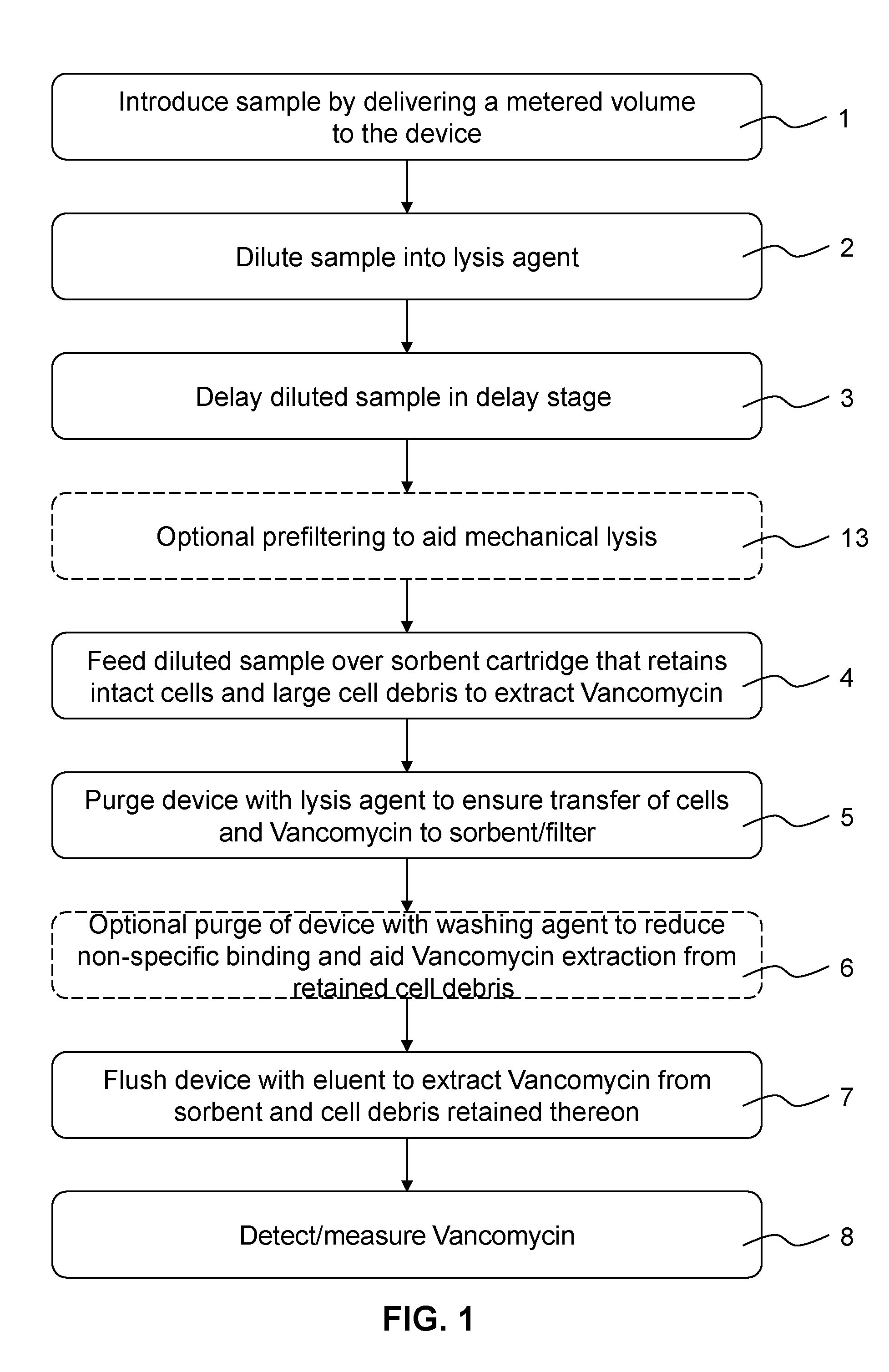
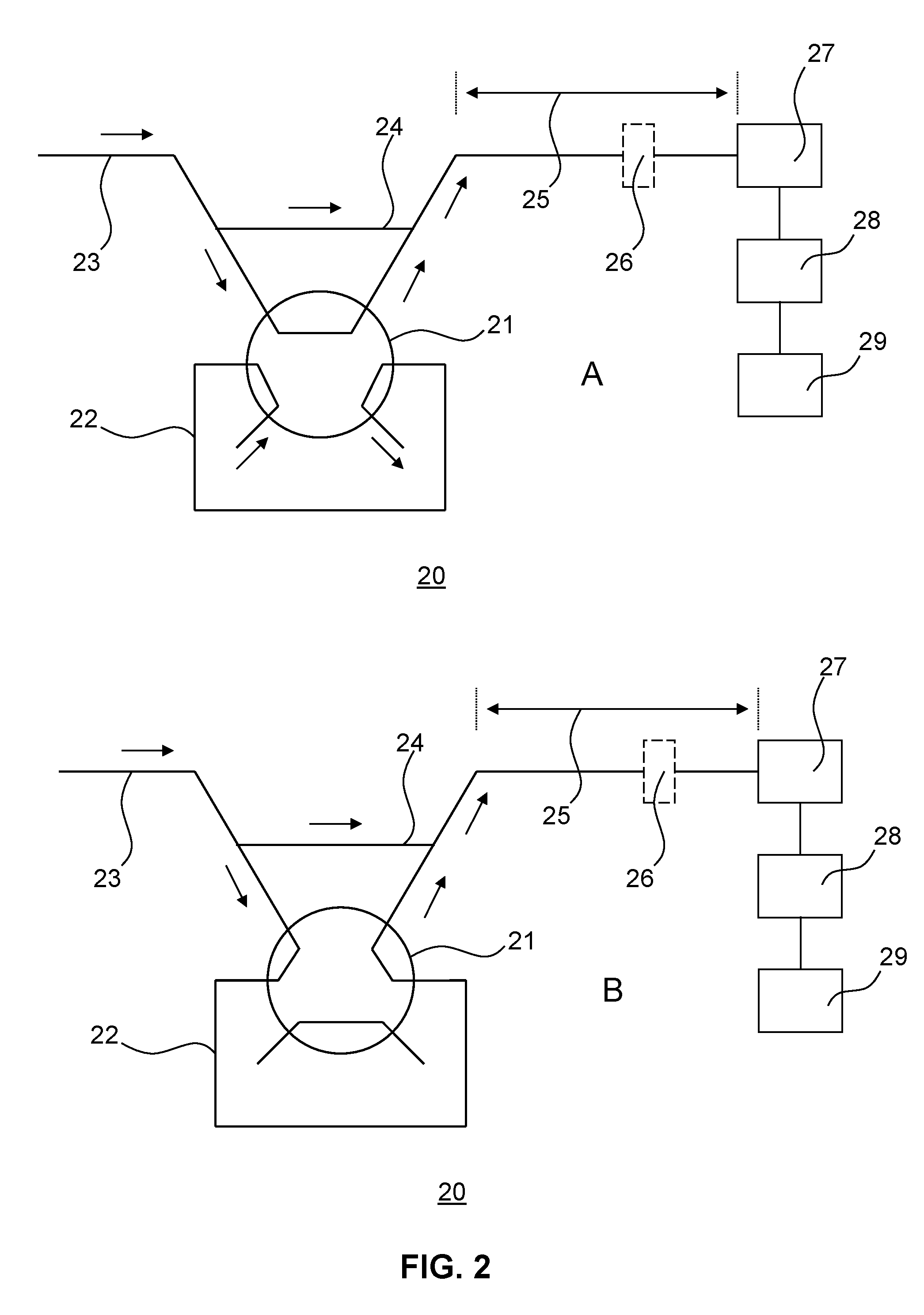
Analyte extraction apparatus and method
ActiveUS20160003858A1Reliable detectionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingGibbs ReagentPHENOL LIQUID
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for determining a concentration of a glycopeptide antibiotic containing a phenol moiety such as Vancomycin in a complex sample matrix by extracting the glycopeptide antibiotic from a metered portion of the complex sample matrix by exposing said metered portion to an extraction material having an affinity with the glycopeptide antibiotic; and exposing the extraction material to a metered portion of an eluent for releasing the glycopeptide antibiotic from the extraction material; and by determining a concentration of the glycopeptide antibiotic by adding a Gibbs reagent (2,6 dichloroquinone-4chloroimide) to the metered portion of the complex sample matrix or the eluent; activating the Gibbs reagent and, after the reaction between the activated Gibbs reagent and the antibiotic has stabilized; detecting the reaction product of the activated Gibbs reagent and the antibiotic in said eluent; and determining the concentration of the antibiotic in the complex sample matrix from the detected reaction product. A method of designing a personalized drug administration regime using the thus obtained concentration is also disclosed.
Owner:SPHERE MEDICAL +1
Stabilized vancomycin formulations
ActiveUS20190022232A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationPulmonary infection
Owner:INSMED INC
Glycopeptide antibiotic derivatives
Novel glycopeptide antibiotic derivatives, processes for their preparation, their use as a medicine, their use to treat or prevent viral infections and their use to manufacture a medicine to treat or prevent viral infections are provided. The present invention relates to the use of glycopeptide antibiotics and their semisynthetic derivatives to treat or prevent viral infections and their use to manufacture a medicine to treat or prevent viral infections of subjects, more in particular infections with viruses belonging to Retroviridae, Herpes viridae, Flaviviridae and the Coronaviridae, like HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), HCV (hepatitis C virus), BVDV (bovine viral diarrhoea virus), SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) causing virus, FCV (feline coronavirus), HSV (herpes simplex virus), VZV (varicella zoster virus) and CMV (cytomegalovirus).
Owner:K U LEUVEN RES & DEV
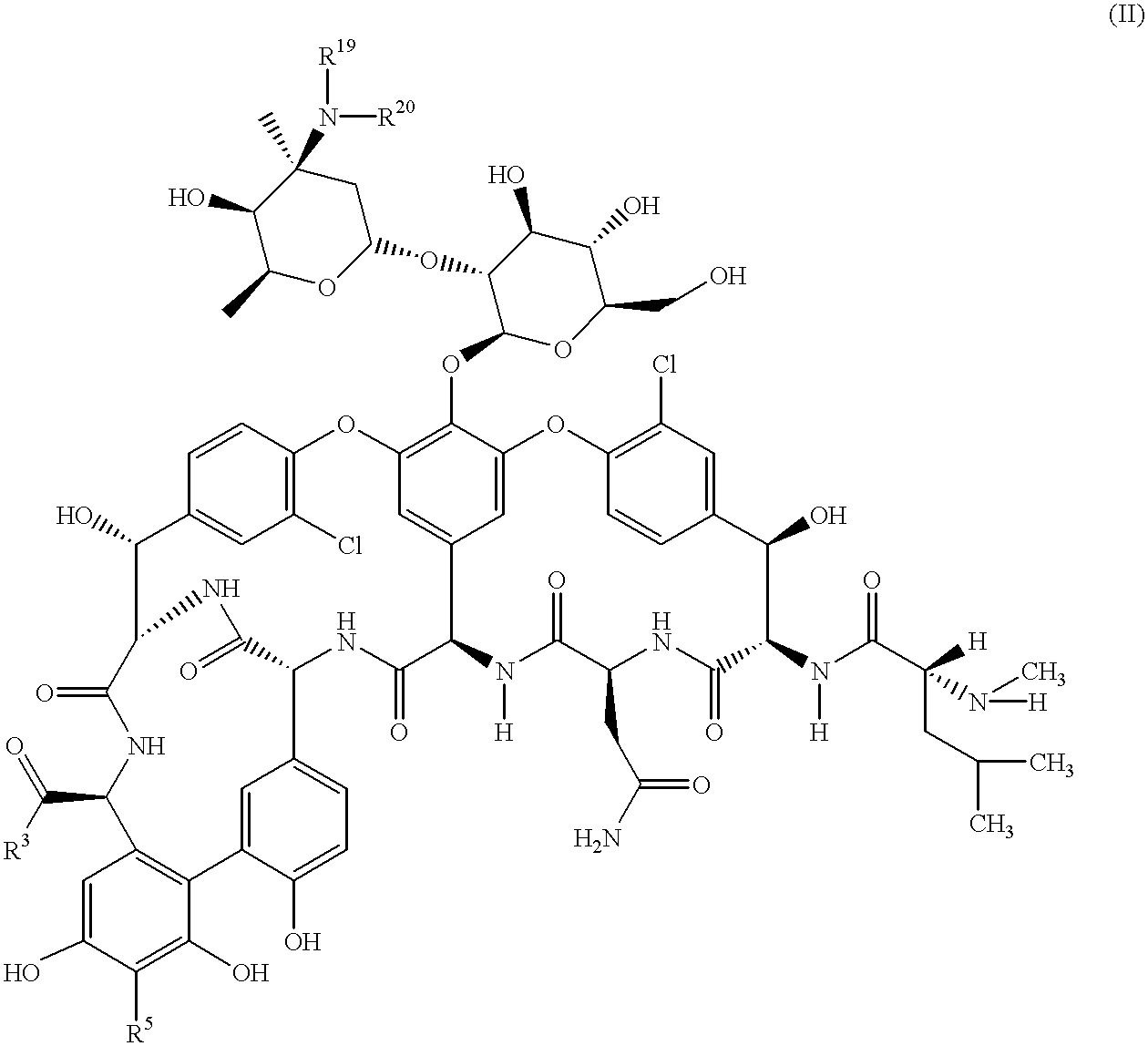
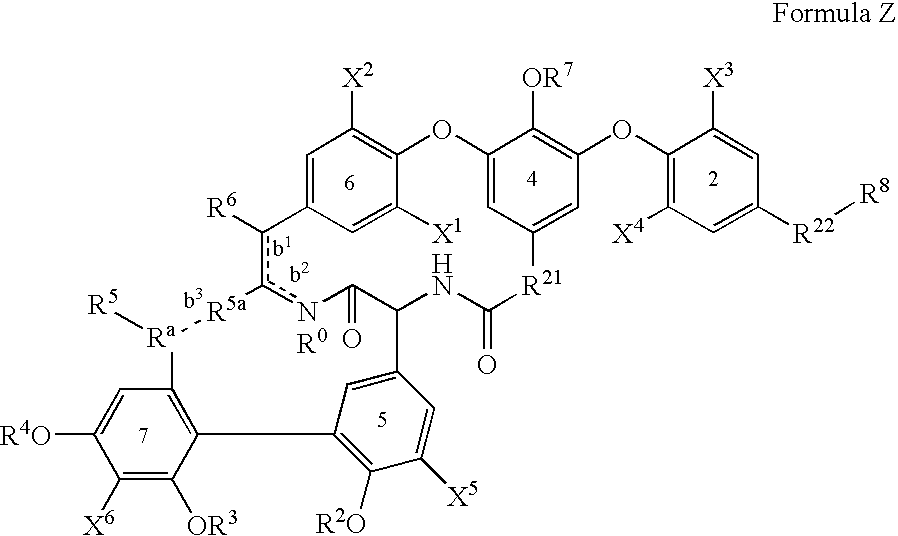
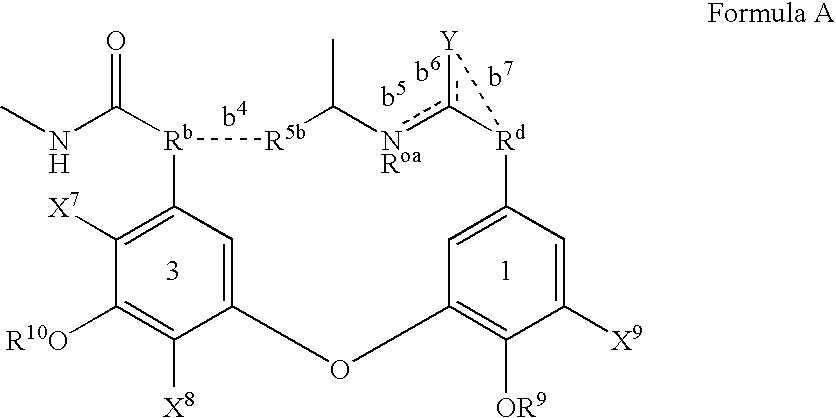
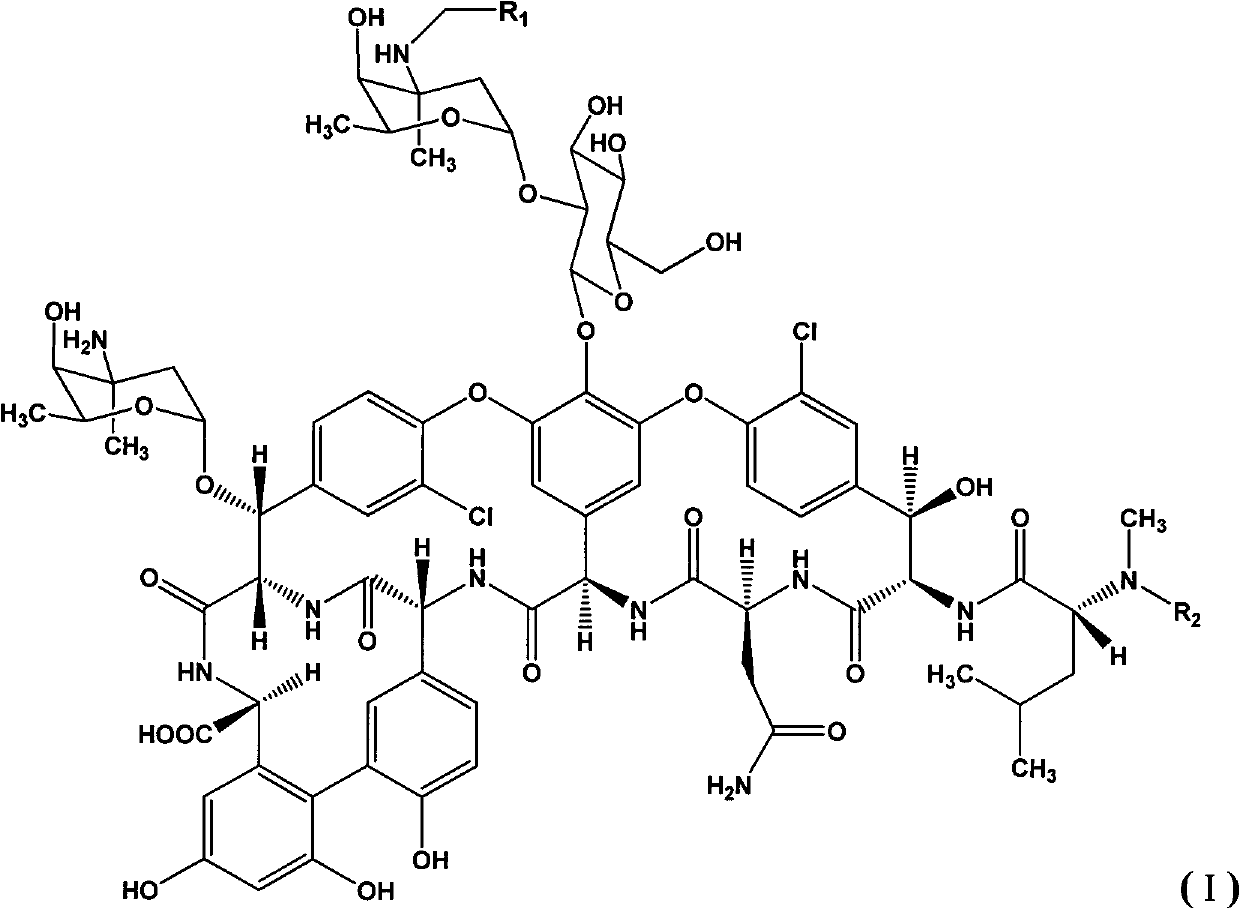
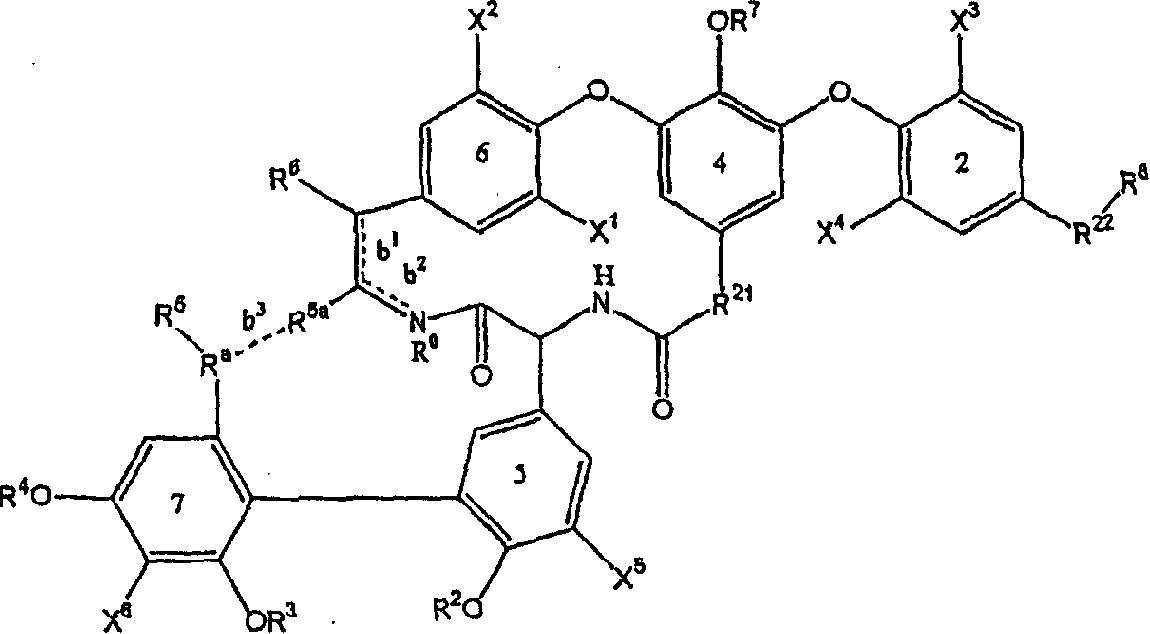
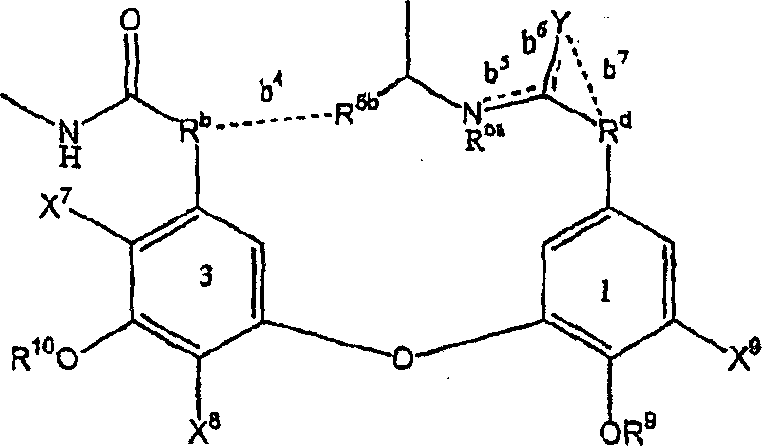
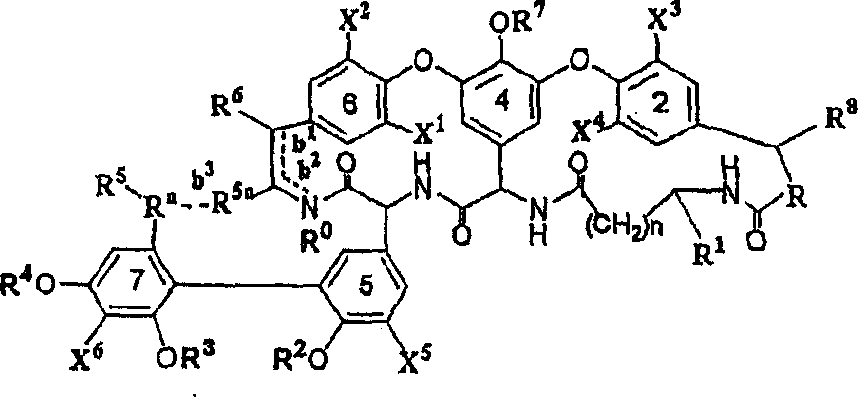
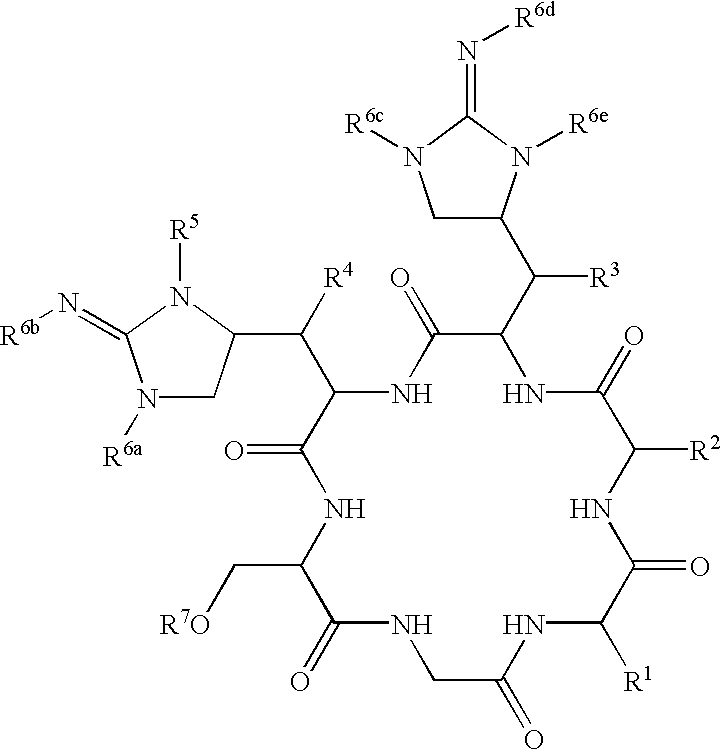
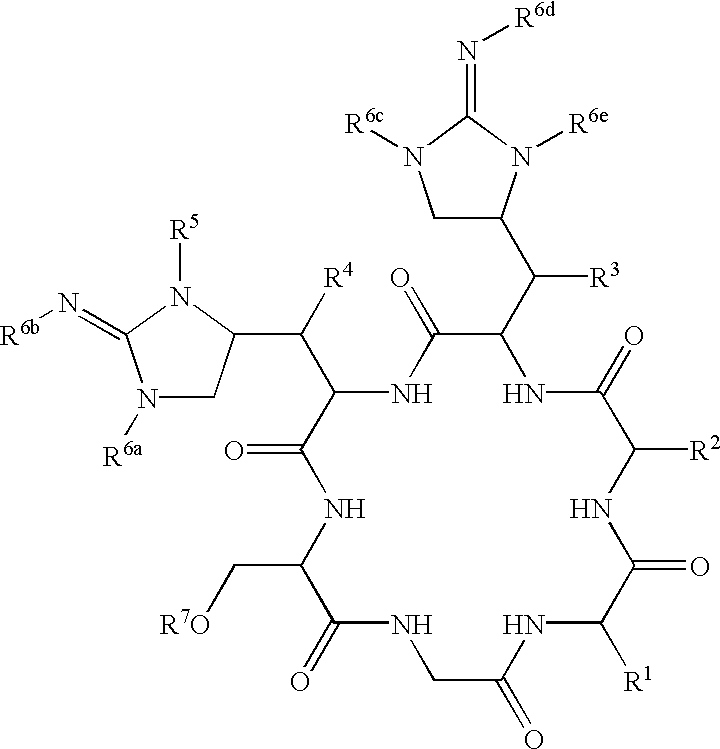
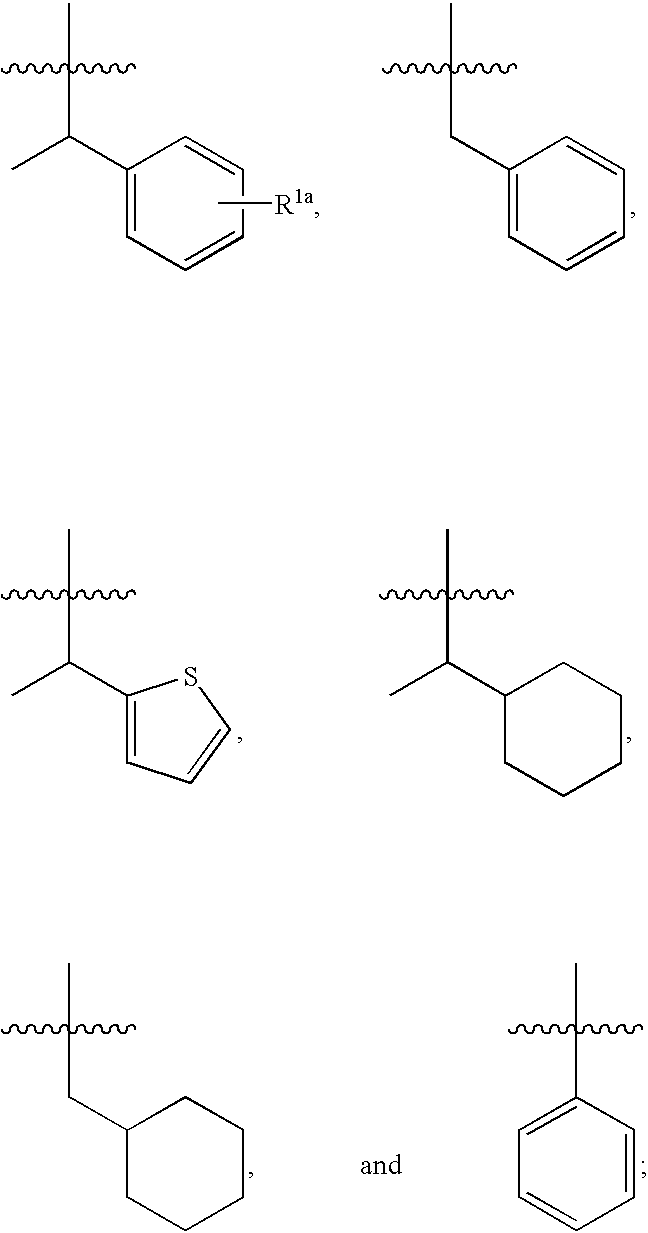
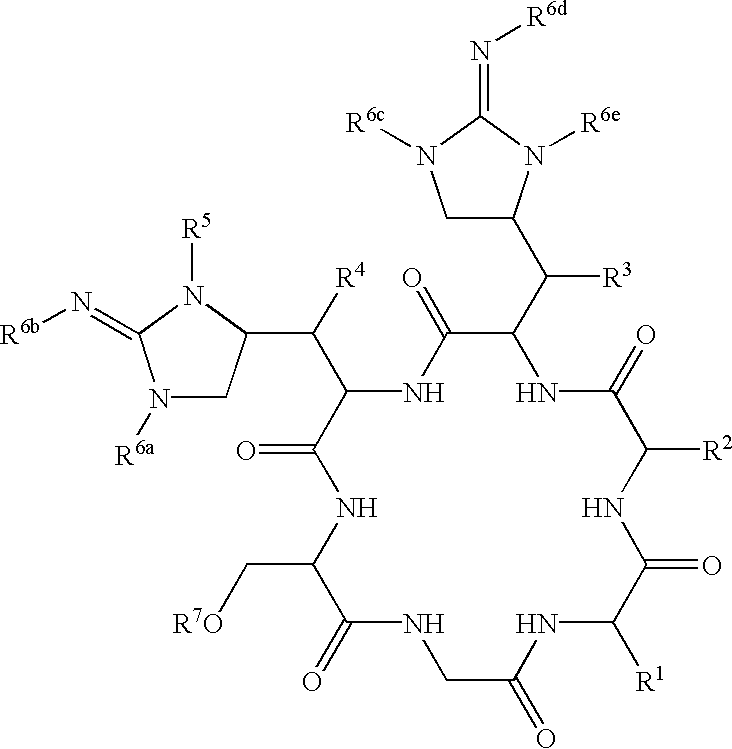
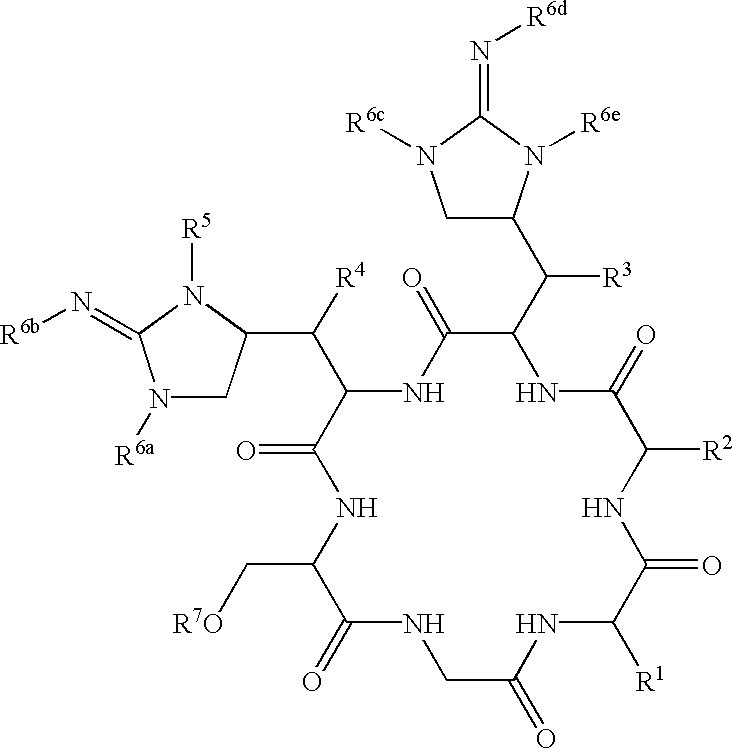
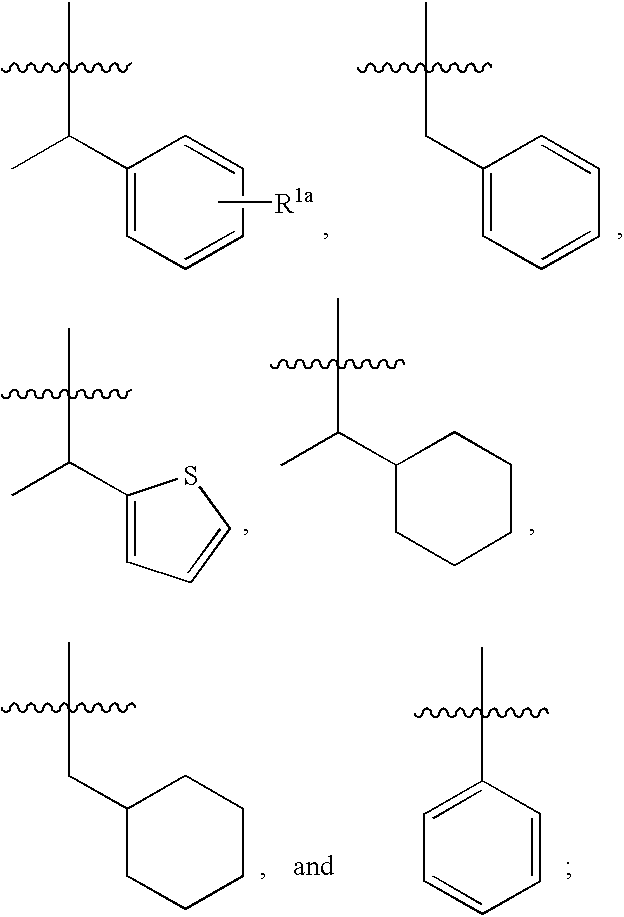
Glycopeptide antibiotics
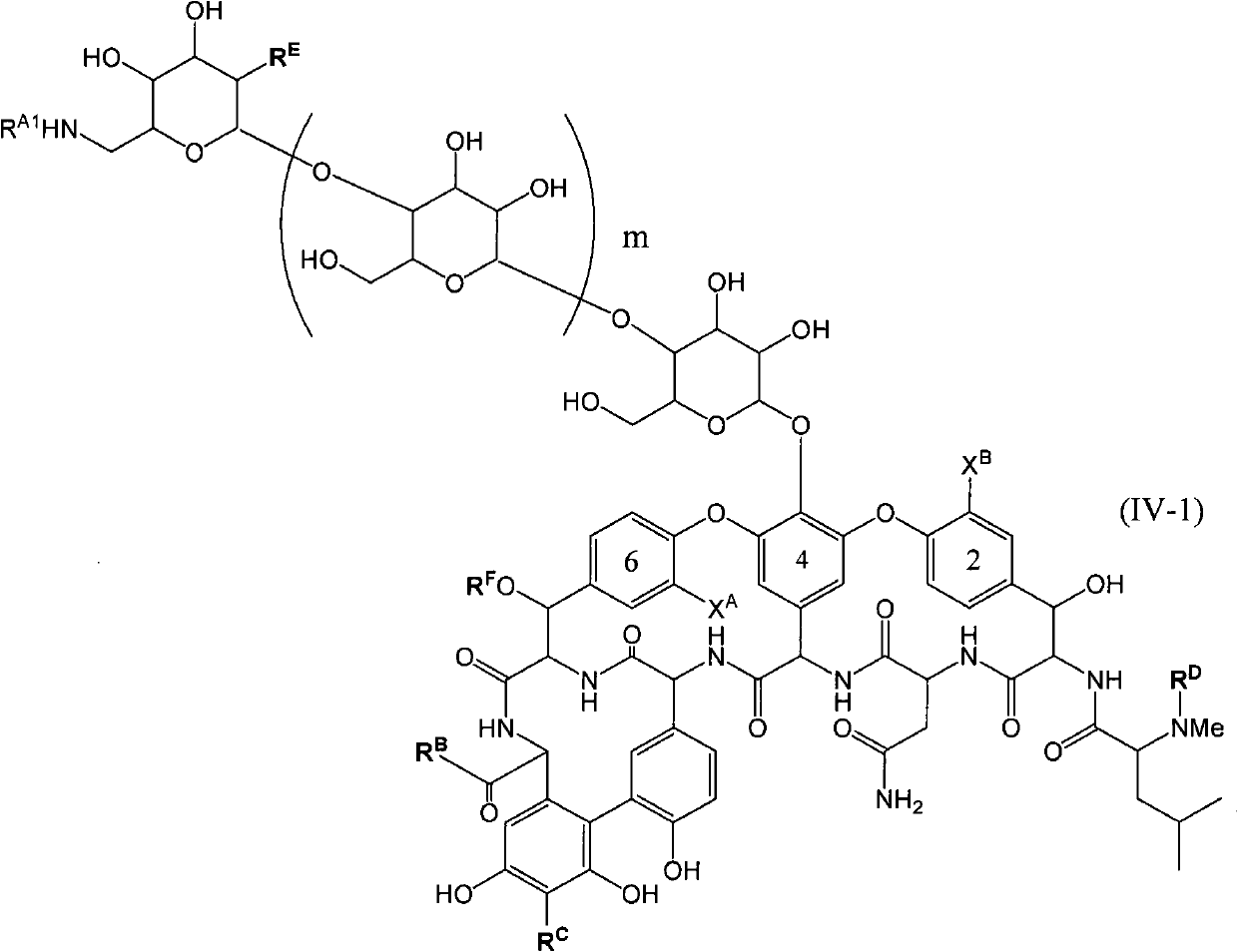
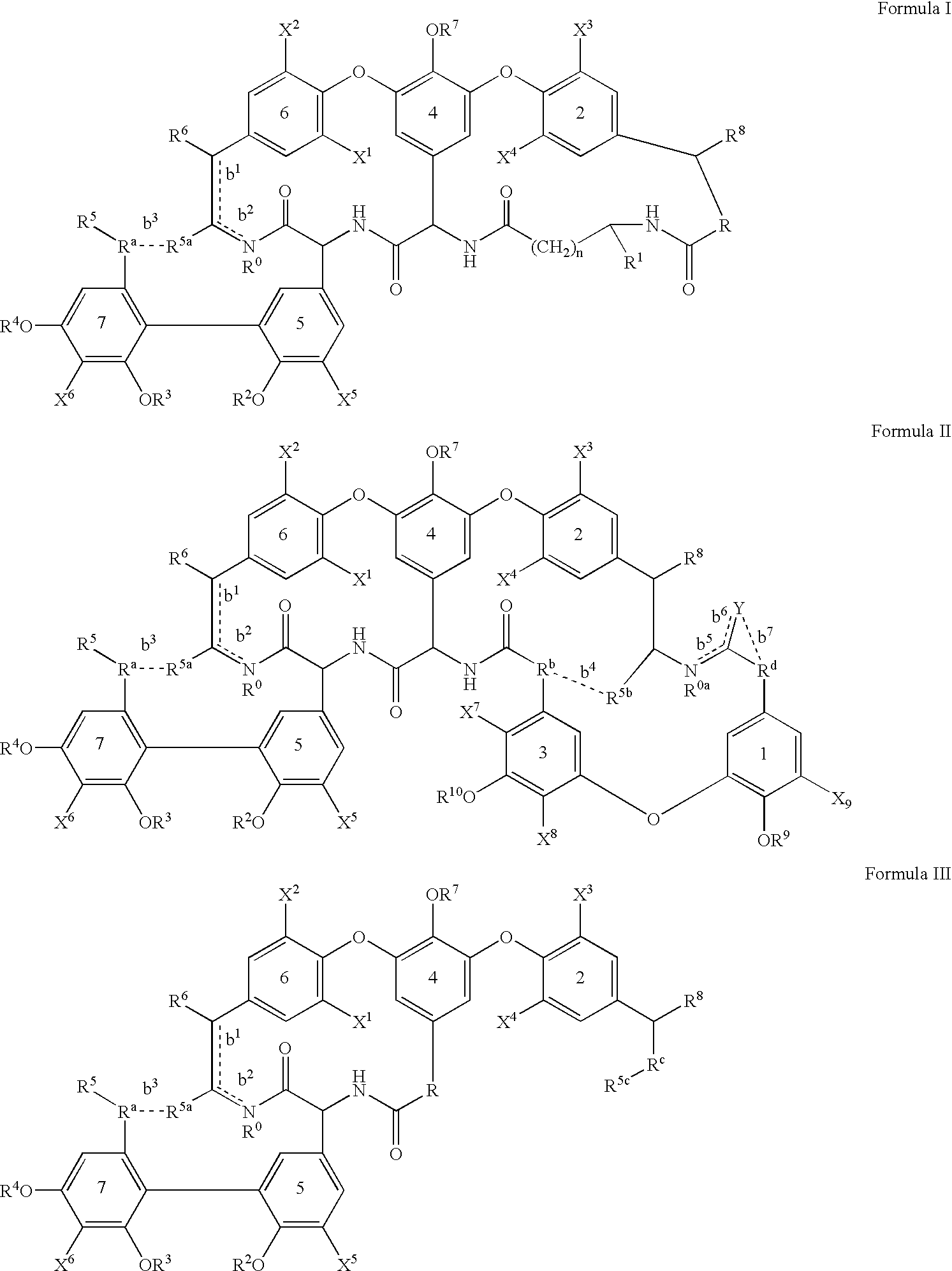
The invention provides compounds of formula Wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6a, R6b, R6c, R6d, R6e and R7 are defined in the specification. These compounds are useful as antibiotic agents.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
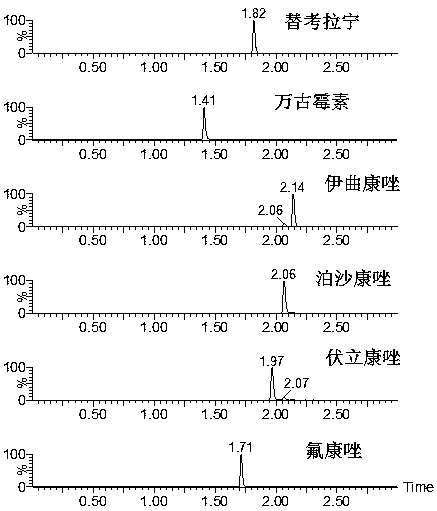
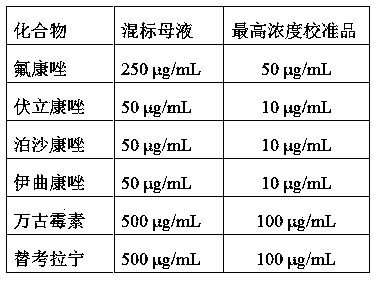
Kit for simultaneously detecting triazole antifungal drugs and glycopeptide antibiotics and detection method thereof
PendingCN111398480ARich varietyStrong specificityComponent separationTriazole antifungalsAntifungal drug
The invention discloses a kit for simultaneously detecting triazole antifungal drugs and glycopeptide antibiotics, the kit comprises an extracting solution, a diluent, a mobile phase, a calibrator anda quality control material, the calibrator and the quality control material comprise fluconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, itraconazole, vancomycin and teicoplanin; wherein the extracting solutioncomprises an isotope internal standard substance and a methanol aqueous solution, and the isotope internal standard substance comprises fluconazole-d4, voriconazole-d3, posaconazole-d4 and itraconazole-d5; wherein the diluent is distilled water or ultrapure water. The invention has the advantages that the invention firstly provides a kit capable of detecting a micromolecular antifungal drug and simultaneously detecting macromolecule glycopeptide antibiotics; the kit is simple in sample pretreatment and short in pretreatment time, improves the detection efficiency, can detect multiple types ofmedicines, can meet the detection requirements of clinically high-throughput samples, has a very good application prospect, and is convenient to popularize.
Owner:AUTOBIO DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Preparation method for multi-mode-combined vancomycin stationary phase of chromatography
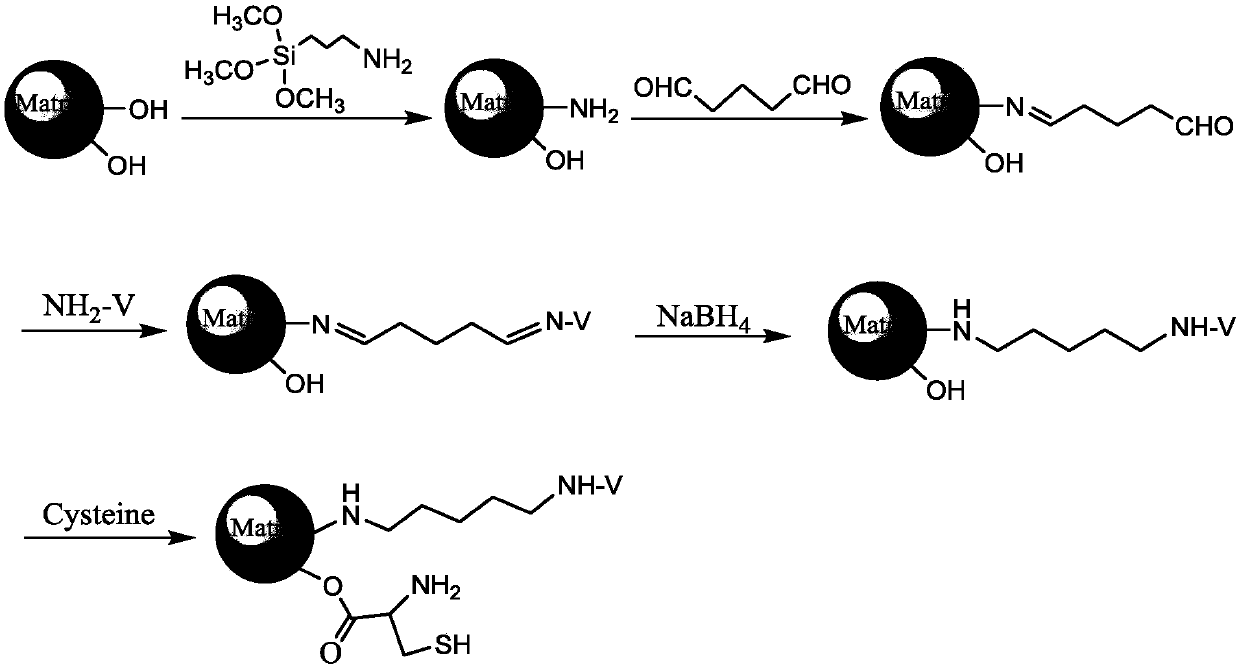
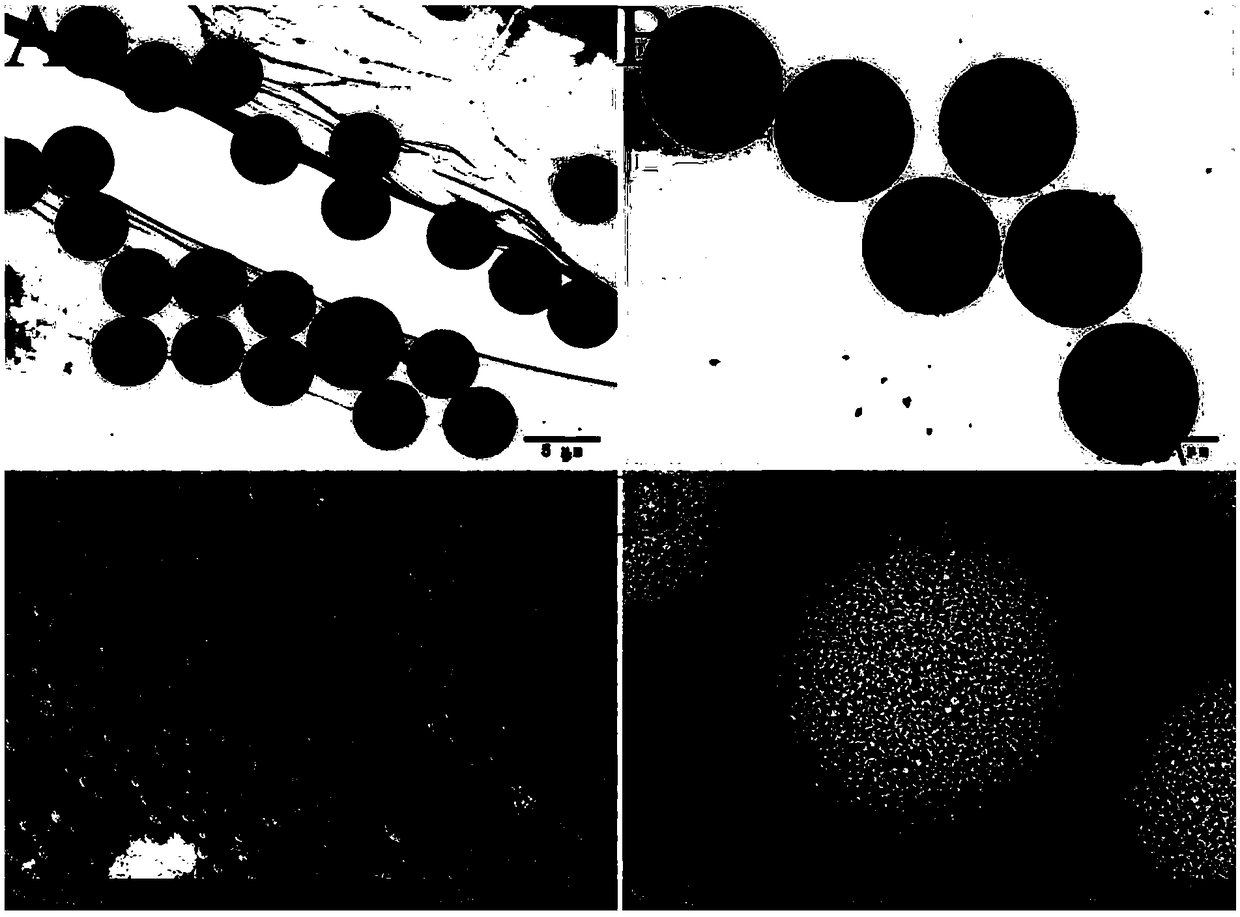
InactiveCN108043375AReduce the impactImprove bonding efficiencyOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationChromatographic separationChiral stationary phase
The invention relates to a preparation method for a multi-mode-combined vancomycin stationary phase of chromatography. The preparation method comprises the following steps: modifying the surface of asilicon sphere with an amino group; then with glutaraldehyde as a spacer, bonding the macrocyclic glycopeptide antibiotic vancomycin onto the surface of the silicon sphere through an aldimine condensation reaction; and carrying out bonding and terminating by using small-molecular amino acids or sugar so as to prepare the multi-mode-combined chiral stationary phase of chromatography. A vancomycin structure has a plurality of function groups and is applicable to separation operation in different chromatographic separation modes; moreover, glutaraldehyde is used as the spacer for bonding the macrocyclic glycopeptide antibiotic onto the surface of the silicon sphere, so steric-hinerance effect is effectively reduced and bonding efficiency is improved; and termination via small molecules can shield the negative effect of residual silicon hydroxyl groups in chromatographic separation, provide more action sites of different types and improve separation efficiency and separation selectivity.
Owner:南京赢点色谱分离技术有限公司
Use of oritavancin for prevention and treatment of anthrax
ActiveUS20100041585A1Inhibition of colonizationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseOritavancin
Glycopeptide antibiotics, such as oritavancin, demonstrate significant activity against B. anthracis. Methods for the treatment, prophylaxis and prevention of B. anthracis infection and disease in animals, including humans, are described.
Owner:MELINTA THERAPEUTICS
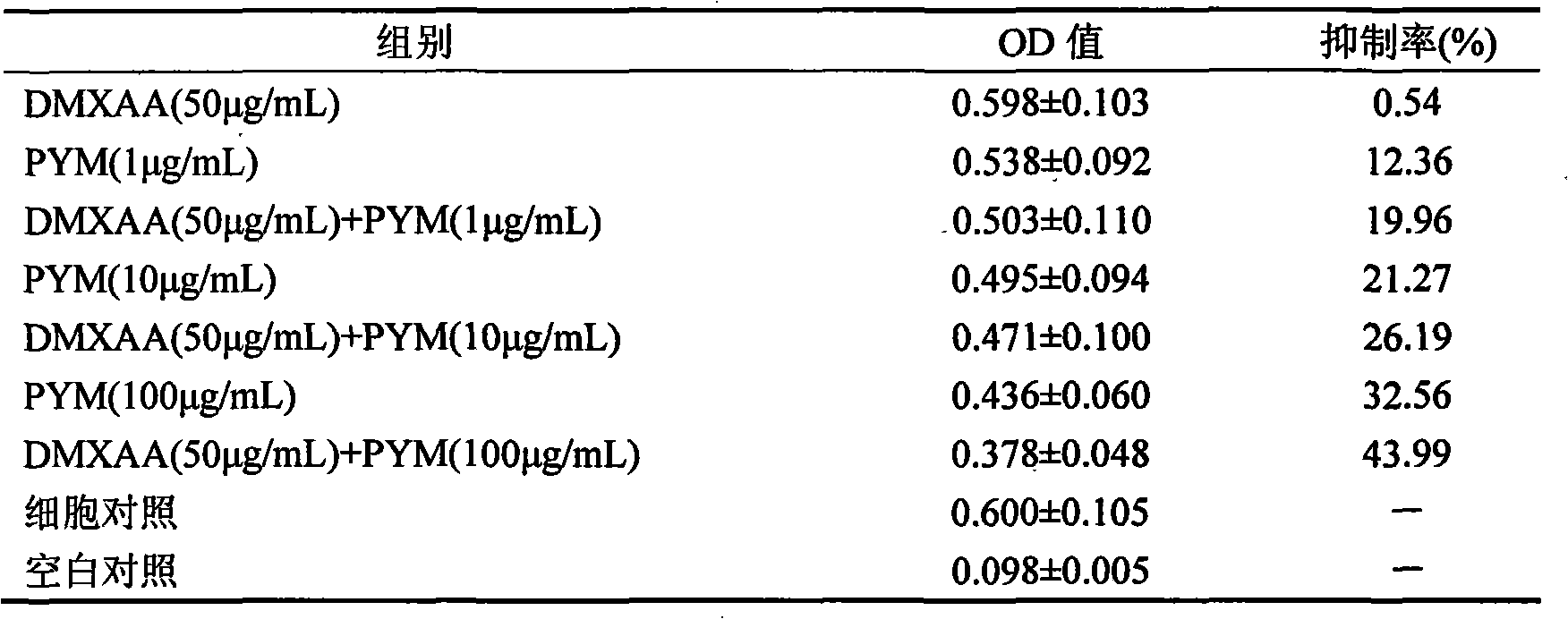
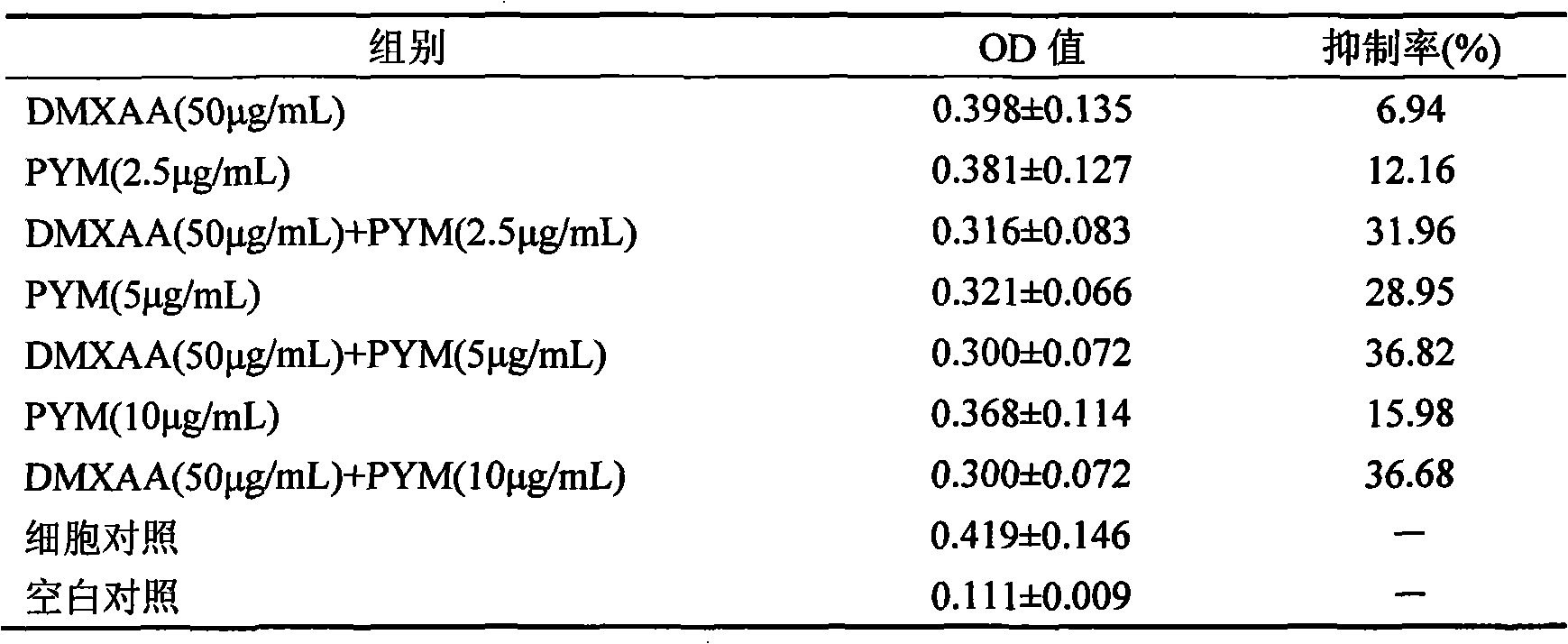
Medicine combination with antitumor activity
InactiveCN101336915AImprove anti-tumor activityOrganic active ingredientsSaccharide peptide ingredientsAromataseNK1 receptor antagonist
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition, particularly to a pharmaceutical composition with antitumor activity. The pharmaceutical composition with antitumor activity comprises 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA) or an pharmaceutically acceptable salt or ester thereof and one drug component selected from glycopeptide antibiotics, actinomycins, mitomycins, glucoside antibiotics, Colchicum alkaloid, elemenes, aromatic enzyme inhibitors, LH-RH receptor antagonists, animal antitumor drugs and somatostatin analogues. The synergic composition has better antitumor activity. More specifically, the invention provides an application of the composition in treating tumors.
Owner:沈阳斯佳科技发展有限公司
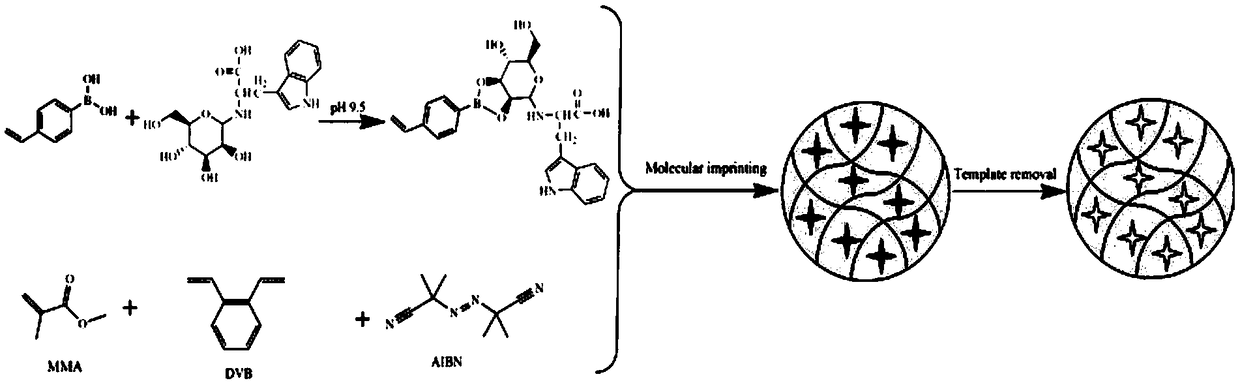
Molecularly imprinted microsphere for detecting teicoplanin and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108659159AHigh recovery rateLow detection limitOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationFunctional monomerMicrosphere
The invention discloses a molecularly imprinted microsphere for detecting teicoplanin and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method includes: selecting a molecule similar toa glycosyl portion in a teicoplanin molecular structure as a template molecule, 4-vinylphenylboronic acid and methyl methacrylate as functional monomer and divinyl benzene as a crosslinking agent toprepare the molecularly imprinted microsphere. When pH value is 9.0, the synthesized molecularly imprinted microsphere can be combined with target glycopeptide antibiotic; when the pH value is loweredto below 4.0, the combined glycopeptide antibiotic can be released, so that a glycosyl molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction column prepared on this principle can intercept the glycopeptide antibiotic in the solid-phase extraction column in a slightly alkaline condition, then the glycopeptide antibiotic is eluted in an acidic condition. On the basis of the glycosyl molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction column, teicoplanin in serum and urine samples can be detectedly effectively, and the molecularly imprinted microsphere has high recovery rate, low detection limit and good application prospect.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION (GUANGZHOU HYGIENE INSPECTION CENT GUANGZHOU CENT FOR FOOD SAFETY RISK SURVEILLANCE & ASSESSMENT INST OF PUBLIC HEALTH OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV)
Glycopeptides compounds with anti-resistance bacterial activity, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108409837AImprove securityStrong inhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsInorganic non-active ingredientsDiseaseOritavancin
The invention discloses a group of glycopeptides compounds with anti-resistance bacterial activity. The glycopeptides compounds in accordance with a general formula (I) are as shown in the following specification. The invention further provides a preparation method and an application for the above glycopeptides compounds. Through testing, compared with a second-generation glycopeptides pharmaceutical oritavancin, the glycopeptides antibiotic compounds have the higher inhibitory activity to endurance strains, especially MRSA or VRE. Through further testing, the most of the glycopeptides compounds have the higher safety than the oritavancin, and can be used for preparing pharmaceuticals for treating or preventing various diseases, such as skin and soft tissue infection, cephalomeningitis, sepsis, pneumonia, arthritis, peritonitis, bronchitis, and empyema, caused by bacterial infection.
Owner:SHANGHAI LAIYI BIOMEDICAL RES & DEV CENT +1
Vancomycin derivative as well as preparation method and pharmaceutical use thereof
The invention discloses a vancomycin derivative as well as a preparation method and a pharmaceutical use thereof. The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines and relates to a glycopeptide antibiotics derivative substituted by heterocyclic nitrogen with a general formula (1) as shown in the specification, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of glycopeptide antibiotics derivative, an isomer of the glycopeptide antibiotics derivative, a preparation method of the compounds and uses of the compounds in preparation of medicines for treating or preventing bacterial infectious diseases. An extraneous bacteriostasis experiment shows that the antimicrobial activity of the compounds is 60 times the antimicrobial activity of vancomycin or norvancomycin, particularly the bacteriostatic activity of the compounds to various gram-positive bacteria is obviously higher than that of vancomycin or norvancomycin. Thus, by adopting the preparation method, medicines containing the derivative as an active ingredient can be prepared, particularly medicines resisting to bacterial infection. The structure formula is as shown in the specification.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
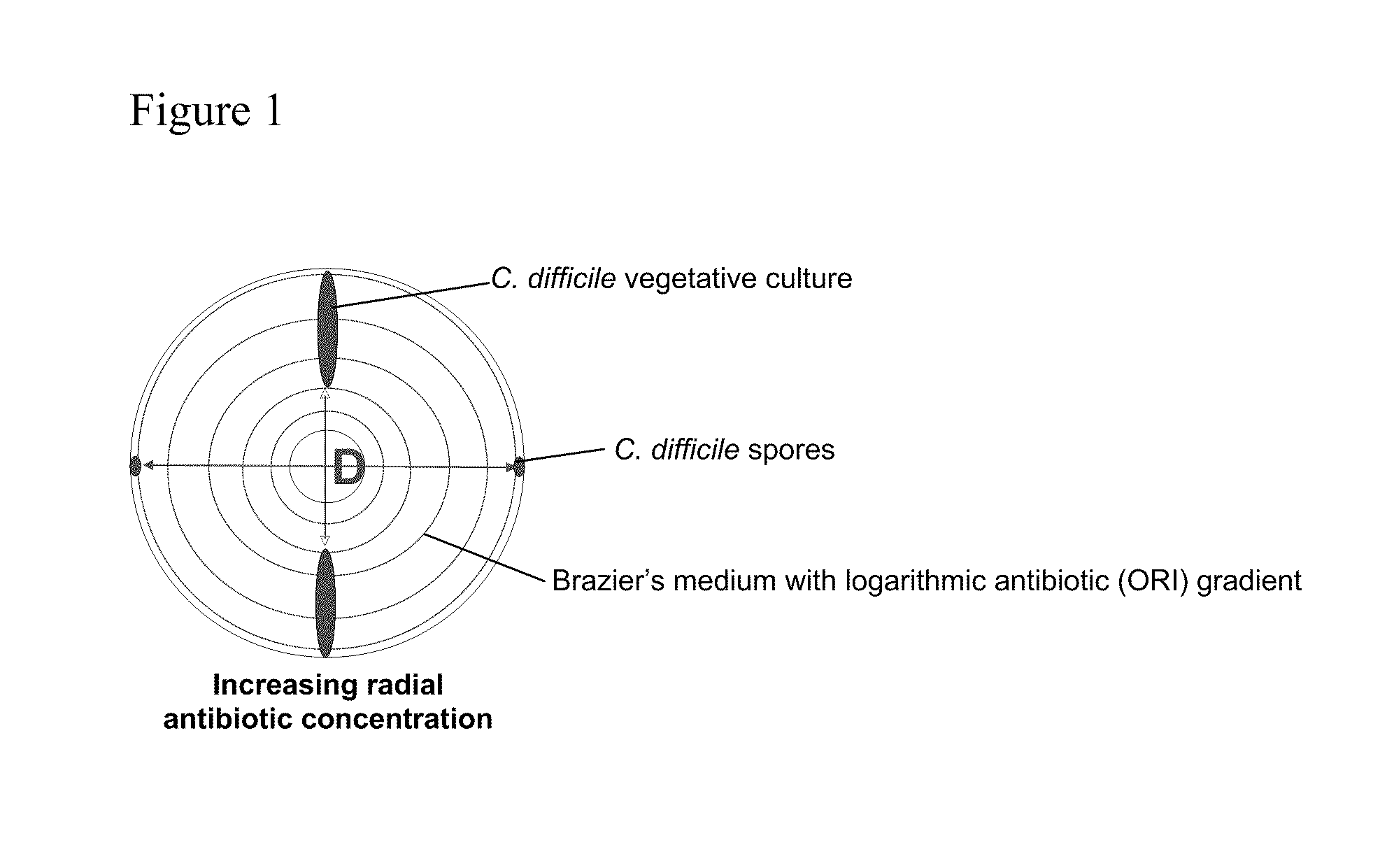
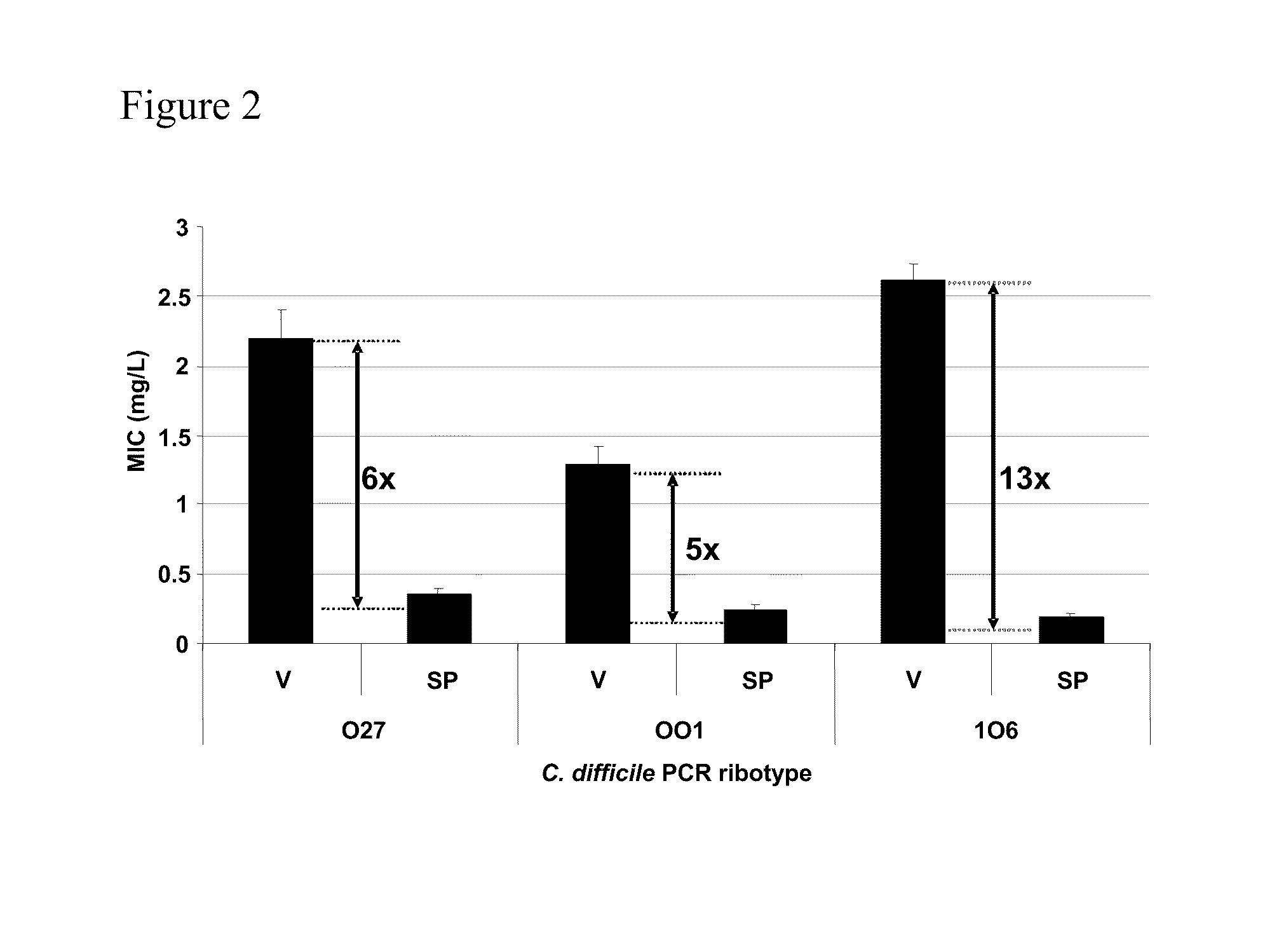
Method of inhibiting clostridium difficile by administration of oritavancin
Glycopeptide antibiotics, such as oritavancin, demonstrate significant activity against both a vegetative form of C. difficile and C. difficile spores. Methods for the treatment, prophylaxis and prevention of C. difficile infection and disease in animals, including humans, are described.
Owner:MELINTA THERAPEUTICS
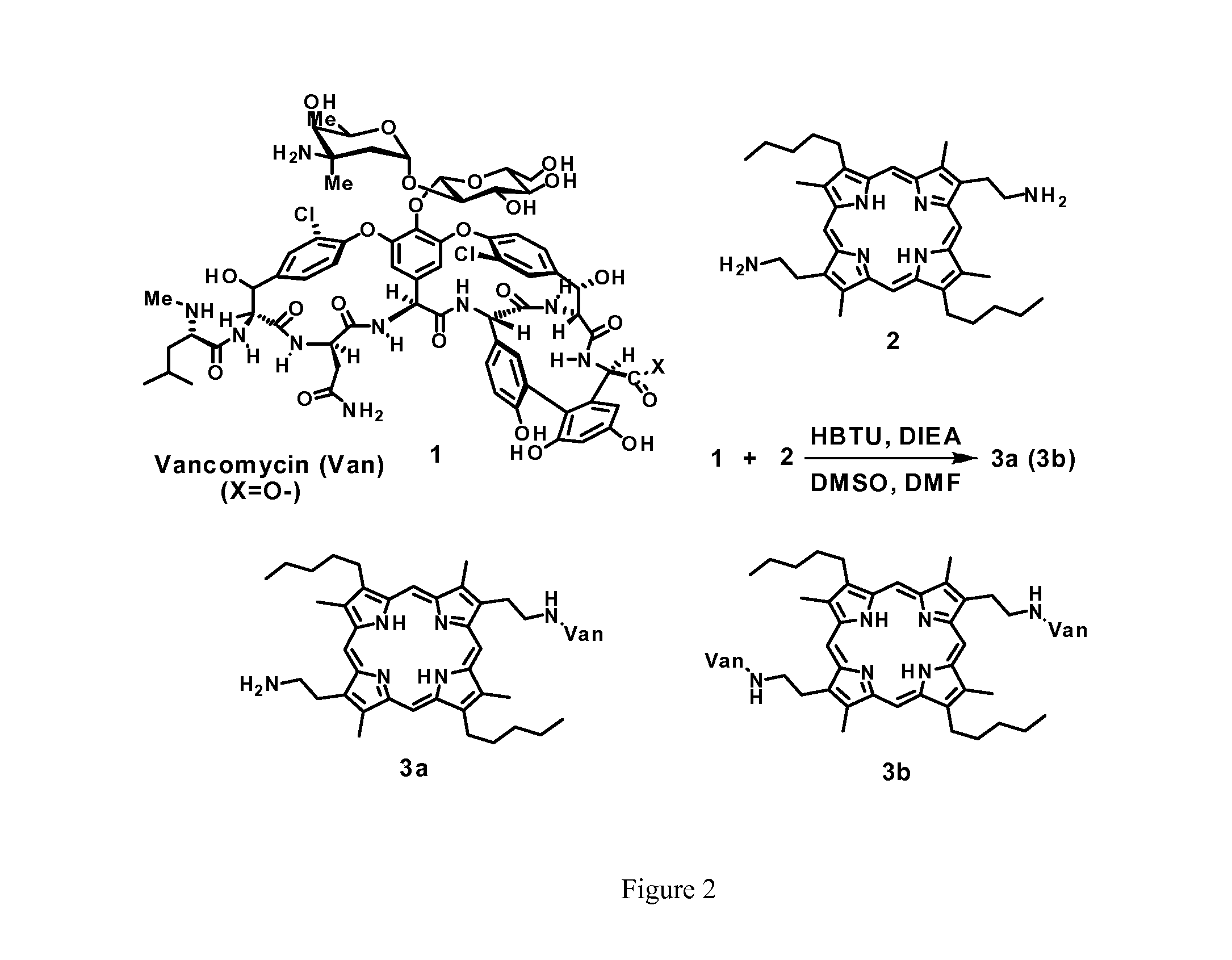
Multifunctional glycopeptide antibiotic derivatives for fluorescent imaging and photoactive antimicrobial therapy
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Glycopeptide antibiotics
The invention provides compounds of formula Wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6a, R6b, R6c, R6d, R6e and R7 are defined in the specification. These compounds are useful as antibiotic agents.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
A thermosensitive gel pharmaceutical preparation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103622902BImprove burst issuesImprove medication compliancePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAdjuvantBurst effect
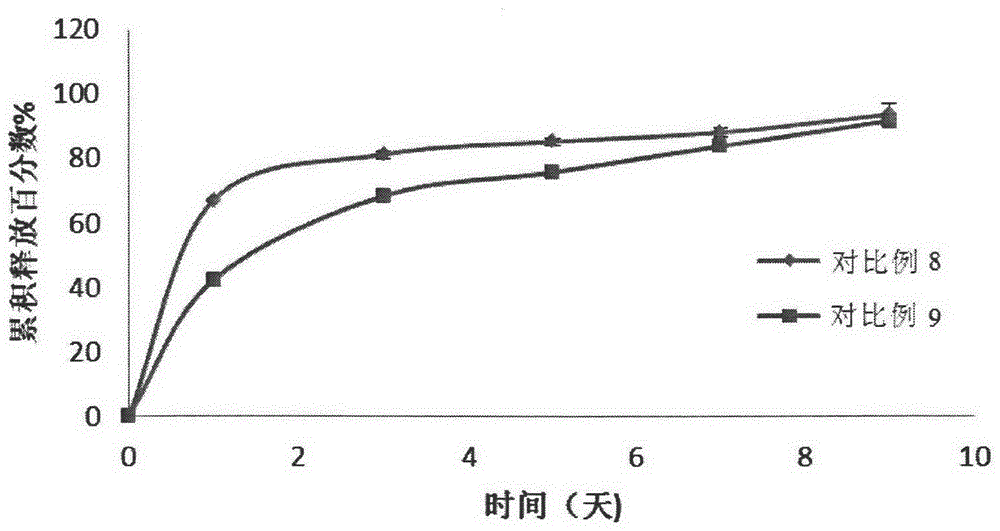
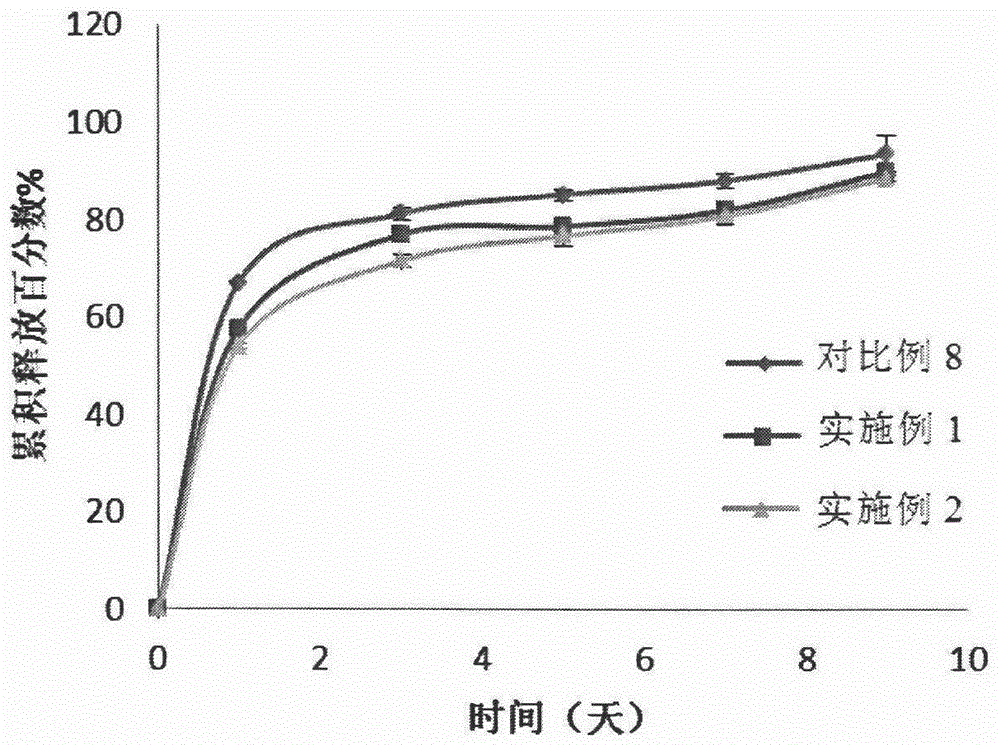
The invention discloses a temperature-sensitive gel pharmaceutical preparation and a preparation method thereof. The raw material formula of the temperature-sensitive gel pharmaceutical preparation contains a drug, a temperature-sensitive gel composition, and an excipient C; the excipient C is one or more of metal salts, carbohydrates, and hydrophilic polymers for injection; The metal salt is a pharmaceutically acceptable metal salt that dissociates divalent metal cations in an aqueous solution; the drug is a substance A that exists in an anion form in an aqueous solution, and the substance A is a protein drug, a polypeptide One or more of class drugs and glycopeptide antibiotics. The preparation method comprises the following steps: according to the formula of raw materials, the drug is dissolved in the temperature-sensitive gel composition in the form of solution. The temperature-sensitive gel pharmaceutical preparation is especially suitable for water-soluble drugs, reduces the burst release effect, releases the drugs slowly, and achieves the purpose of sustained release.
Owner:SHANGHAI MODERN PHARMA ENG INVESTIGATION CENT
Genes and Proteins For the Biosynthesis of the Glycopeptide Antibiotic A40926
InactiveUS20080145892A1Efficient expressionIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsMicroorganismsBiosynthetic genesGene product
The present invention relates to the field of antibiotics, and more specifically to the isolation of nucleic acid molecules that code for the biosynthetic pathway of the glycopeptide antibiotic A40926. Disclosed are the functions of the gene products involved in A40926 production. The present invention provides biosynthetic genes that code for A40926 production, the encoded polypeptides, the recombinant vectors comprising the nucleic acid sequences that encode said polypeptides, the host cells transformed with said vectors and methods for producing glycopeptide antibiotics using said transformed host cells, including methods for producing A40926, a precursor thereof, a derivative thereof or a modified glycopeptide different from A 40926 or a precursor thereof.
Owner:VICURON PHARM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com