Mesenchymal stem cell substitute product containing degradable biomedical sustained-release material and application thereof
A slow-release material and biomedical technology, applied in the direction of medical preparations containing active ingredients, medical preparations with non-active ingredients, drug combinations, etc., can solve the problem of conditional medium that is difficult to achieve batch-to-batch quality stability and difficulty Stable batch-to-batch quality, difficult to develop drugs and other issues, to achieve the effect of simple storage and transportation, low cost, and clear functional ingredients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
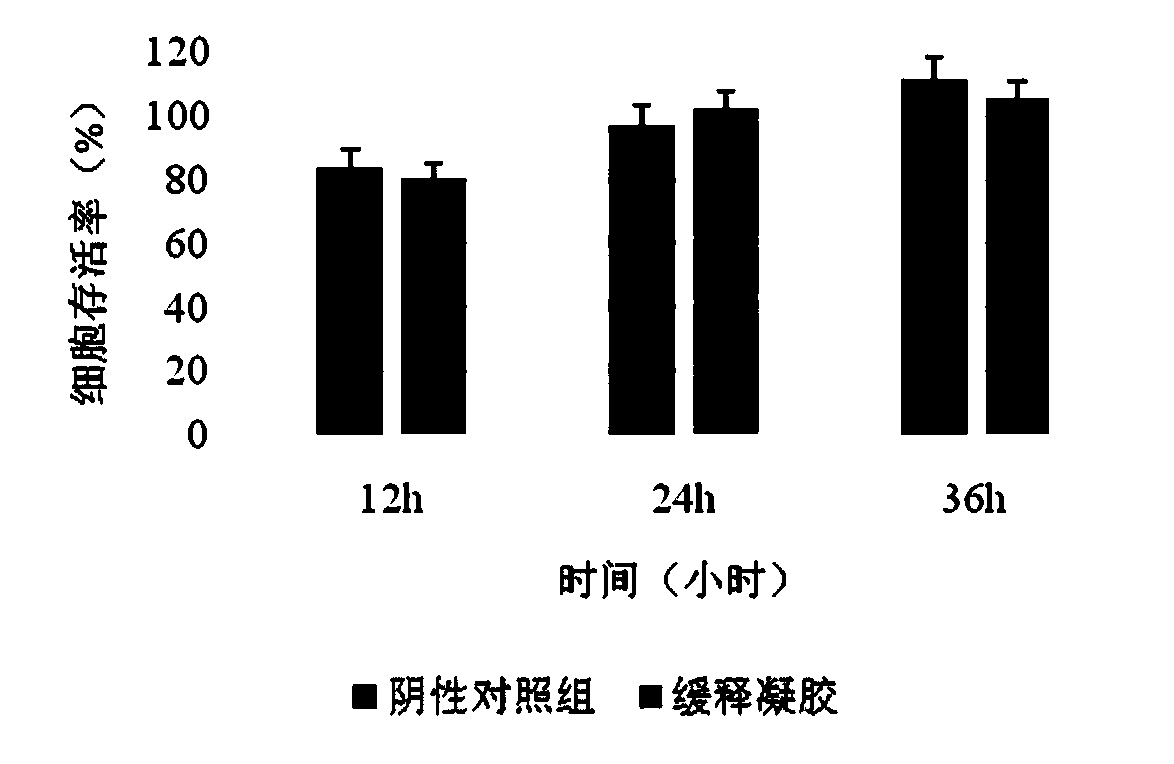
[0049] [Example 1]: sodium alginate / gelatin / EGF / VEGF / bFGF / PGE 2 Cytotoxicity profile of sustained-release gel (skin damage)
[0050] Combine 0.1mg of sterile sodium alginate and 0.1mg of gelatin into a blended powder, dissolve it in 8.8ml of amino acid injection, swell at room temperature for 24 hours, then add 500ulEGF, 100ulVEGF, 100ulbFGF, 500ulPGE 2 , fully stirred and mixed to prepare a slow-release gel; prepare the extract of the slow-release gel sample according to the above method, after 12h, 24h and 36h of the sample extract and L929 cells were co-cultured, the experimental results showed ( figure 1 ), as the culture time prolongs, there is no significant difference between the sample group and the negative control group (p * 2 Sustained-release gel has good cell compatibility.
Embodiment 2
[0051] [Example 2]: sodium alginate / gelatin / EGF / VEGF / bFGF / PGE 2 Three-dimensional structure diagram of sustained-release gel (skin damage)
[0052] Such as figure 2 Shown, is embodiment 1 sodium alginate / gelatin / EGF / VEGF / bFGF / PGE 2 Three-dimensional structural electron microscope image, it can be seen that microporous structures with different diameters and sizes are formed on the surface of the slow-release gel, and a uniform texture structure appears, which is caused by the accumulation of sodium alginate and gelatin molecules, and sodium alginate / gelatin The structure after physical blending between them is relatively stable. In addition, the microporous structure of the slow-release gel can provide channels for vascularization, accelerate the formation of blood vessels, and facilitate the release of secreted factors, which is beneficial to the repair of skin damage.
Embodiment 3
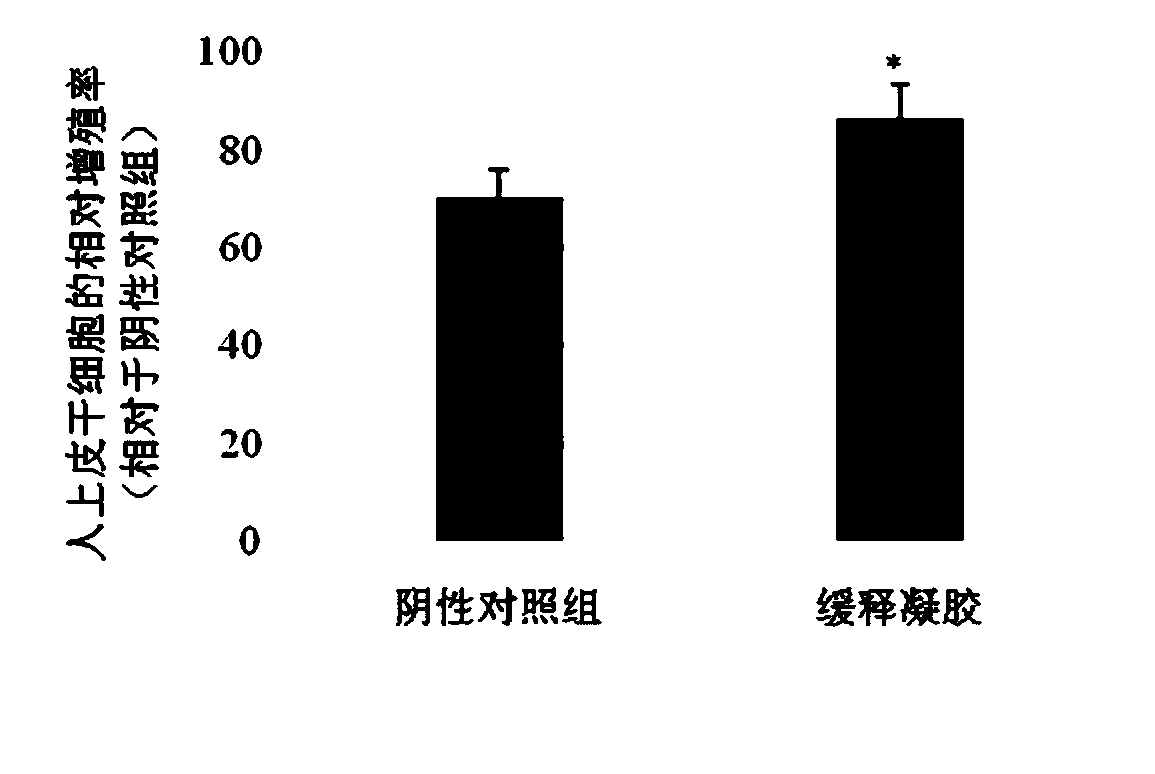
[0053] [Example 3]: sodium alginate / gelatin / EGF / VEGF / bFGF / PGE 2 Sustained-release gel on the proliferation of human epithelial stem cells (skin damage)
[0054] Human epithelial stem cells in good condition and in the logarithmic growth phase were used in this experiment, and commercially purchased human epithelial stem cells were used in 1×10 4 The cells / well are inoculated in a 96-well plate containing the test sample and negative control, the test sample and negative control are sodium alginate / gelatin / EGF / VEGF / bFGF / PGE respectively 2 Slow-release gel (medium containing 1% serum) and medium containing 1% serum, placed at 37°C, 5% CO 2 The culture was continued for 24 h in the incubator, and the proliferation rate of the cells was detected with Alamar Blue reagent (purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific). The results show( image 3 ), compared with the negative control group, the sustained-release gel significantly increased the proliferation rate of human epithelial ste...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com