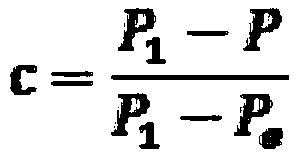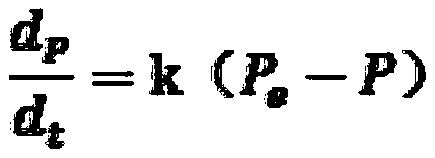Method for refining additive manufactured titanium alloy grains
A technology of additive manufacturing and titanium alloy, which is applied in the field of additive manufacturing, can solve the problems of changing structure performance, limited improvement ability of structure performance, and cracking of parts, so as to refine grains, reduce the possibility of cracking, and reduce internal The effect of stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
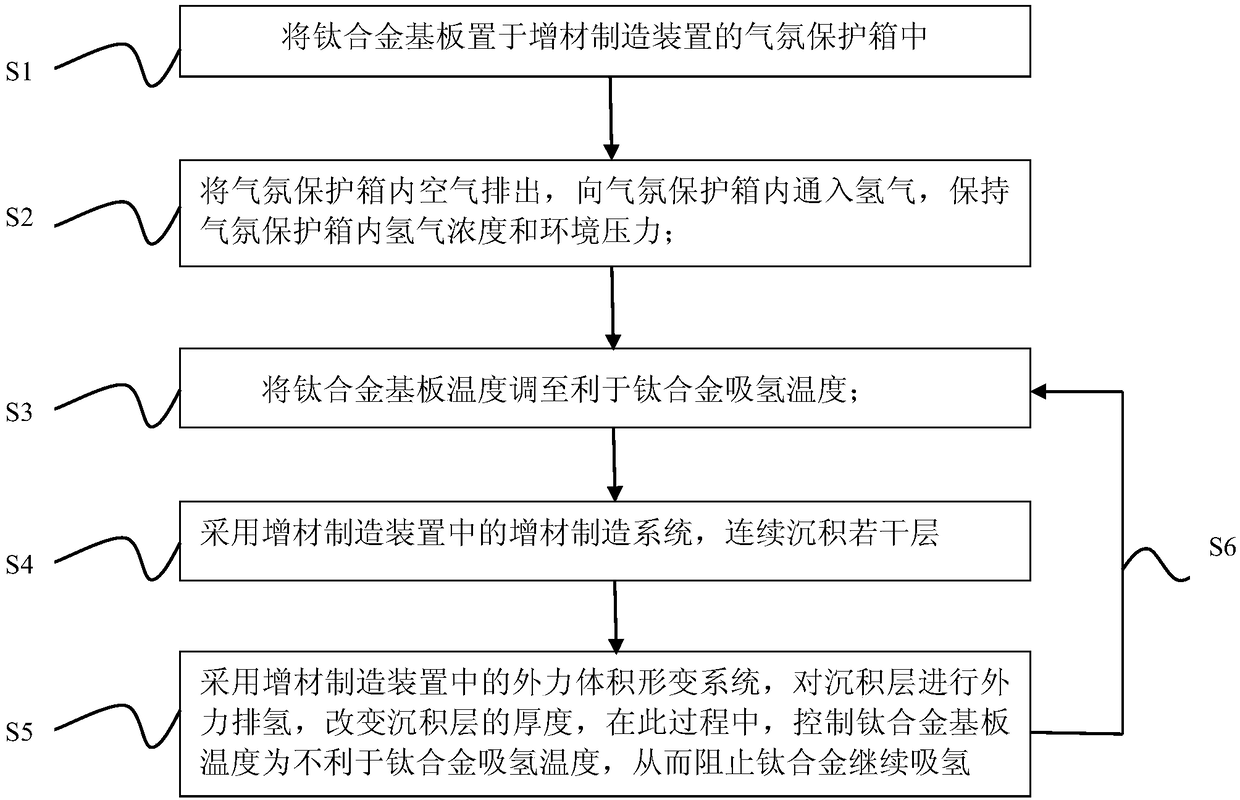
[0038] A method for refining titanium alloy grains by additive manufacturing, which involves a device for refining titanium alloy grains by laser additive manufacturing, including an atmosphere protection box, a laser additive manufacturing system, an external force volume deformation system, and a control system. The working part of the laser additive manufacturing system and the working part of the external force volume deformation system are installed in the atmosphere protection box, and a high-precision hydrogen concentration monitoring device is installed outside the atmosphere protection box, and a hydrogen concentration alarm device is installed at the same time to prevent hydrogen The concentration reaches the deflagration point (when the volume percentage of hydrogen contained in the air is 4.0%-74.2% in the mixed gas, it will explode when ignited).
[0039] A method for refining and additively manufacturing titanium alloy grains, the flow chart of which is shown in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com