Extraction and purification method of DNAs of fagaceae plant sample
A purification method, the technology of Fagaceae, applied in the field of plant DNA extraction and purification, can solve the problems of high price, unstable chemical properties of DNA, protein polyphenol pollution, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing polyphenol pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
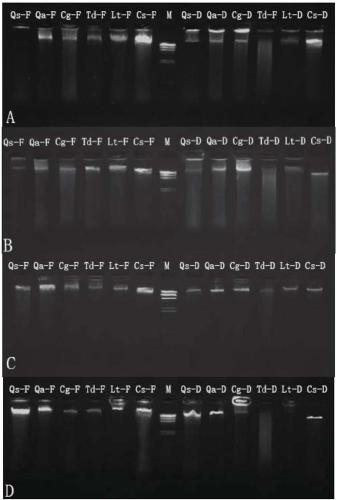
[0074] The DNA extraction process of the silica gel dry leaves and fresh leaves of Quercus thorny leaf, Quercus japonica, Qinggang, Fructus japonica, Quercus chinensis, and Quercus trigonum provided by the present embodiment is as follows:
[0075] (1) Both fresh leaves and silica gel-dried leaves were cut into 2×2cm squares, ground into powder in liquid nitrogen, and used for DNA extraction;
[0076] (2) Add 1ml of special rinse solution (2% PVP, 1% L-Ascorbic Acid, 3% Triton-X 100, 4% β-mercatoeyhanol) to the ground powder, shake, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 1min, and discard the supernatant ( If the supernatant is viscous, repeat this step until the supernatant is colorless and has a clear boundary with the precipitate);
[0077] (3) Add 800 μL of 2% CTAB extract (2% CTAB (m / v), 1.4M NaCl, 100mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 20mM EDTA pH 8.0, 10% (w / v) N- Lauroylsarcosine Sodium salt, 1.4% β-mercatoeyhanol, 50mg RNase A), placed in a water bath at 60°C for 40 minutes, and gently mixed u...
Embodiment 2
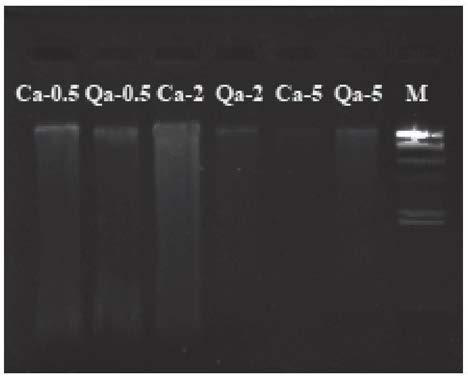
[0083] The DNA extraction process of Quercus japonica provided by the present embodiment, the specimen preserved for half a year, the specimen preserved for 2 years and the specimen preserved for 5 years is as follows:
[0084] (1) Both fresh leaves and silica gel-dried leaves were cut into 3x 3cm squares, ground into powder in liquid nitrogen, and used for DNA extraction;
[0085] (2) Add 1ml of special rinse solution (4% PVP, 2% L-Ascorbic Acid, 4% Triton-X 100, 5% β-mercatoeyhanol) to the ground powder, shake, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 1min, and discard the supernatant ( If the supernatant is viscous, repeat this step until the supernatant is colorless and has a clear boundary with the precipitate);
[0086] (3) Add 1ml of 4% CTAB extract (4% CTAB (m / v), 1.4M NaCl, 100mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 20mM EDTA pH 8.0, 10% (w / v) N - Lauroylsarcosine Sodium salt, 3% β-mercatoeyhanol, 50mg RNase A), put in a water bath at 60°C for 1 hour, turn it up and down every 5 minutes and mix gentl...
Embodiment 3
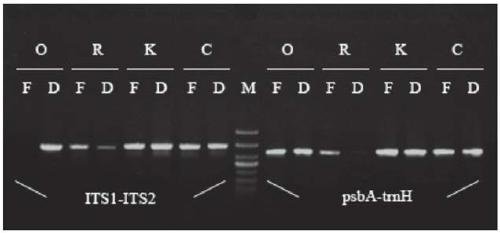
[0143] The total plant DNA extracted by the methods of the above-mentioned Example 1 and Comparative Examples 1-3 was selected from a silica gel sample and a fresh sample, and the total DNA of the plant specimen in Example 2 was purified by the silica gel adsorption nucleic acid method, and the specific steps were as follows:
[0144] (1) Weigh 0.8g of silica gel (silica) powder, add ultrapure water to shake and mix, let it stand for 15min, centrifuge at 13200rpm for 30s and remove the supernatant (repeat the above steps 3 times); in the silica gel powder washed 3 times Add about 2.5ml of ultrapure water to make a silica gel suspension (liquid silica stock; LSK), mix the LSK, and dispense 100 μL to each tube;
[0145] (2) Take 1 tube of LSK, add 1ml of ultrapure water, shake and mix, centrifuge at 13200rpm for 20s, and discard the supernatant;
[0146] (3) Add 700 μL of 6M potassium iodide (KI) to LSK, shake and mix, add 50 μL of DNA (about 100 ng / μL of DNA), place on a small ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com