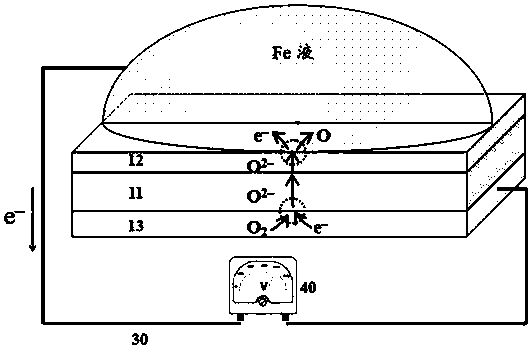
An electrochemical sensor for monitoring nitrogen content in molten iron and its preparation method
An electrochemical and sensor technology, applied in the field of electrochemical sensors for monitoring nitrogen content and their preparation, can solve the problems of single phase number of compounds, poor compatibility and mutual repulsion, and achieve precise control of thickness, small interface internal resistance, interface The effect of low resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
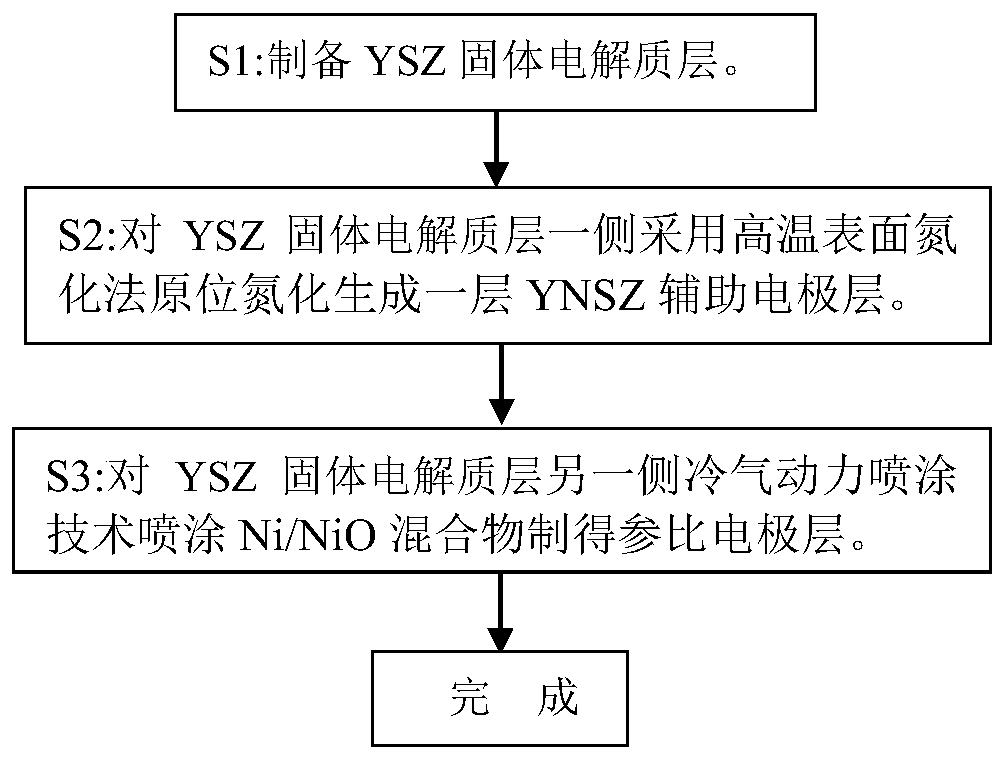
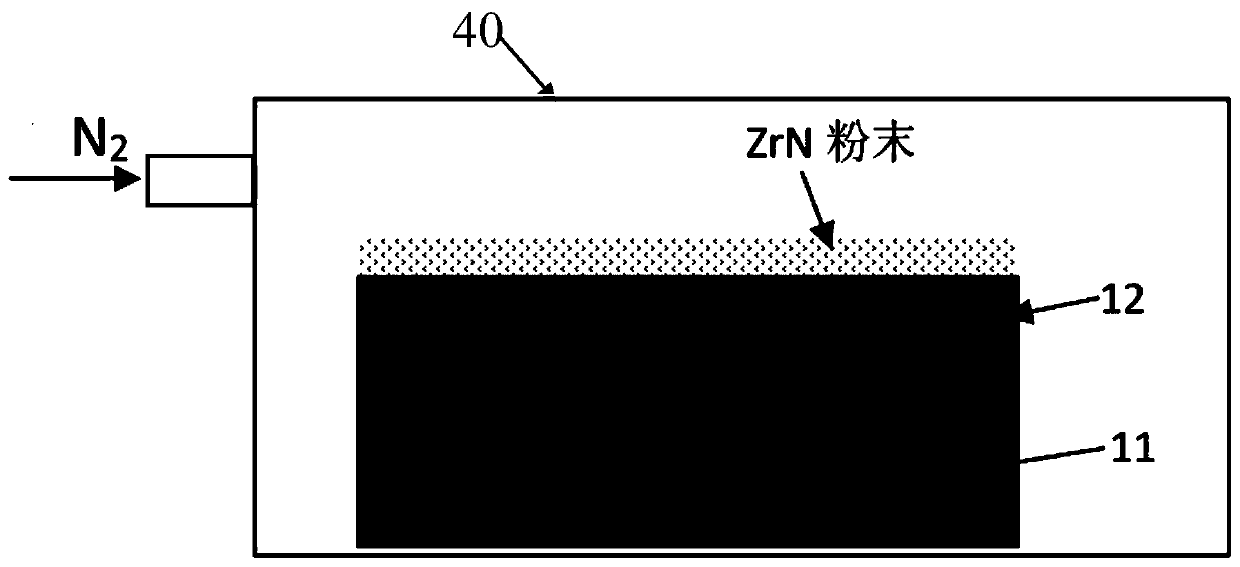
[0049] See figure 2 Shown is a flow chart of the preparation method of an electrochemical sensor for monitoring nitrogen content of the present invention. Basically include the steps: S1: preparing a YSZ solid electrolyte layer; S2: high temperature surface nitriding treatment: using a high temperature surface nitriding method to make one side surface of the YSZ solid electrolyte layer contact with metal nitride powder, baking and nitrogen at high temperature Under the protection of the atmosphere, the side surface of the YSZ solid electrolyte layer is nitridated, and a layer of zirconia layer (YNSZ) co-doped with nitrogen ions and oxygen ions is formed by substituting nitrogen ions for part of the oxygen ions in YSZYSZ. Auxiliary electrode layer); S3: Coating NiO and Ni mixed powder on the other side of the YSZ solid electrolyte layer to prepare a reference electrode layer. Preferably, step S3 is to spray the mixed powder of NiO and Ni onto the surface of the YSZ solid electr...
Embodiment 1
[0076] Step 1. Prepare YSZ solid electrolyte powder: Weigh 7.82g YCl 3 , 148.24g of ZrOCl 2 ·8H 2 O, dissolved in 1L of deionized water to obtain Zr 4+ The concentration is about 0.46mol / L. Under the stirring of a magnetic stirrer, at a constant temperature of 25°C, add ammonia water dropwise for co-precipitation. When the PH=9-10, stop the titration, filter the precipitate, and wash with distilled water and ethanol three times to remove Cl - Plasma impurity ions. Dry the precipitate at a temperature of 75~85℃, dry at a constant temperature for 24h, grind it in an agate mortar for 0.5h, and then roast it in a high-temperature furnace for 10h at a roasting temperature of 600℃ to obtain Y 2 O 3 Stable zirconia solid electrolyte powder YSZ.
[0077] Step 2. Making YSZ solid electrolyte layer: Weigh 30g of solid YSZ powder into a 5cm diameter press mold, apply 300Mpa axial pressure to form a sheet-shaped body, and place it in a high-temperature furnace for sintering. The sintering tem...
Embodiment 2
[0081] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in step 3, the heating temperature in the furnace 40 is controlled to 1600° C. for 8 hours to obtain the YNSZ auxiliary electrode layer 12 with a thickness of 0.8 mm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com