Two-photon fluorescent probe for detecting hypochlorous acid in cellular endoplasmic reticulum
A two-photon fluorescence, endoplasmic reticulum technology, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, luminescent materials, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of poor linear relationship, narrow detection interval, poor water solubility, etc., and achieve a simple and easy synthesis process. , the effect of high specificity and good fluorescence emission spectral characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
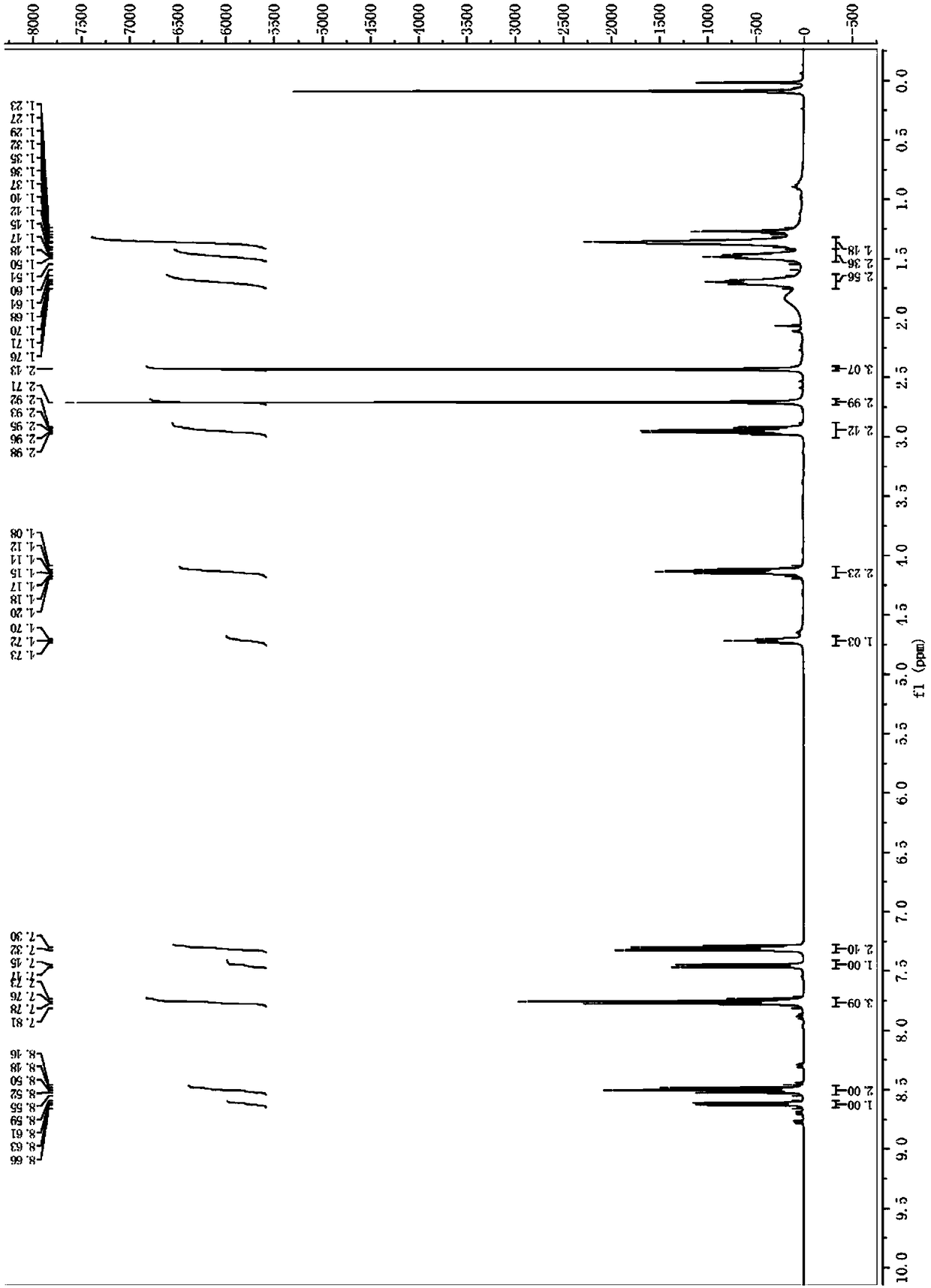
[0038] Example 1 Synthesis of Fluorescent Probes
[0039] (1) Dissolve 120mg of 4-methylthio-1,8-naphthalic anhydride in about 150mL of ethanol and heat under reflux to 90°C for 20min, dissolve BOC-hexamethylenediamine in 2mL of ethanol and add dropwise to the reaction solution. Continue to reflux and stir for 4 hours, filter after cooling, spin the filtrate to dryness, and use ethyl acetate:petroleum ether=3:1 (v / v) to go through silica gel column chromatography to obtain a yellow product (compound 1);
[0040] (2) The product obtained in step (1) was dissolved in about 20 mL of dichloromethane at room temperature, and 2.5 mL of trifluoroacetic acid dissolved in about 1.2 mL of dichloromethane was added dropwise to the reaction solution, and stirred at room temperature for 3 hours. Then the product was spin-dried, and passed through a silica gel chromatography column with methanol:dichloromethane:triethylamine=15:1:0.05 (v / v) as the eluent to obtain a yellow product (compound...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 Responses of fluorescent probes to different concentrations of hypochlorous acid
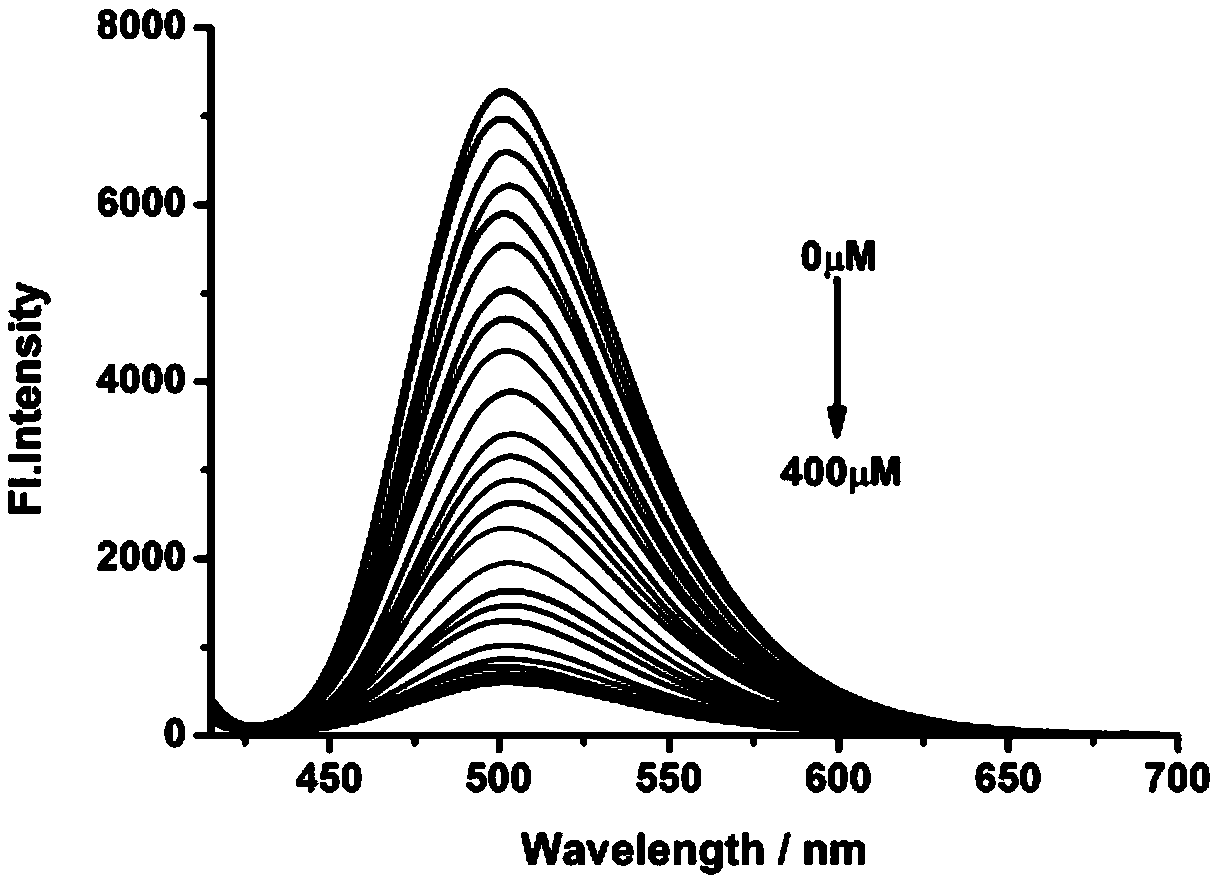
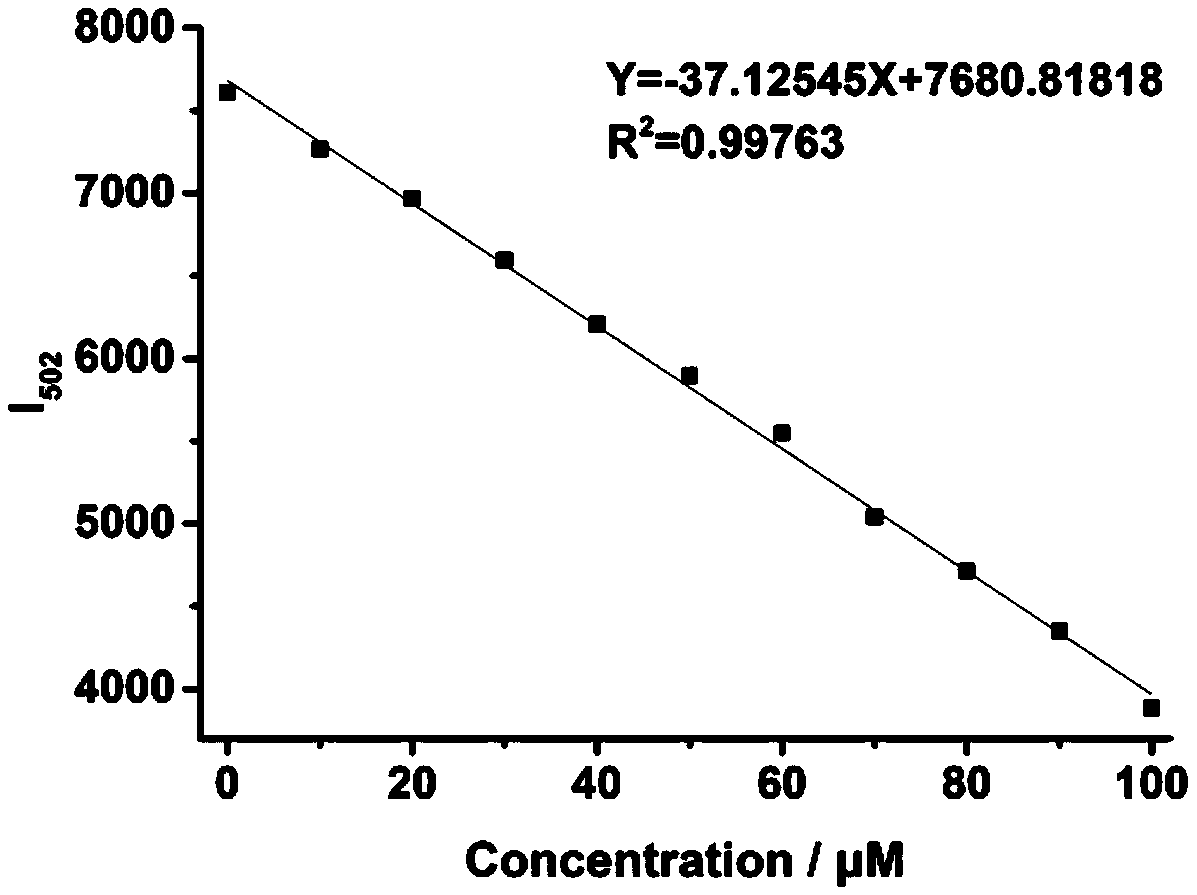
[0044] The probe obtained in Example 1 was dissolved in ethanol, and then prepared into a 10 μM probe buffer solution (containing 10% ethanol) with PBS buffer at pH 7.4. Take 26 parts of the above probe solution, add the same volume of water or sodium hypochlorite solution respectively, so that the concentration of hypochlorite is 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 120, 140 , 160, 180, 200, 220, 240, 260, 280, 300, 320, 340, 360, 380, 400 μM. Then perform a fluorescence scan (λ Ex =405 nm); calculate the relative fluorescence intensity in each system. The response of probe NHS-ER to different concentrations of hypochlorous acid is as follows: figure 2 Shown: Its maximum fluorescence intensity peak is 502nm. The corresponding light intensity at 502 nm (I 502nm ) is the ordinate, and the hypochlorite concentration is the abscissa, we get image 3 , it can be known...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3 Selectivity of Fluorescent Probes
[0046]The probe obtained in Example 1 was dissolved in ethanol, and then prepared into a 10 μM probe buffer solution (containing 10% ethanol) with PBS buffer at pH 7.4. Take 20 parts of the above probe solution and add 400 μL of Hcys and Na at a concentration of 40 mM respectively. 2 S, Na 2 SO 3 、H 2 o 2 , Cys, NaNO 2 , and metal ions in PBS solution, and then perform fluorescence scanning (λ Ex = 405 nm); calculate the relative fluorescence intensity in each system; the response of probe NHS-ER to different concentrations of hypochlorous acid is as follows Figure 4 As shown in (a); the corresponding light intensity at 502 nm (I 502nm ) is the ordinate, and the histogram of the response of the probe to different substances is obtained, such as Figure 4 As shown in (b): Among them, 1-20 represent 1, blank; 2, KI; 3, CaCl 2 ; 4, FeSO 4 ; 5, Cys; 6, CoCl 2 ; 7, MgCl 2 ;8, NaBr; 9, NaF; 10, CuSO 4 ; 11, GSH; 12,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com