Technology for preparing 2, 4-diaminobutyric acid by enzyme catalysis method
A technology of diaminobutyric acid and enzymatic catalysis is applied in the field of preparing 2,4-diaminobutyric acid by enzymatic catalysis, which can solve the problems of difficult separation and purification, small molecular weight, high safety risk, etc. Feasibility of industrial application and high product conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
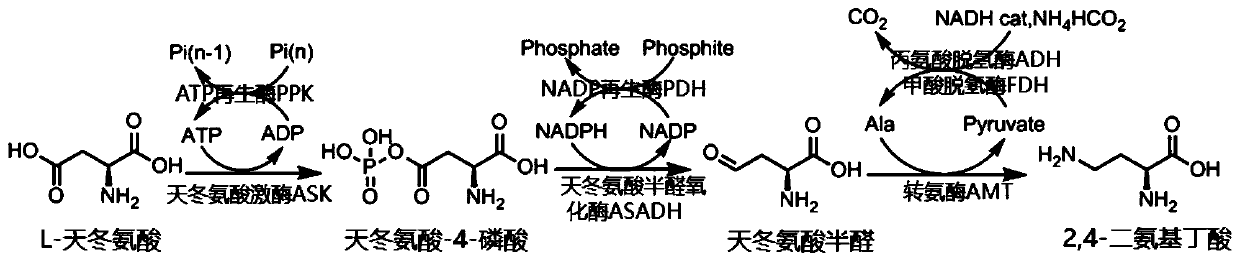
[0039] Example 1: Catalytic production of 2,4-diaminobutyric acid by wet cell one-pot method
[0040] Add 6.65 g of L-aspartic acid (50 mM), 1.1 g of adenosine triphosphate disodium salt ATP (2 mM), and 5.7 g of polyphosphoric acid in 1L of 100 mM pH 8.0 tris-hydrochloride (Tris.HCl) solution. (Sigma, 25 poly, 55mM monophosphate), 0.9g magnesium chloride (10mM), 0.75g potassium chloride (10mM), reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate NADPH monosodium salt 0.76g (1.0mM), reduced Prototype coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NADH disodium salt 0.71g (1.0mM), sodium phosphite 6.8g (55mM), ammonium formate 3.8g (60mM), alanine 89mg (1mM), pyridoxine phosphate Aldehyde 0.7 mg (0.0025mM), after the pH value was adjusted to 8.0, the overexpressed ASK, ASADH, AMT, PPK, Wet cells for PDH, ADH and FDH enzymes. During the reaction process, the pH of the reaction system was maintained between 6.0-9.0 by adding low-concentration HCl and NaOH aqueous solution, stirred g...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2: Catalytic production of 2,4-diaminobutyric acid by liquid enzyme one-pot method
[0045] Collected cell mixture containing aspartokinase ASK, aspartate semialdehyde oxidase ASADH, transaminase AMT, ATP regenerating enzyme PPK, NADP regenerating enzyme PDH, alanine dehydrogenase ADH and formate dehydrogenase FDH In 20 times the volume of 25mM Tris pH 8.0 buffer (buffer A), and then through high-pressure crushing, high-speed centrifugation (16000rpm, 45min) to collect the supernatant containing crude protein, the enzyme crude solution directly for the next reaction to prepare 2 ,4-Diaminobutyric acid.
[0046] Similar to Example 1, 26.6 grams of L-aspartic acid (200 mM), 1.1 grams of adenosine triphosphate disodium salt ATP (2 mM) were successively added to 1 L of 100 mM pH 8.0 trishydrochloride (Tris.HCl) solution , 22.8 g polyphosphoric acid (Sigma, 25 poly, 220 mM monophosphate), 0.9 g magnesium chloride (10 mM), 0.75 g potassium chloride (10 mM), reduced n...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3: Catalytic production of 2,4-diaminobutyric acid by immobilized enzyme in one pot
[0051] Collected cell mixture containing aspartokinase ASK, aspartate semialdehyde oxidase ASADH, transaminase AMT, ATP regenerating enzyme PPK, NADP regenerating enzyme PDH, alanine dehydrogenase ADH and formate dehydrogenase FDH In 20 times the volume of 25mM Tris pH 8.0 buffer (buffer A), then through high-pressure crushing, high-speed centrifugation (16000rpm, 45min) to collect the supernatant containing crude protein, add ammonium sulfate solids to the solution until Wash out (35%-55%, w / v ammonium sulfate / buffer). The enzyme solid was collected by centrifugation (10000rpm, 12min) and then slowly dissolved into 10 times the volume of buffer A, passed through a G25 size exclusion chromatography column (purchased from Sigma) for desalination, and was exchanged with DEAE Seplite FF (Xi'an Lanxiao Company) for anion exchange. After column separation, the primary purified enzy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com