A kind of injectable hydrogel and preparation method thereof
A technology for injecting water and gel, which is applied in the field of biomedical materials and tissue engineering, can solve the problems of uncontrollable degradation rate, destruction of three-dimensional matrix cross-linked network, and reduced clearance rate, etc., and achieves the effect of controllable degradation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A preparation method of an injectable hydrogel, comprising the following steps:
[0034] (1) Take the adipose tissue and freeze and thaw it for 3 times, then soak it in 0.4mol / L NaCl hypertonic liquid for 4 hours, and then soak it in 0.9mol / L NaCl for 4 hours to break the fat cells; then use 0.24wt% NaCl The trypsin solution was digested at 35°C for 3 hours, rinsed with deionized water for 3 hours, treated with isopropanol for 12 hours to remove fat, and then treated with 0.9 wt% sodium dodecyl sulfate for 2 hours. 0.9% polyethylene glycol octyl phenyl ether was treated for 48 hours to perform decellularization treatment to obtain an acellular matrix, and the decellularized matrix was lyophilized for 36 hours at minus 80°C and 0.038 mbar for use;
[0035] (2) using 0.5 mg / mL pepsin to enzymolyze the lyophilized acellular matrix in an acidic environment for 12 hours, and then inactivating the pepsin to obtain a 6 mg / mL extracellular matrix protein solution for future use...
Embodiment 2
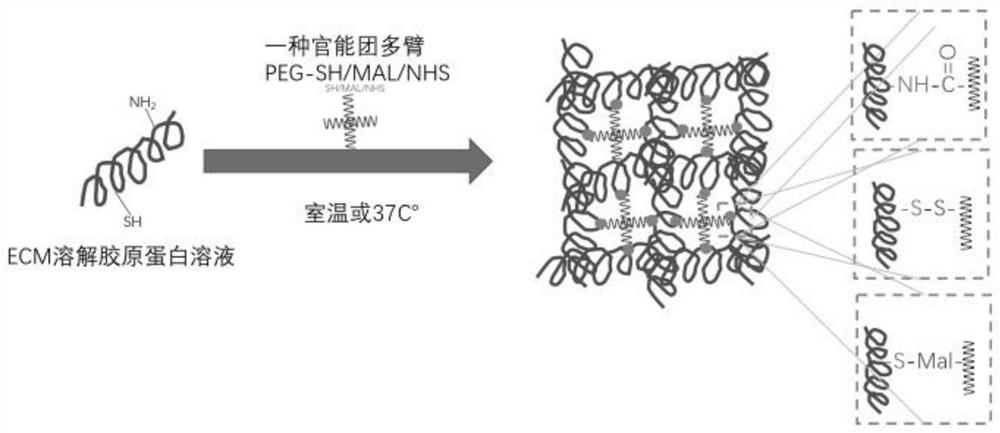
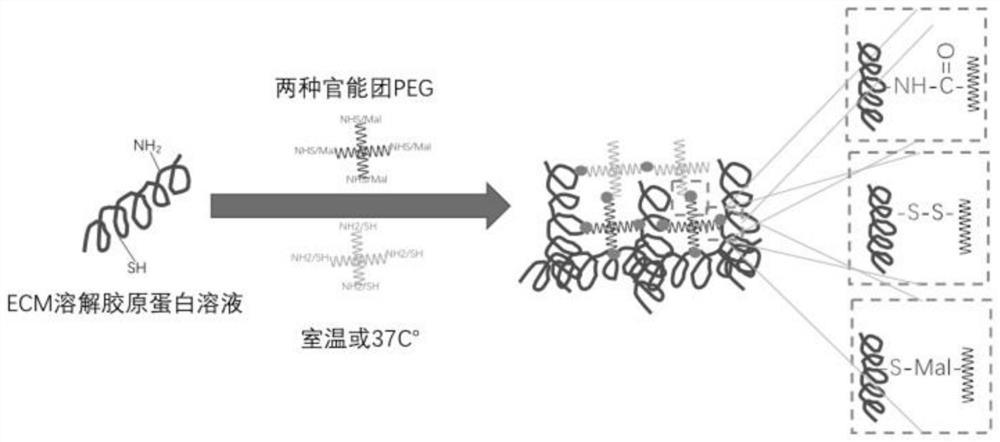
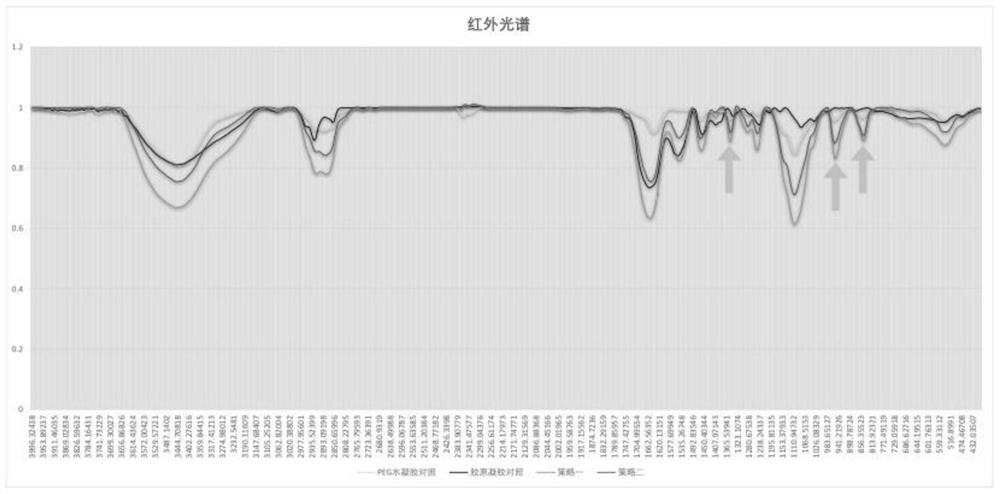
[0038] like figure 1 As shown, a preparation method of an injectable hydrogel comprises the following steps:
[0039] (1) Take the adipose tissue repeatedly freeze and thaw 4 times, then put it into 0.5mol / L NaCl hypertonic liquid for 4 hours, and then soak it in 1mol / L NaCl for 4 hours to break the fat cells; then use 0.25t% pancreas The protease solution was digested at 37°C for 6 hours, rinsed with deionized water for 4h, treated with isopropanol for 18h after washing to remove fat, then treated with 1wt% sodium dodecyl sulfate for 18h, and then treated with 1% The polyethylene glycol octyl phenyl ether was treated for 48h to carry out decellularization treatment to obtain an acellular matrix, which was lyophilized at minus 80°C and 0.04mbar for 36h for use;
[0040] (2) using 3 mg / mL pepsin to hydrolyze the lyophilized acellular matrix in an acidic environment for 18 hours, and then inactivating the pepsin to obtain a 20 mg / mL extracellular matrix protein solution for lat...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A preparation method of an injectable hydrogel, comprising the following steps:
[0044] (1) Take the adipose tissue repeatedly freeze and thaw 6 times, then put it in 0.6mol / L NaCl hypertonic liquid for more than 4 hours, and then soak it in 1.1mol / L NaCl for 5 hours to break the fat cells; then use 0.26wt% The trypsin solution was digested at 38 °C for 10 hours, rinsed with deionized water for 4 hours, treated with isopropanol for 24 hours to remove fat, and then treated with 1.1 wt% sodium dodecyl sulfate for 24 hours. Treat with 1.1% polyethylene glycol octyl phenyl ether for 50 hours to perform decellularization treatment to obtain an acellular matrix, which is lyophilized at minus 80°C and 0.042 mbar for 38 hours for later use;
[0045] (2) using 5 mg / mL pepsin to enzymolyze the lyophilized acellular matrix for 24 hours in an acidic environment, and then inactivating the pepsin to obtain a 40 mg / mL extracellular matrix protein solution for future use;
[0046] (3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com