Preparation method and application of biochar-loaded nano zero-valent iron sulfide material
A zero-valent iron and biochar technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of reduced reaction rate, reduced flow performance, and reduced specific surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] The invention provides a preparation method of biochar-loaded nanometer zero-valent iron sulfide material, comprising the following steps:
[0029] Under vacuum or inert atmosphere, the biomass and FeSO 4 The solutions were mixed, evaporated to dryness, ground, and dried to obtain the loaded FeSO 4 biomass;
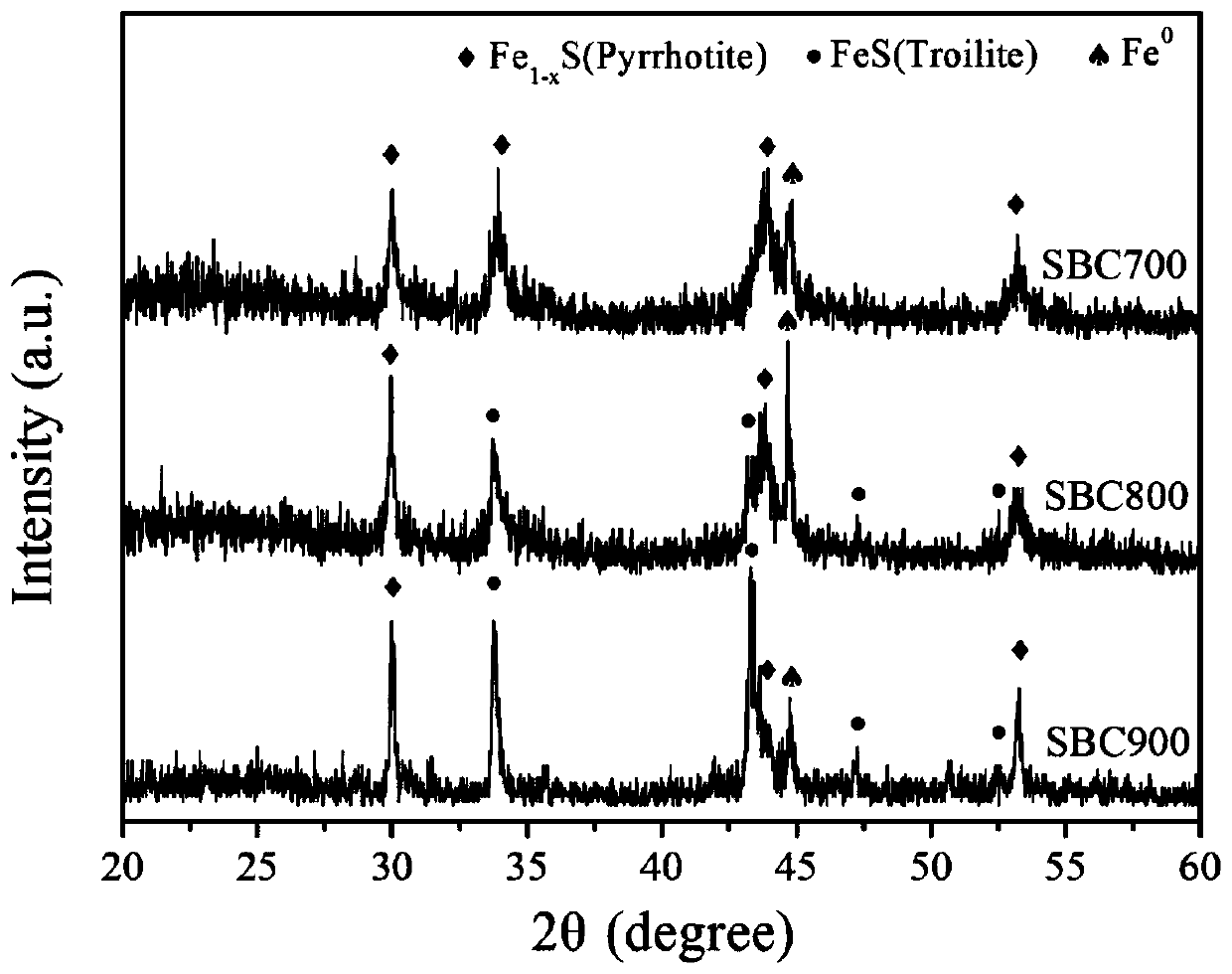
[0030] The loaded FeSO 4 The biomass is pyrolyzed at 800-1000°C under an inert atmosphere to obtain biochar-supported nano-zero-valent iron sulfide materials.
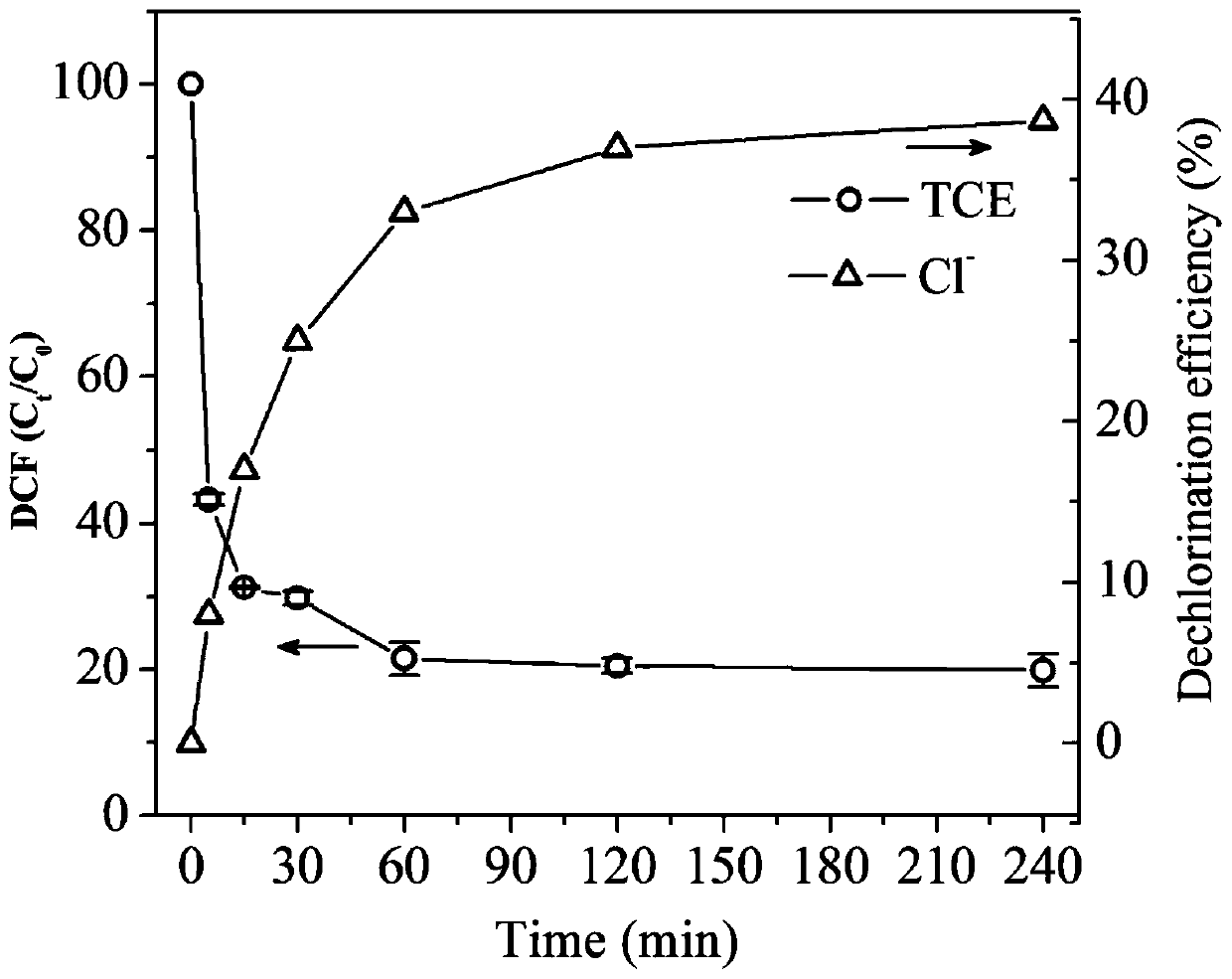
[0031] Compared with the prior art, the present invention adopts the one-pot pyrolysis method to prepare the biochar-loaded nano-sulfurized zero-valent iron material, without adding additional chemical reduction reagents and vulcanization reagents, and achieves simultaneous biochar reduction of zero-valent iron. The purpose of loading and vulcanization modification is simple, and the prepared material can quickly and effectively treat sewage containing halogenated organic matter.
[0032] In the present...
Embodiment 1
[0044] 1.1 Raw material pretreatment: pulverize the sawdust, sieve, keep the 100-200 mesh sieved sawdust, and dry it at 80°C for later use.
[0045] 1.2 Add 5mmol FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O. 5g of sawdust treated in 1.1 and 200ml of deoxygenated water were mixed and dispersed under the assistance of ultrasound, then the mixed solution was transferred to a flask, deoxygenated with nitrogen for 30min, shaken at 180r / m in a water bath shaker at 25°C for 12h, and then used The moisture in the flask was evaporated to dryness by a rotary evaporator, and the solid composite was dried in a vacuum drying oven at 80° C., and after uniform grinding, the biomass loaded with ferrous sulfate was obtained.
[0046] 1.3 Under a nitrogen atmosphere, use a rapid pyrolysis furnace to rapidly pyrolyze 2 g of the above-mentioned sawdust loaded with ferrous sulfate at 800 ° C for 1 hour to obtain biochar-supported nano-zero-valent iron sulfide (SBC-800) .
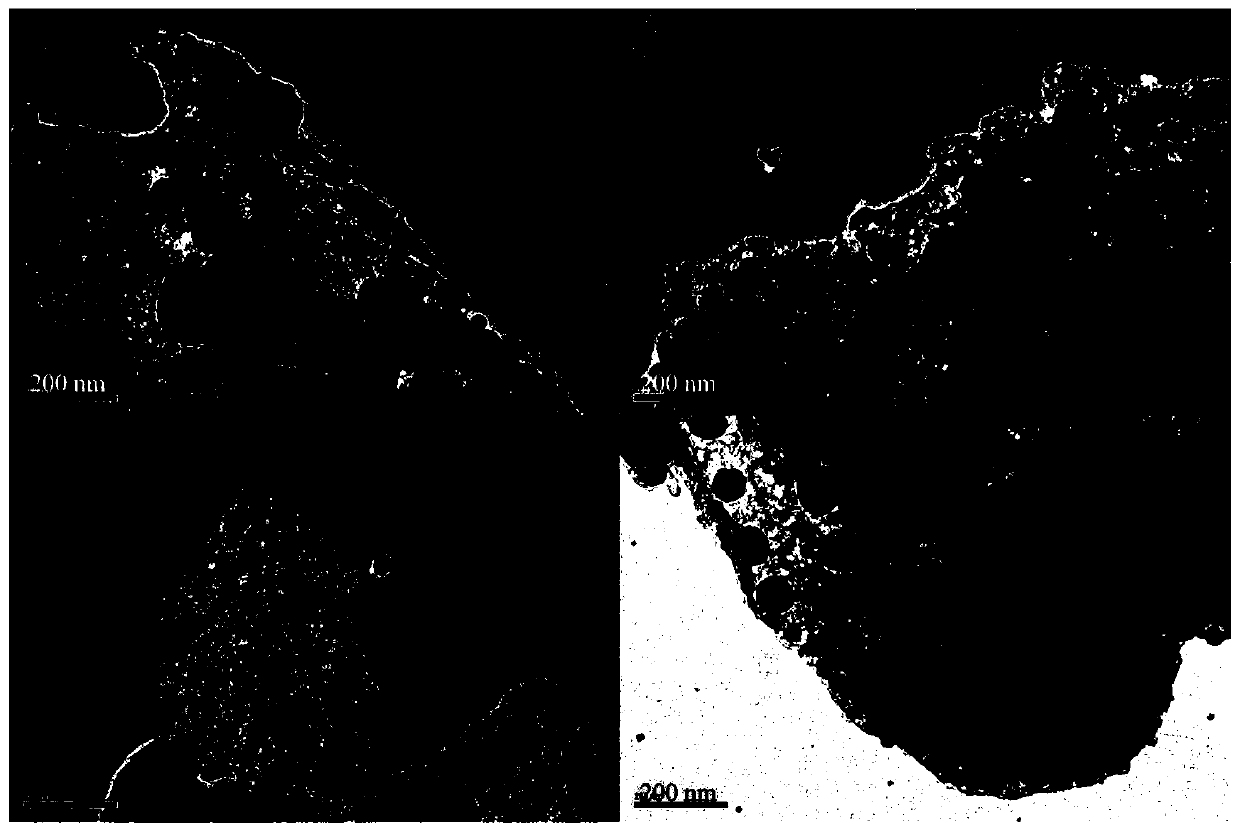
[0047] figure 1 It is the TEM figure of the bioch...
Embodiment 2
[0050] 1.1 Raw material pretreatment: pulverize the sawdust, sieve, keep the 100-200 mesh sieved sawdust, and dry it at 80°C for later use.
[0051] 1.2 Add 5mmol FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O. 5g of sawdust treated in 1.1 and 200ml of deoxygenated water were mixed and dispersed under the assistance of ultrasound, then the mixed solution was transferred to a flask, deoxygenated with nitrogen for 30min, shaken at 180r / m in a water bath shaker at 25°C for 12h, and then used The moisture in the flask was evaporated to dryness by a rotary evaporator, and the solid composite was dried in a vacuum drying oven at 80° C., and after uniform grinding, the biomass loaded with ferrous sulfate was obtained.
[0052] 1.3 Under a nitrogen atmosphere, use a rapid pyrolysis furnace to rapidly pyrolyze 2 g of the above-mentioned sawdust loaded with ferrous sulfate at 900 ° C for 1 hour to obtain biochar-supported nano-zero-valent iron sulfide (SBC-900) .
[0053] Biochar-loaded nano-zero-valent iron sulfid...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com