Epoxide hydrolase mutant and application thereof
A technology of epoxide and hydrolase, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of low catalytic activity, poor thermal stability, and sudden drop in enzyme activity, so as to improve the activity and thermal stability of the enzyme, improve the activity and The effect of service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of epoxide hydrolase gene and the construction of genetically engineered bacteria
[0031] According to the coding gene of Bacillus alcaligenes epoxide hydrolase (GenBank accession number E50984), Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. was commissioned to synthesize the gene sequence, its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.8, and Add 6 histidine tags to the N-terminus of the protein, use Nde I and BamHI restriction endonuclease sites, insert it into pET22b vector, and transform Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). Then, a genetically engineered bacterium containing Alcaligenes epoxide hydrolase was obtained from Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Error-prone PCR (error-prone PCR) method to construct a random mutation library of epoxide hydrolase
[0033] (1) The above-mentioned epoxide hydrolase gene was randomly mutated using the GeneMorph II Random Mutagenesis kit (purchased from Agilent, Code No. 200550). The primers used are T7 and T7t, the nucleotide sequences of which are shown in SEQ ID No.9 and SEQ ID No.10. The reaction conditions were: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3 min, denaturation at 95°C for 30 s, annealing at 55°C for 30 s, and extension at 72°C for 1 min, a total of 25 cycles. After PCR, run 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and use a gel recovery kit (purchased from Sangon, CodeNo.B518131) to recover gene fragments.
[0034] (2) Digest the recovered fragment with Nde I and BamH I double enzymes, and perform ligation reaction with the pET 22b(+) vector (ampicillin resistance) that has undergone the same enzyme digestion. The reaction conditions are: vector and fragment according to 1: M...
Embodiment 3
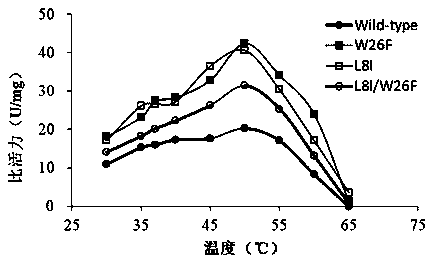
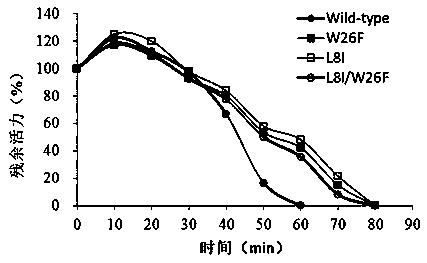
[0039] Embodiment 3: Preparation of double mutants
[0040] Extract the plasmid of the single mutant L8I strain in Example 2, transform Escherichia coli DH5α competent cells, then extract the plasmid as a template in this bacterial strain, design site-directed mutagenesis primers W26F (+) and W26F (-), its nucleotide The sequences are shown in SEQ ID No.11 and SEQ ID No.12. Fasta-II rapid site-directed mutagenesis kit (Beijing Saibaisheng Gene Technology Co., Ltd.) was used for site-directed mutagenesis to obtain double mutants (L8I / W26F), and passed Sequencing verification, its nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID No.7.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com