Method for recovering acid solution and separating vanadium in the process of reducing acid leaching vanadium-containing waste catalyst
A waste catalyst and catalyst technology, applied in the direction of process efficiency improvement, etc., can solve the problems of only 85%, low leaching rate, and a lot of waste, and achieve the effects of recycling, mild leaching conditions, and low leaching temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
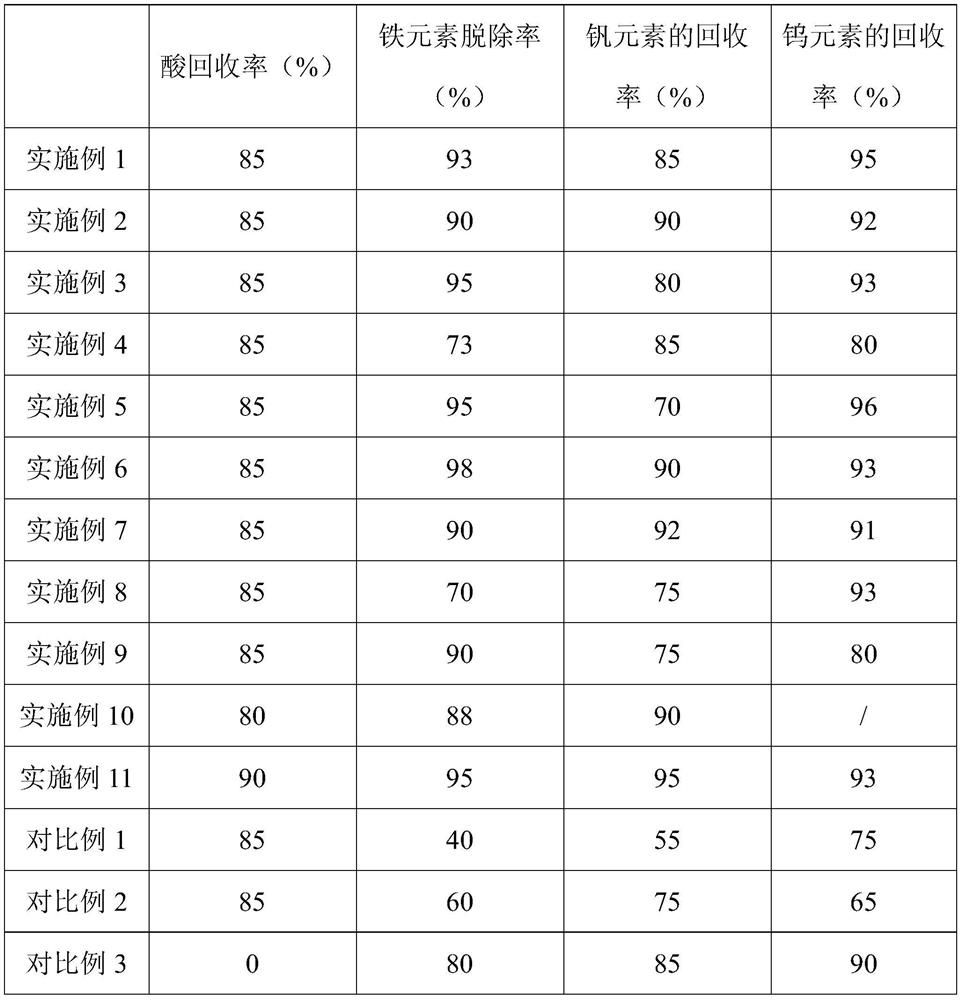
Embodiment 1
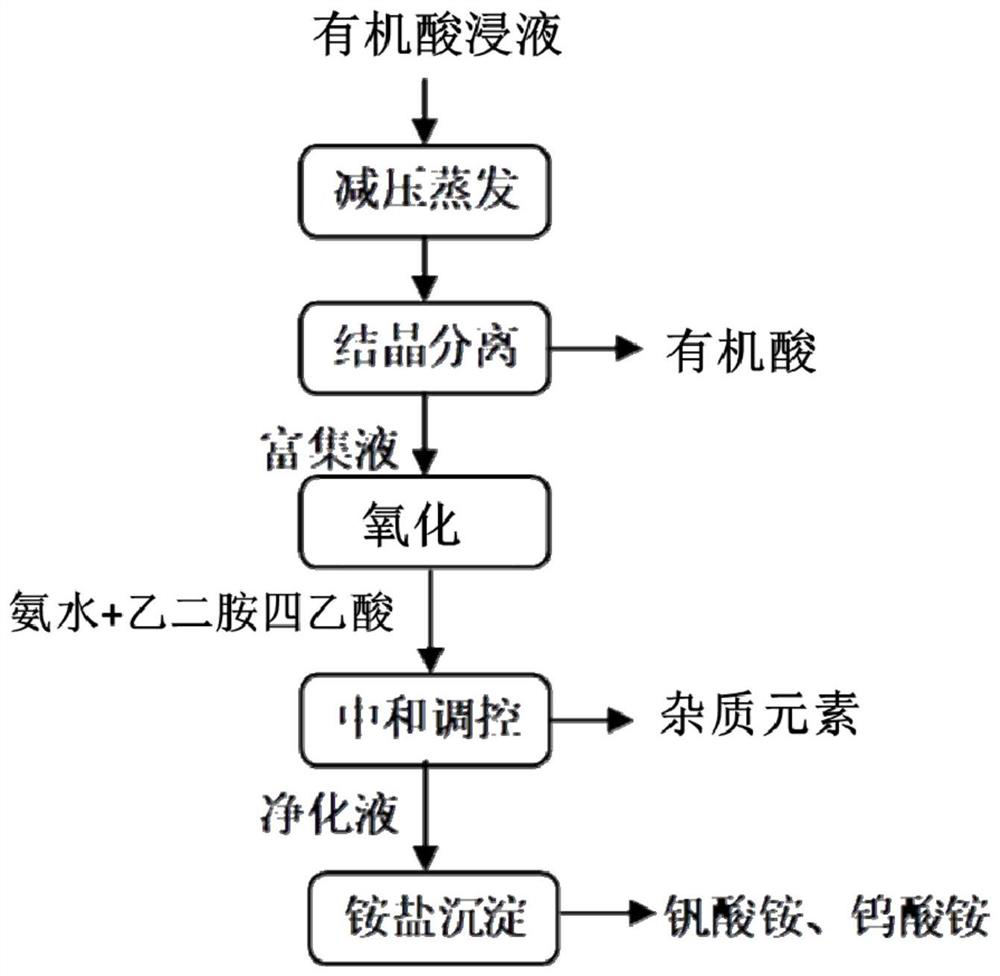
[0064]A method of reducing acid recovery and separation vanadium in a reduction acid immersed catalyst is included in the following steps:
[0065](1) The vanadium titanium aluminum system catalyst is added to 70 ° C in ethacealate to obtain an organic acid dip for a vanadium element content of 4.5 g / L, and evaporate at 80 ° C in the organic acid dip. The evaporation volume is 80% of the organic acid immersion volume, and then crystallized at 0 ° C for 8 h, and the mixed liquid is obtained by filtration of ethylenedic acid crystals;
[0066](2) Comparison of the rich concentration and hydrogen peroxide is 10: 1, and the rich concentration is mixed with the hydrogen peroxide, oxidized at 70 ° C, and the ammonia water is added to the enriched liquid after oxidation to 3, 1 g of ethylenediamine tetracetic acid was added, and the removal process of iron element at 50 ° C was added to obtain a purified liquid, and then an ammonia water was added to the purifying liquid to adjust the second p...
Embodiment 2
[0068]The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the first pH value to 2 is adjusted in step (2).
Embodiment 3
[0070]The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the first pH value to 4 is adjusted in step (2).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com