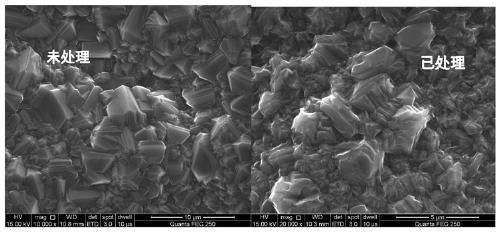
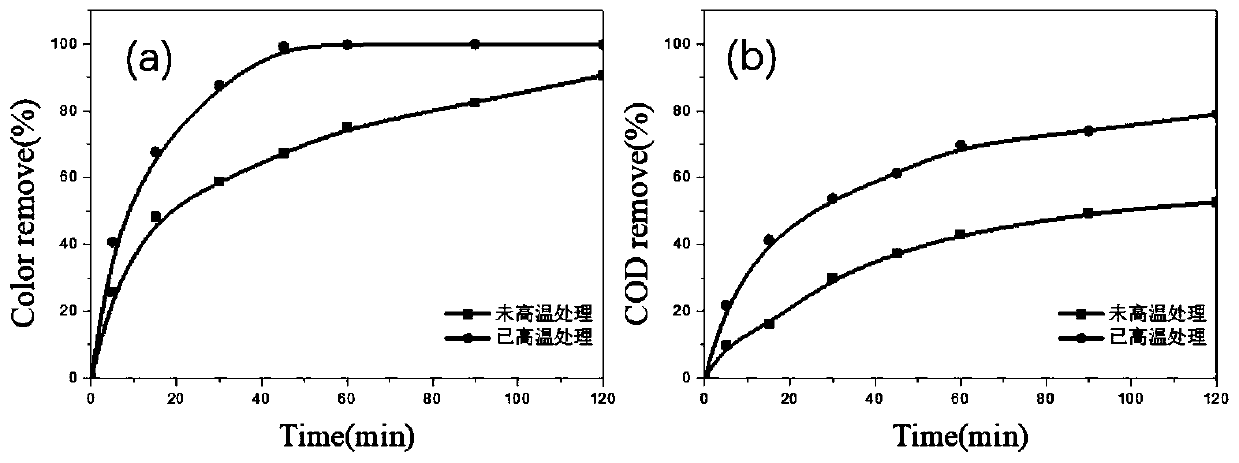
High-specific-surface-area super-hydrophilic gradient boron-doped diamond electrode and preparation method and application thereof
A diamond electrode, high specific surface area technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of BDD material pollution, water pollution, high equipment requirements, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Ti substrate BDD electrode material
[0068] The BDD electrode chooses titanium (Ti) as the substrate for depositing BDD, because the carbonized transition layer is easy to form on the surface of Ti, and the thermal expansion coefficients of Ti and C match, so it is easy to form a BDD film with good adhesion. Both have good corrosion resistance and stability at the same time. The preparation process is as follows
[0069] 1. Preparation of BDD materials
[0070] 1.1 Substrate material pretreatment
[0071] First cut the Ti into a sheet sample with a size of 30×20×2mm, and polish it with 600#, 800#, 1000# metallographic sandpaper; then immerse the polished Ti substrate in acetone (CH 3 COCH 3 ), absolute ethanol (C 2 h 5 OH) for 10 minutes of ultrasonic oscillation; then the Ti substrate was placed in the nano-diamond suspension and the seed crystal was ultrasonically planted for 30 minutes to enhance the nucleation. Finally, rinse with deionized ultrapure water a...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Preparation of nickel substrate BDD material
[0084] Nickel (Ni), as a common electrocatalytic material that is easily electrodeposited, can be processed into complex structures and shapes. Therefore, this example prepares BDD films on the surface of Ni substrate materials.
[0085] 1. Preparation of BDD materials
[0086] 1.1 Substrate material pretreatment
[0087] First cut Ni into sheet samples with a size of 25×30×2mm, then immerse the Ni substrate in acetone (CH3COCH3) and absolute ethanol (C2H5OH) for 10 minutes of ultrasonic oscillation, then rinse with deionized ultrapure water and dry stand-by.
[0088] 1.2 Preparation of transition layer
[0089] Metal Ni can easily catalyze diamond into other amorphous carbons, so it is impossible to directly deposit boron-doped diamond films; at the same time, the thermal expansion coefficient difference between Ni and C is large, and an effective carbonized transition layer cannot be formed, and the bonding between the...
Embodiment 3
[0102] Silicon substrate BDD electrode material
[0103] Silicon (Si) is the most common BDD substrate material because of its good corrosion resistance and low thermal expansion coefficient. Therefore, it has a high degree of lattice matching with the BDD film and a good binding force. In this example, a flat p-type doped silicon is used as the substrate material for experiments.
[0104] 1. Preparation of BDD materials
[0105] 1.1 Substrate material pretreatment
[0106] First cut the Si into a sheet sample with a size of 20×30×0.5 mm, then immerse the Si substrate in acetone (CH3COCH3) and absolute ethanol (C2H5OH) for 10 min and ultrasonically vibrate, then rinse with deionized ultrapure water and bake. Dry and set aside.
[0107] 1.2BDD film deposition
[0108] The hot wire used in this paper is The straight tungsten wire is used to completely cover the straight wire directly above the substrate, and then the pretreated substrate is put into the cavity of the HFCV...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com