Preparation method and application of molecular imprinting ratio type fluorescence sensor for detecting hepatitis B virus
A hepatitis B virus and fluorescence sensor technology, applied in the field of analytical chemical detection, can solve the problems of limiting the imprinting efficiency of macromolecular viruses, and achieve the effects of low detection limit, high specific surface area, and high specific recognition ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
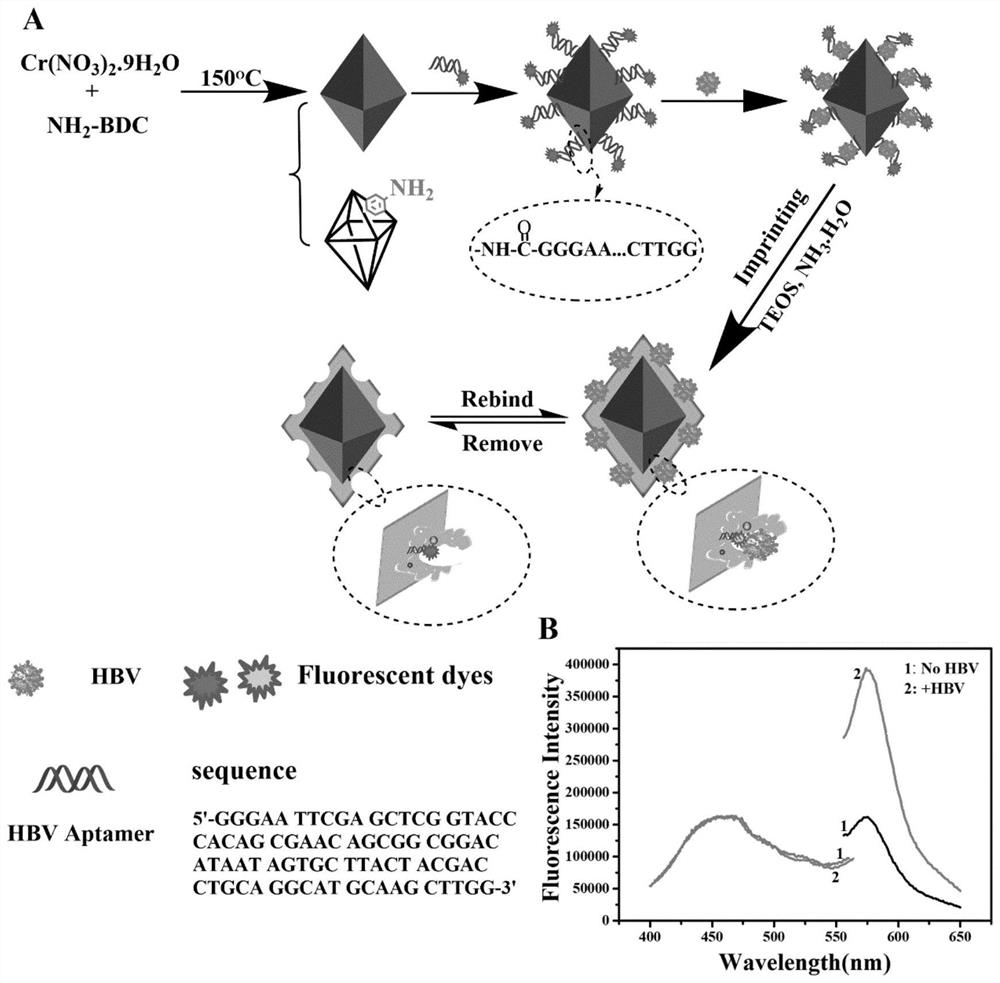
[0029] Example 1: A method for preparing a molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescent sensor for dual recognition and detection of HBV.
[0030] (1) MIL-101-NH 2 Preparation: 800mg (2mmol) Cr(NO) 3· 9H 2 O, 360 mg (2 mmol) NH 2 BDC and 159.02 mg NaOH were added into 15 mL water and stirred for 1 hour, then the solution was transferred to a Teflon-based reactor and reacted at 150 °C for 12 hours. After the reaction, the reactor was taken out and naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain a green suspension.
[0031] (2)MIL-101-NH 2 Purification: first wash the obtained MIL-101-NH with DMF solvent 2 Crude product, most of the unreacted impurities were removed. Then solvent heat treatment was used to further wash away a small amount of impurities in the imprinted wells: the product was dispersed in 25mL of ethanol and placed in an oven, reacted at 90°C for 6 hours and then taken out to obtain pure MIL-101-NH 2 .
[0032] (3) Preparation of MIL-101-Apt: first use ED...
Embodiment 2
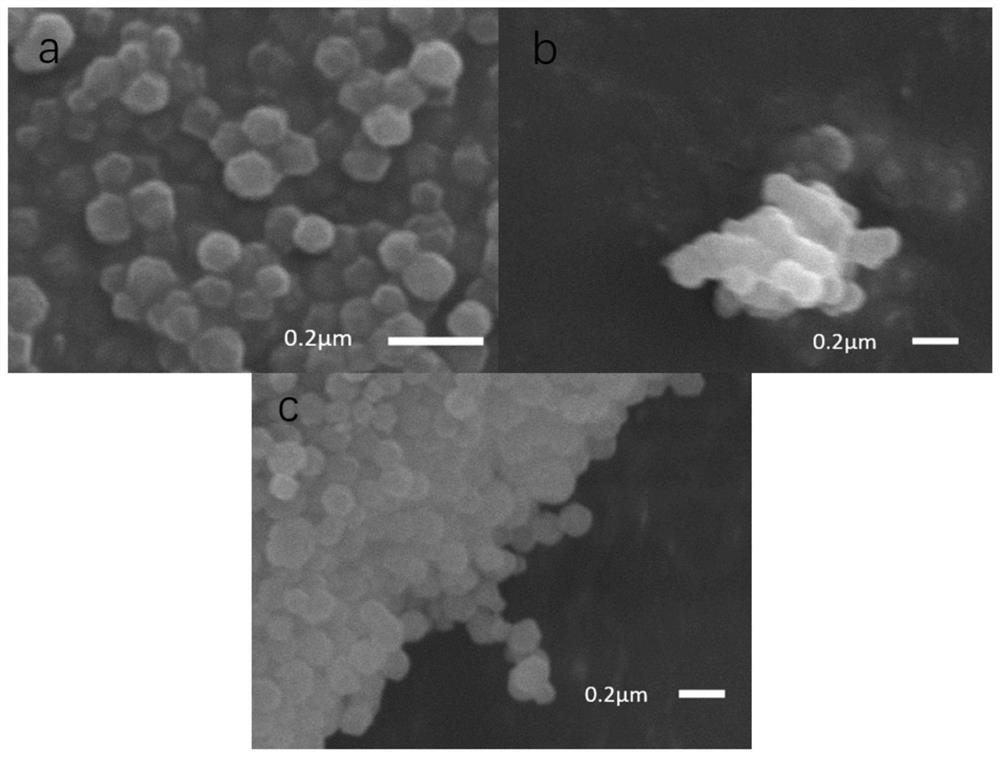
[0035] Example 2: Morphological and structural characterization of the molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescent sensor and intermediate products.
[0036] Using Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffractometer (XRD), thermogravimetric analyzer and N 2 The structure and morphology of all the prepared materials were characterized by adsorption-desorption experiments.
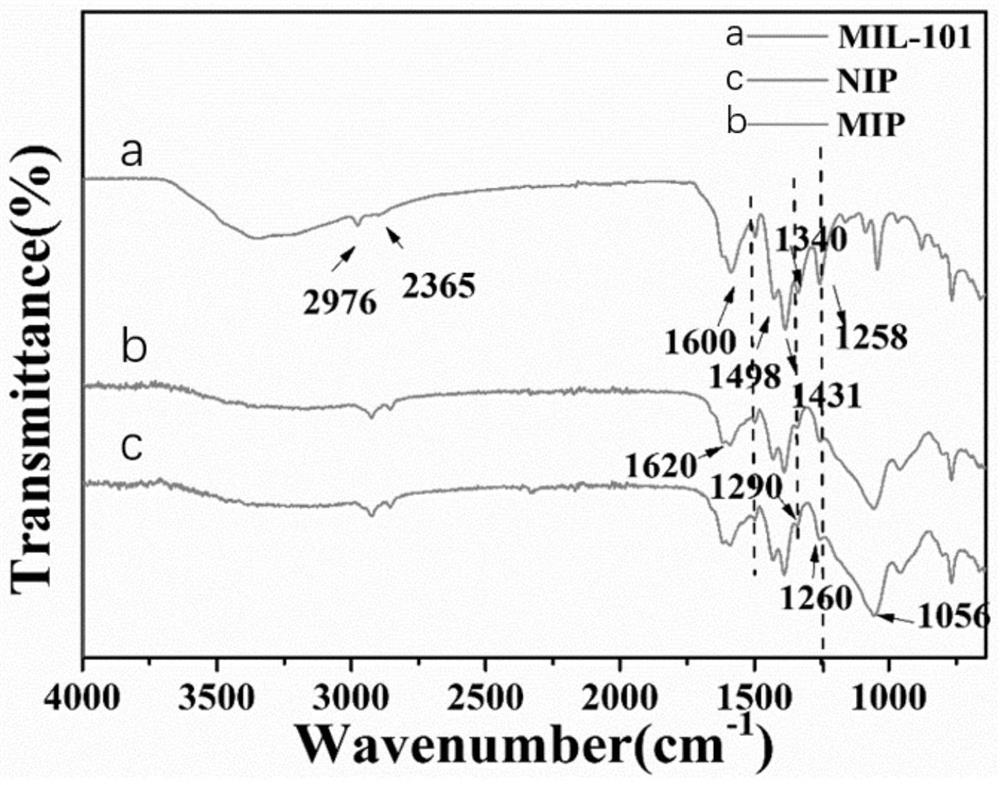
[0037] figure 2 Infrared spectra of MIL-101, MIL-Apt, MIP and NIP. 2976 and 2365cm -1 is the C-H stretching vibration peak of the benzene ring, 1600cm -1 is the amino N-H bending deformation vibration peak, 1498 and 1431cm -1 at MIL-101-NH 2 The stretching and stretching vibration peaks of -(OCO)- in the framework, 1340 and 1258cm -1 is the C-N stretching vibration peak on the aminobenzene ring, indicating that MIL-101-NH 2 The material was prepared successfully, forming NH 2 BDC skeleton. 1600cm -1 The stretching vibration peak of the aptamer C=O is at 12...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: Application of the molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescent sensor.
[0043] The experimental conditions of this example are: the dosage of aptamer is 250 μL, the dosage of monomer TEOS is 40 μL, the concentration of MIP is 0.8 mg / L, the pH is 7.4, the adsorption time is 20 min, and the temperature is 25°C. The specific implementation method is: take a specific concentration of HBV and add it to 0.8 mg / L MIP solution, adjust the pH of the whole system to 7.4, and measure the fluorescence intensity after shaking and absorbing at 25°C for 20 minutes.
[0044] (1) Detection of different concentrations of HBV by MIL-101-MIP ratiometric fluorescent sensor
[0045] According to the above experimental steps, the HBV solutions of different concentrations are detected and analyzed with the ratiometric fluorescent sensor of the present invention, and the results are as follows: Figure 8 As shown, the fluorescence intensity of MIP at 570nm changes, while the fluo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com