Novel chitosanase chi1, its coding gene and its application
A technology of chitosan enzyme and coding gene, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of a large amount of waste water, waste, non-compliance with energy saving and emission reduction, and consumption of large water resources, etc., and achieve the effect of high enzyme activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Example 1 Construction of metagenomic library of intestinal contents of small yellow croaker
[0054] 1.1 Extraction of metagenomic DNA from intestinal contents of small yellow croaker
[0055] (1) Sample pretreatment and DNA extraction
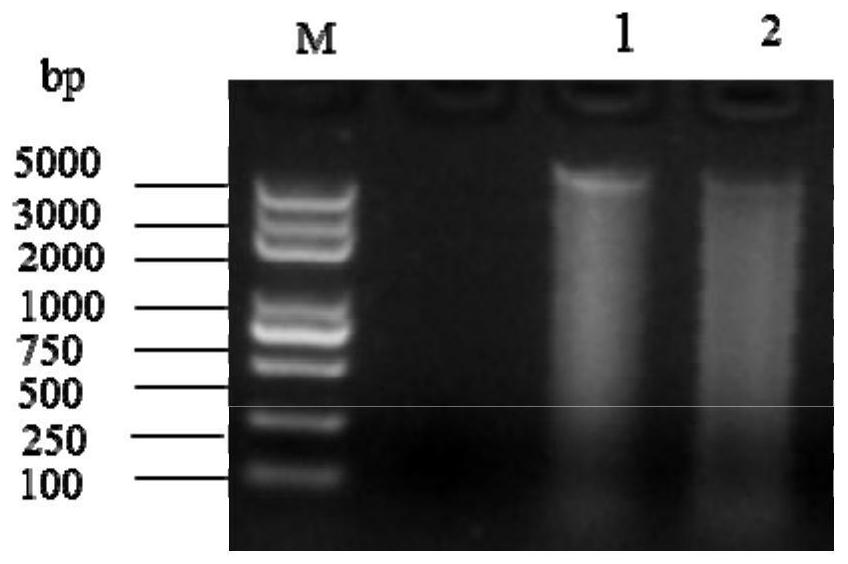
[0056] Fish samples were processed on a sterile operating table. First, 75% alcohol was used to wipe the surface of the fish and tweezers and other utensils, and then the anus was cut upwards and forwards in an arc with dissecting scissors. The outer wall of the digestive tract was wiped with 75% alcohol, and rinsed several times with sterile flushing solution (0.9% sterile saline). The alimentary canal was isolated with sterile scissors, rinsed with sterile irrigating solution and the contents of the alimentary canal were collected. Next, the metagenomic DNA of the digestive tract contents of the small yellow croaker was extracted by CTAB method, and the extracted metagenomic DNA was detected by electrophoresis. The results are show...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Example 2 Screening of small yellow croaker intestinal metagenomic library chitosanase
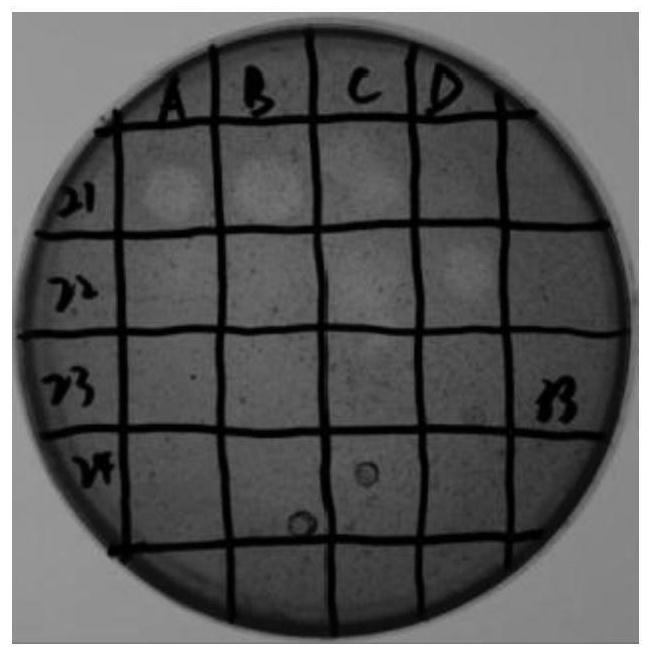
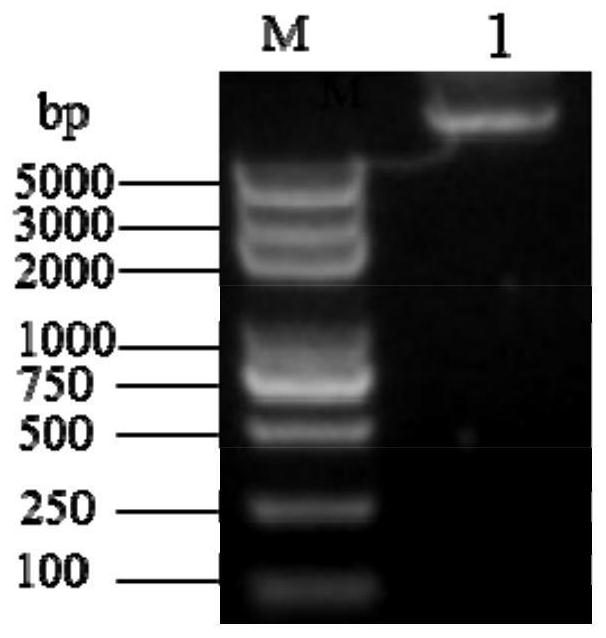
[0083] Screening method: Select white positive colonies from many clones in the library, and spot them on the LB (Amp+IPTG+X-gal) medium plate containing 1% colloidal chitosan, culture at 37°C for 1-2d , observe whether there is a hydrolysis circle around the colony. After the colony grows, it will be stained with 1 mg / mL Congo red solution for 10-15 minutes and then decolorized. The colony with a transparent circle is the target colony. Purify the target colony by streaking to obtain a single colony of the target bacterium. The above-mentioned clones with hydrolysis circles were extracted with plasmids, and the plasmid sequencing was completed by Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Co., Ltd.
[0084]Experimental results: After a large number of screenings, it was found that there were many different library clones that could produce transparent circles, and the one with the best effect...
Embodiment 3
[0085] The bioinformatics analysis of embodiment 3 chitosanase gene CHI1
[0086] Carry out various biological information analysis of chitosanase gene CHI1 according to different tools in the following table 1:
[0087] Table 1 Bioinformatics analysis tools
[0088]
[0089]
[0090] 3.1 Multiple sequence alignment results
[0091] The sequences of CHI1 and chitosanases of family 8 were compared, and the results of the comparison can be found in Image 6 . The comparison results show that the protein sequence information of chitosanase CHI1 can be found in SEQ ID No.1 in the sequence table. This enzyme belongs to the glycoside hydrolase 8 family. The primary structure comparison of chitosanase CHI1 shows that the most similar sequence is WP -053425757.1 is a chitosanase from Rheinheimera sp., with a similarity of 72%. The above results indicate that CHI1 has a low similarity with the known sequence and is a new chitosanase gene.
[0092] 3.2 Analysis results of prot...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com