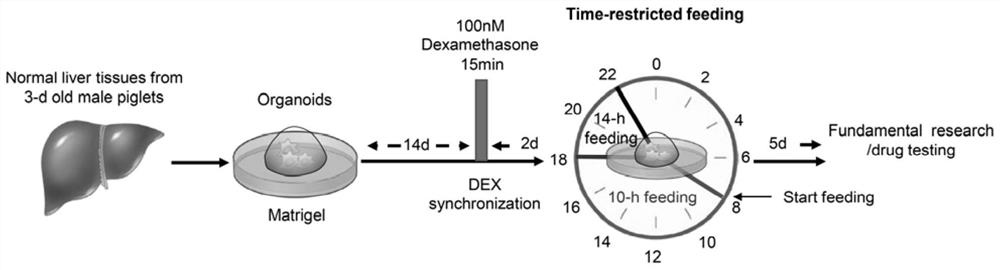
Pig liver tissue organoid model and in-vitro construction method thereof
A construction method and organoid technology, which is applied in the field of in vitro construction of pig liver tissue organoid models, can solve the problems of lack of intercellular matrix in organoids and the inability to truly simulate the physiological functions of the liver, achieving rapid construction, simple methods, and reduced The effect of sampling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 In vitro construction of porcine liver organoids
[0032] In this example, 3-day-old male piglet liver tissue was used to establish pig liver organoids for experiments.
[0033] Specific steps are as follows:
[0034] 1), three-day-old newborn piglets were anesthetized in a sterile laboratory, and about 500 mg of liver tissue was removed. The collected fresh piglet liver tissue was repeatedly washed with PBS cleaning solution containing 5 times of penicillin, streptomycin, gentamycin and amphotericin B, cut into pieces, and then washed with 5 times of penicillin, streptomycin, gentamicin The PBS washing solution of amphotericin and amphotericin B was centrifuged until the supernatant was clear.
[0035] 2) Transfer the shredded and cleaned tissue to a 50mL sterile centrifuge tube, add 10mL of digestion solution, and seal the centrifuge tube with parafilm. Digestion was incubated at 200 rpm in a constant temperature shaking incubator at 37°C; the digestion s...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2 Dexamethasone Treatment and Organoid Biological Cycle Reset
[0046] On day 15 after organoid inoculation, the organoids were treated with 100 nM (final concentration) of dexamethasone (DEX, Sigma-Aldrich) for 15 min to reset the organoid clock, synchronizing it to 0 o'clock. Organoids were then washed three times with PBS wash (37°C) and cultured in expansion medium. After 48 hours of DEX treatment, the organoids in 6 wells were used as the control group, exposed to the expansion medium from 8:00 am to 10:00 pm, and then exposed to the basal medium at 10:00 pm ~ 8:00 am, the total time is 24 hours + 1 hour. Organoids from the other 6 wells served as the limiting nutrient group and were exposed to expansion medium for 10 h from 8:00 am to 6:00 pm and +1 to basal from 6:00 pm to 8:00 am in a 24 hour cycle medium for 14 hours. Exposure was continued for 5 days in a 24-hour cycle, after which organoids were harvested and analyzed.
Embodiment 3
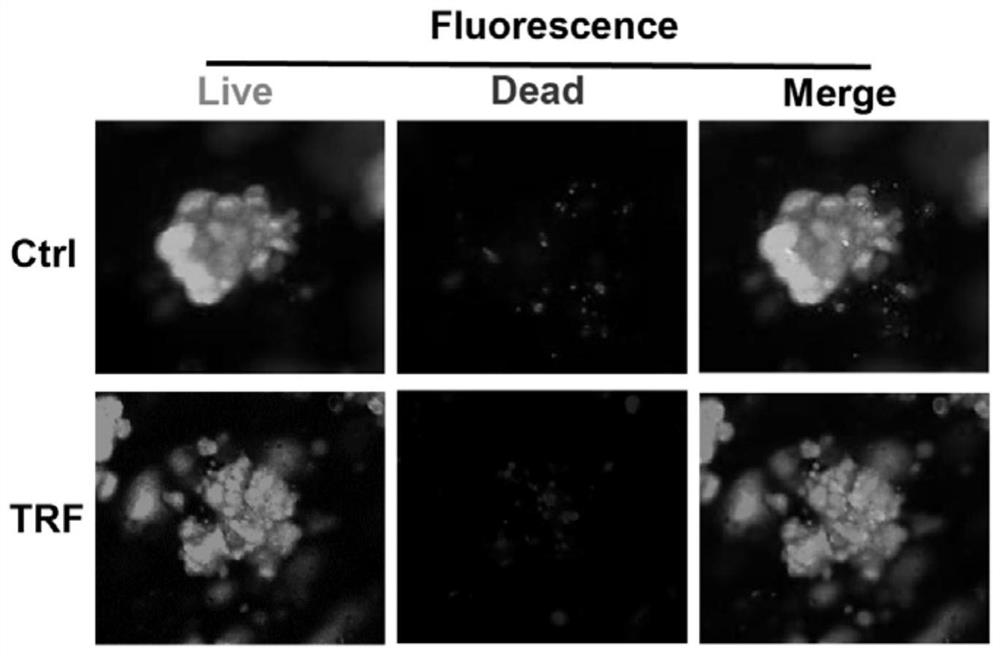
[0047] Example 3 Detection of organoid cell viability
[0048] (1) Detection of organoid viability by staining
[0049] Add 100 μL live / dead cell double staining kit (calcein-AM / ethidium bromide homodimer-1, Thermofisher Scientific) to decibels in control and nutrient-restricted group organoids and incubate at room temperature for 30 min. Fluorescence microscopy was used to capture the signal of calcein-AM to represent live cells and the signal of ethidium bromide homodimer-1 to identify dead cells.
[0050] Fluorescent staining results such as figure 2 As shown, the results showed that nutrient restriction did not affect the viability of liver cells.
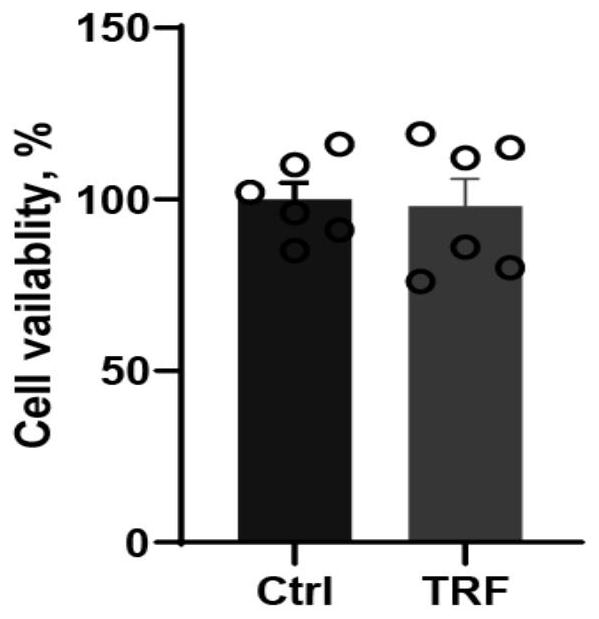
[0051] (2) Cell-Titer GLO detection of cell activity
[0052] Organoid cell viability assays were performed on the control and nutrient-restricted groups separately by adding Cell-Titer GLO reagent (Promega) and measuring luminescence on a GLOMAX microplate luminometer (Promega) according to the manufacturer's instructions....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com