Method for screening microorganisms by using supermolecular fluorescence microfluidic technology
A microfluidic technology, a microfluidic technology, is applied in the field of high-throughput screening of microorganisms by supramolecular fluorescence microfluidic technology, which can solve the problems of inability to detect metabolites, complicated labeling process, and limited application range, etc. High sensitivity, low detection cost, and simple experimental operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Analysis of tryptophan acid concentration in microfluidic droplets by supramolecular fluorescence;
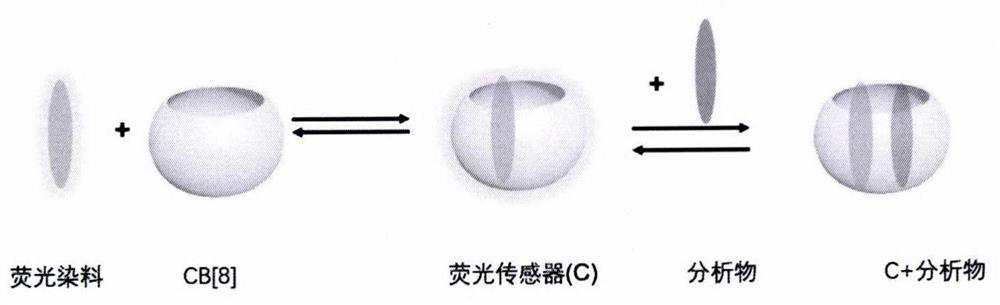
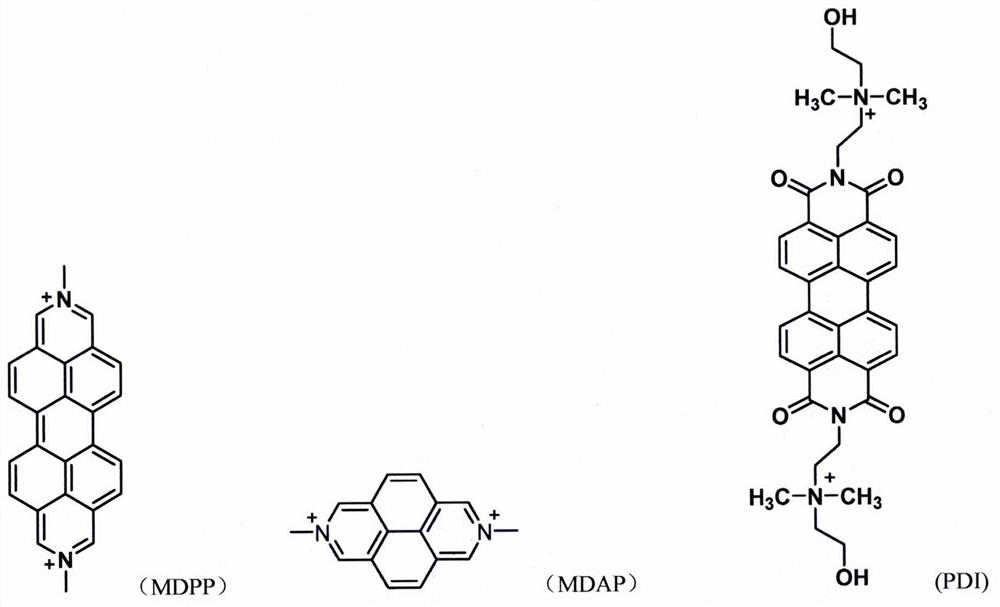
[0026] 1. Add different concentrations of tryptophan to the supramolecular fluorescent supramolecular solution of CB[8] and MDPP with a molar ratio of 1:1, and use a microplate reader to detect the fluorescence intensity of the supramolecular solution. attached by Figure 4 It can be seen that when tryptophan is added to the supramolecular fluorescence system, the fluorescence of the system decreases gradually with the addition of tryptophan. A π-π stacking occurs, resulting in a fluorescence quenching effect.
[0027] 2. Prepare three sets of solutions as aqueous phase (1): CB[8] (5 μM) and MDPP (5 μM); aqueous phase (2): CB[8] (5 μM), MDPP (5 μM) and tryptophan ( 5 μM); aqueous phase (3): CB[8] (5 μM), MDPP (5 μM) and tryptophan (10 μM). The flow rate of the aqueous phase was 1 μL / min, and the flow rate of the oil phase was 3 μL / min. Droplets were generated into a 1...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Using supramolecular fluorescence to analyze the concentration of tryptophan metabolized by Escherichia coli in microfluidic droplets;
[0030] The E. coli suspension was diluted to 10 with liquid medium 6 individual / mL. The basic components of the medium are: trace elements 0.1%, K 2 HPO 4 2.5%, KH 2 PO 4 0.9%, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 0.45%, Glucose 0.3%, MgSO 4 0.01% pH7.2. , select the cell-wrapped chip to wrap the cells with droplets, set the flow rate of the oil phase to 3 μL / min, and the flow rate of the E. coli cell diluent to 1 μL / min, and generate droplets into a 1mL syringe. The droplet diameter is 30 μm, according to the Poisson distribution , the proportion of droplets without cells was 0.6065, the proportion of droplets embedded with single cells was 0.3033, and the proportion of droplets embedded with two or more cells was 0.0902. Put the syringe into a 37°C incubator and incubate for 24 hours, inject the cucurbituril / fluorescent dye supramolecular co...
Embodiment 3
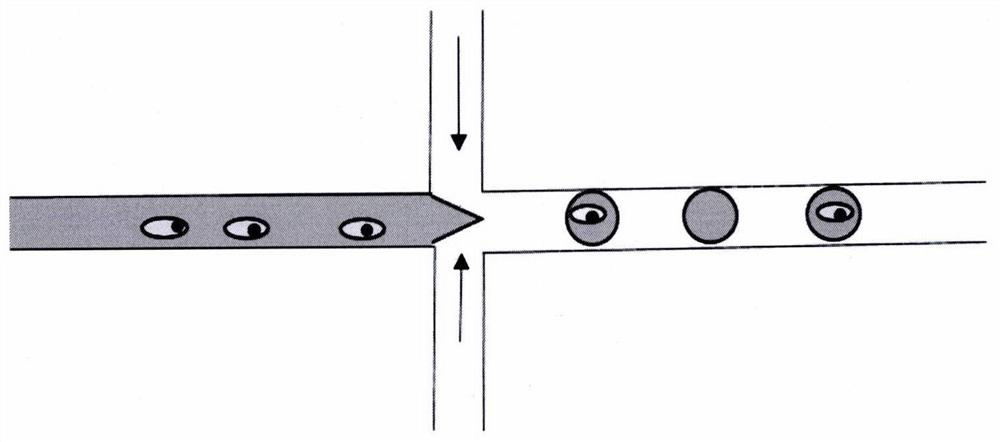
[0032] Screening of Escherichia coli with different tryptophan metabolic abilities using supramolecular fluorescent microfluidic technology;
[0033] The droplet detection chip is placed on the stage, and the position of the stage is adjusted to make the droplet detection chip image clearly on the high-speed camera. Set the droplet flow rate to 0.1μL / min, the oil phase flow rate to 2μL / min, inject the droplet into the droplet detection chip, turn on the laser, set the laser wavelength to 442nm, and the detection wavelength to 500-520nm, adjust the droplet detection chip The position aligns the laser light to the channel detection point of the droplet detection chip. Turn on the photomultiplier tube, set the trigger value of the signal analysis and processing software, the gain value of the photomultiplier tube, and the waveform diagram shows the trigger threshold and the droplet fluorescence intensity value. When the detection value of the detected target droplet exceeds the p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com