ExPEC (extraintestinal pathogenic escherichia coli) double-gene deleted strain and vaccine prepared from same
A double-gene, deletion strain technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of inconvenient immunization pathways and poor immunization effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1 Construction of ExPEC double gene deletion strain DE205BΔrelA / spoT
[0019] In the present invention, the ExPEC double-gene deletion strain DE205BΔrelA / spoT is derived from the wild-type extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli virulent strain, and the strain name is DE205B, which is isolated from ducks suffering from colibacillosis (ZhuGe X, Wang S, FanH, Pan Z, Ren J, Yi L, Meng Q, Yang X, Lu C, and Dai J.Characterization and Functional Analysis of AatB, a Novel Autotransporter Adhesin and VirulenceFactor of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli[J].Infection and Immunity.July2013 81:7 2437-2447). The present invention mainly adopts the method of Red homologous recombination to knock out the relA gene and the spoT gene in the virulent extra-intestinal Escherichia coli strain DE205B one by one to construct an ExPEC double-gene-deleted extra-intestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli.
[0020] The deleted ribosomal protein relA gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Effect of double deletion of relA and spoT genes on the pathogenicity of extra-enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli
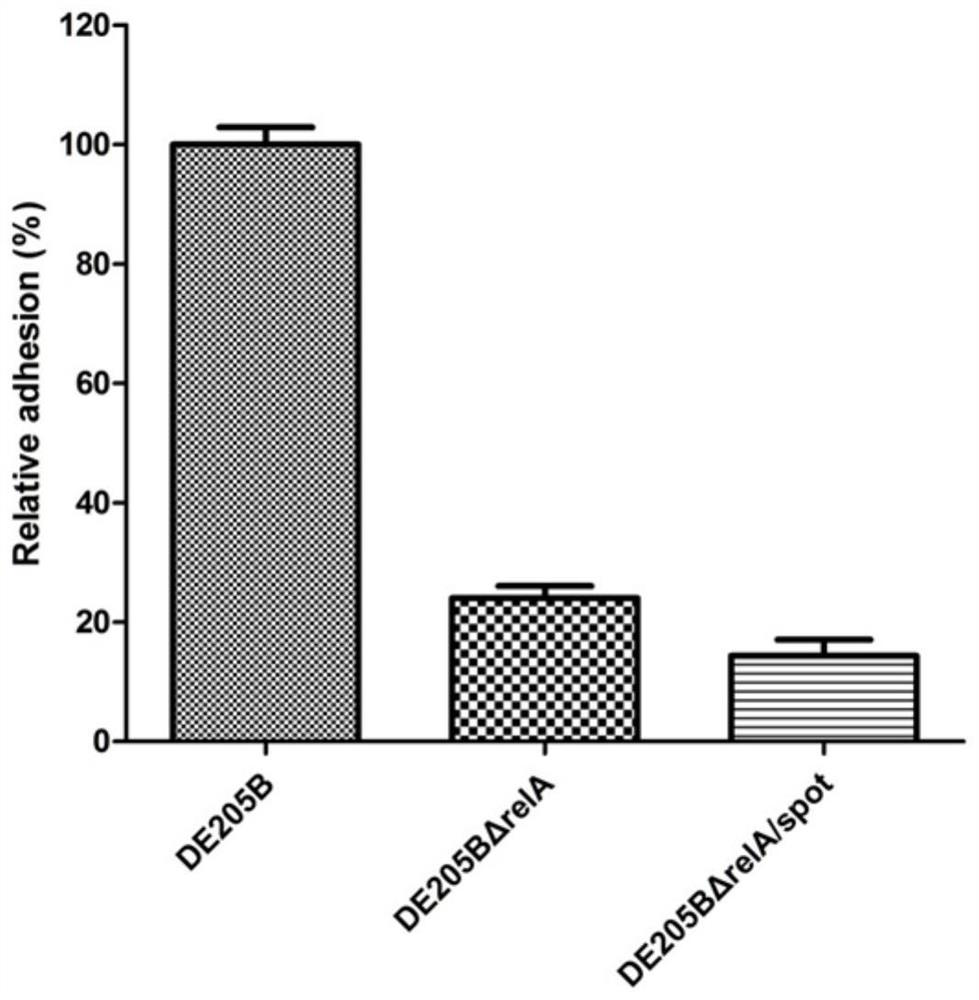
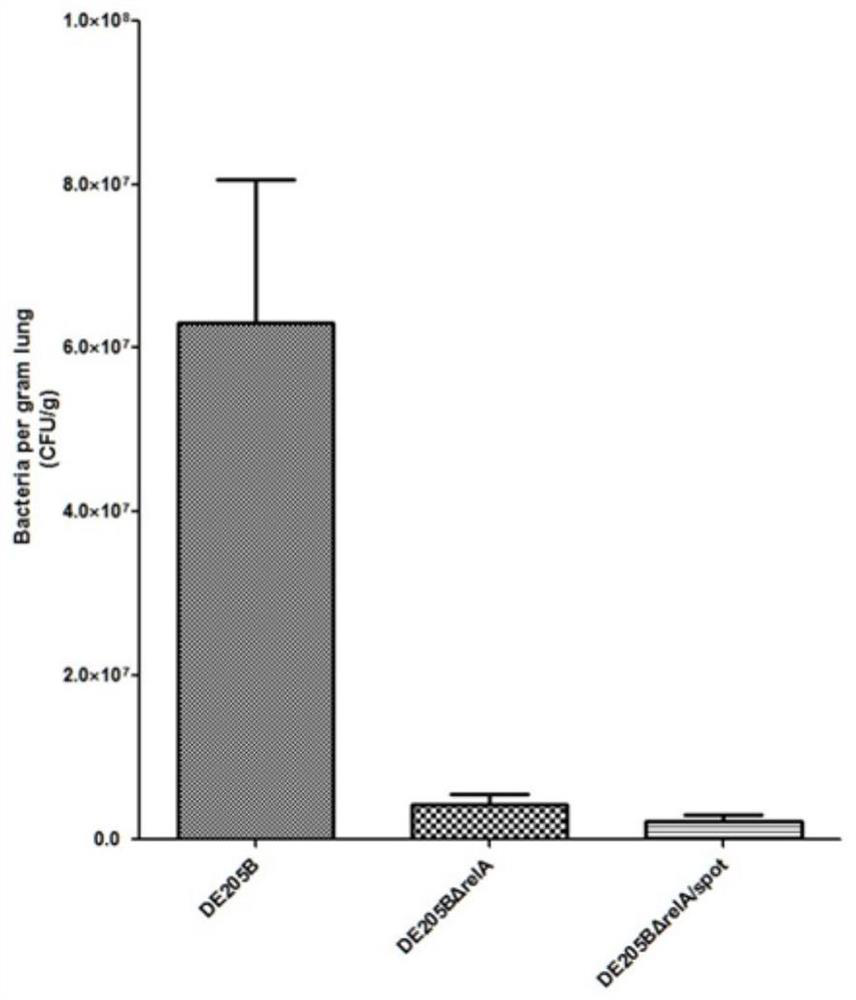
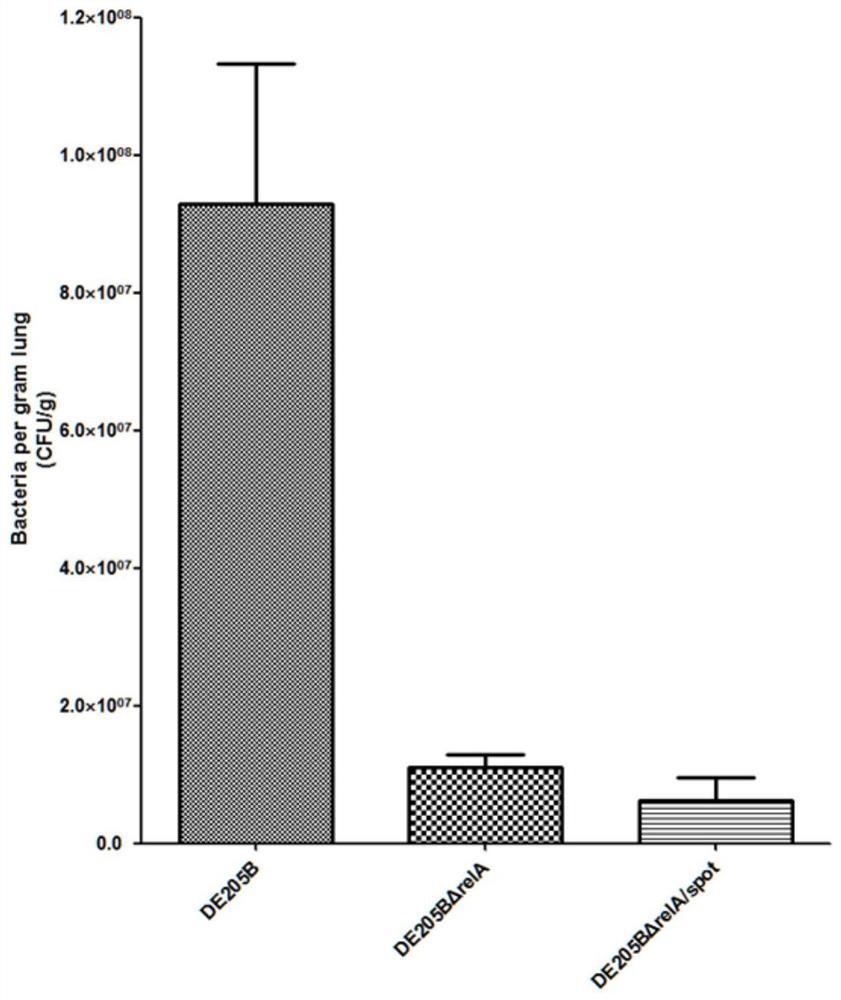
[0033] In order to verify the attenuation effect of the deletion strain of the present invention on extraintestinal pathogenic E. The effect of strain and deletion strain on the lethality of animals. And test the effect of wild strain and deletion strain on the ability to infect DF-1 cells, as well as the detection of bacterial colonization levels in various viscera when infecting chicks and ducklings. The results showed that the double deletion of relA and spoT genes significantly reduced the pathogenicity of extra-intestinal Escherichia coli, and the deletion strain DE205BΔrelA / spoT was an attenuated strain.
[0034] 1. Chick embryo lethal test
[0035] Chicken embryo lethality test was used to determine the pathogenicity of wild-type DE205B and deletion strain DE205BΔrelA / spoT. The strains were cultured to mid-late logarithmic period, wash...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3 Parenteral Pathogenic Escherichia coli Double Gene Deletion Vaccine
[0069] Identify the extra-intestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli double-gene deletion strain DE205BΔrelA / spoT, inoculate each generation on LB agar medium to observe the colony color, and use the genes of extra-intestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli to detect and identify the deletion Genetic stability of bacteria. After sub-passaging, it was found that DE205BΔrelA / spoT maintained the phenotypic characteristics of gene deletion, and the identified gene was still missing, and heredity was stable. The double-gene deletion strain DE205BΔrelA / spoT was cultured on solid medium, and a single colony was picked and cultured in liquid medium until the concentration of viable bacteria reached 5.0×10 9 CFU / mL. The preparation method of the gelatin protectant is as follows: add 40g of sucrose and 9g of gelatin to every 100mL of deionized water, fully melt, sterilize at 121°C for 30min, and store for l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com