Split gate trench power semiconductor device
A power semiconductor and split gate technology, which is applied to semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems such as the imbalance of the compromise relationship between chip on-state loss and switching loss, the adverse effects of chip turn-on and turn-off, and the increase of chip switching loss. , to reduce parasitic effects, shorten the Miller platform, and improve reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
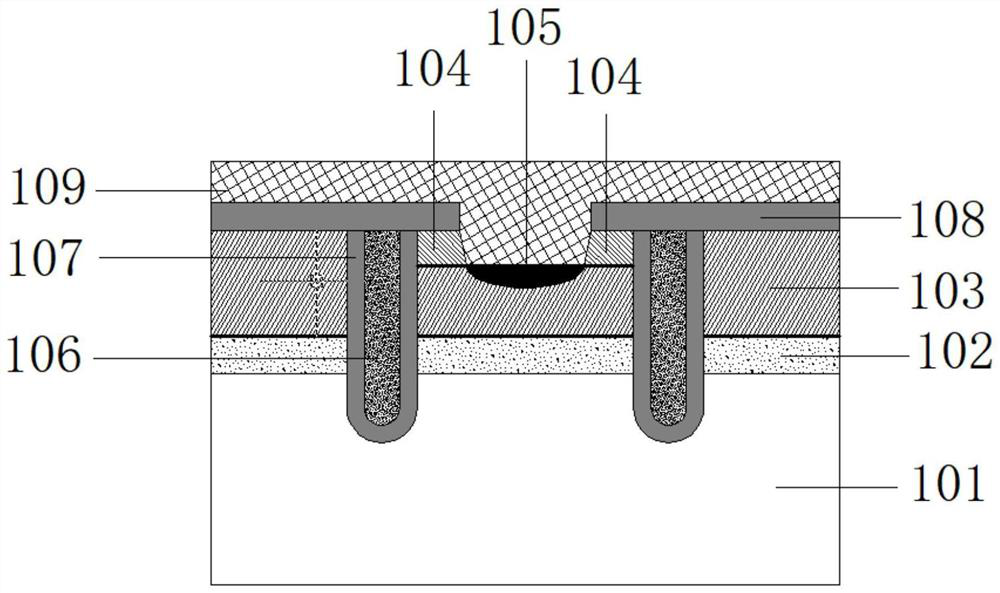
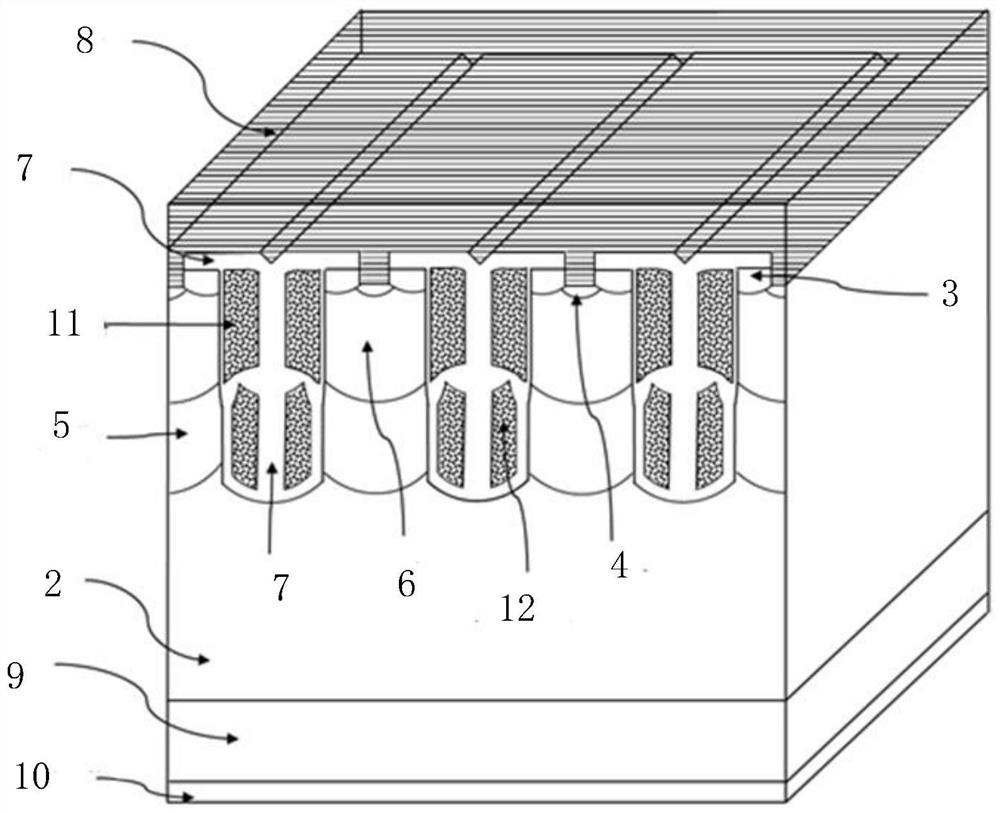
[0041] figure 2 It is a schematic structural diagram of a power semiconductor device with a split gate trench according to Embodiment 1. Such as figure 2 As shown, it may include: a semiconductor substrate 2, an N+ region 3, a P+ region 4, an N well region 5, a P well region 6, a plurality of stripe-shaped trench split polysilicon gates (including a polysilicon main gate 11, a polysilicon auxiliary gate 12 ), oxide layer 7, emitter metal layer 8, anode P region 9, and collector metal layer 10.
[0042] “Inside the surface of the semiconductor substrate 1 ” in this specification refers to a region extending downward from the surface of the semiconductor substrate 1 to a certain depth, which is a part of the semiconductor substrate 1 .
[0043] Wherein, the semiconductor substrate 2 may include semiconductor elements, such as silicon or silicon germanium of single crystal, polycrystalline or amorphous structure, or a mixed semiconductor structure, such as silicon carbide, al...
no. 2 example
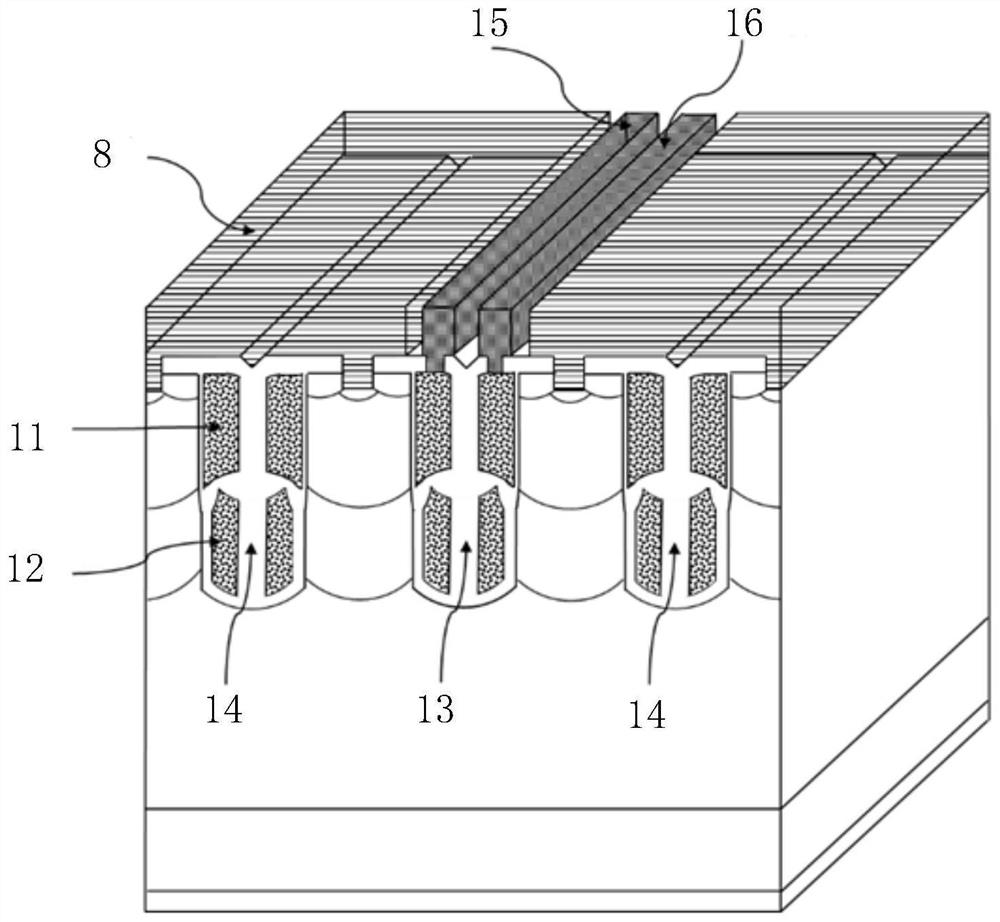
[0058] Figure 5a It is a schematic structural diagram of a split-gate power semiconductor device with floating double-split dummy gates according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, Figure 5b It is a schematic structural diagram of a split-gate power semiconductor device with double-split dummy gates grounded according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. Such as Figure 5a As shown, it may include: a semiconductor substrate 2, an N+ region 3, a P+ region 4, an N well region 5, a P well region 6, a double-split dummy gate 17 of a stripe trench (comprising a polysilicon main dummy gate 171 and a polysilicon auxiliary dummy gate 171) gate 172), the true gate 13 split by the stripe trench (including the polysilicon main gate 131 and the polysilicon auxiliary gate 132), the oxide layer 7, the emitter metal layer 7, the anode P region 9, and the collector metal layer 10. The polysilicon main dummy gate 171 is a floating structure, which can change the input and outpu...
no. 3 example
[0070] Figure 6 It is a schematic structural diagram of a double split gate power semiconductor device using an oxide layer with a uniform thickness according to another embodiment of the present invention, Figure 6 is a schematic structural diagram of a split-gate power semiconductor device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Such as Figure 6As shown, it may include: a semiconductor substrate 2, an N+ region 3, a P+ region 4, an N well region 5, a P well region 6, and a stripe-shaped trench split-type true gate 13 (including a polysilicon main gate 131 and a polysilicon auxiliary gate 132) , double-split dummy gate 18 (including polysilicon main dummy gate 181 and polysilicon auxiliary dummy gate 182 ), oxide layer 7 , emitter metal layer 8 , anode P region 9 , and collector metal layer 10 . The polysilicon main dummy gate 181 is a floating structure, which changes the input and output capacitance of the trench power semiconductor device, thereby mediatin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com