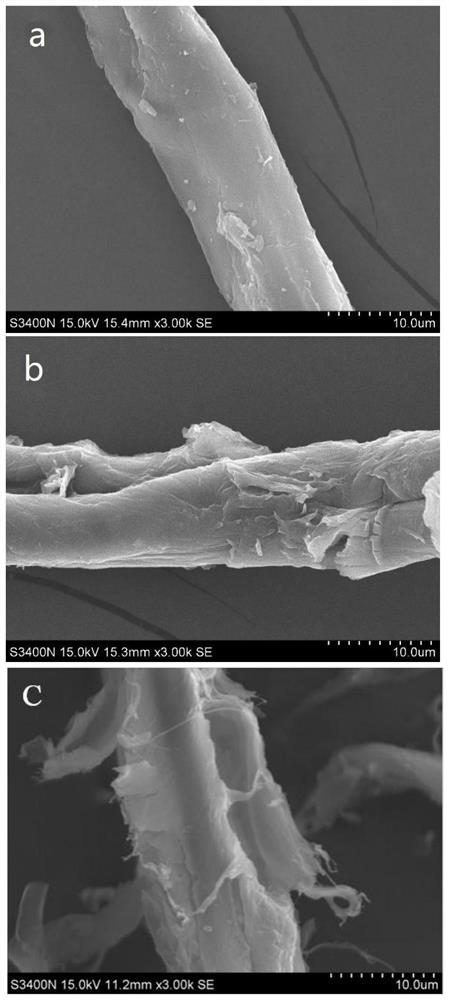
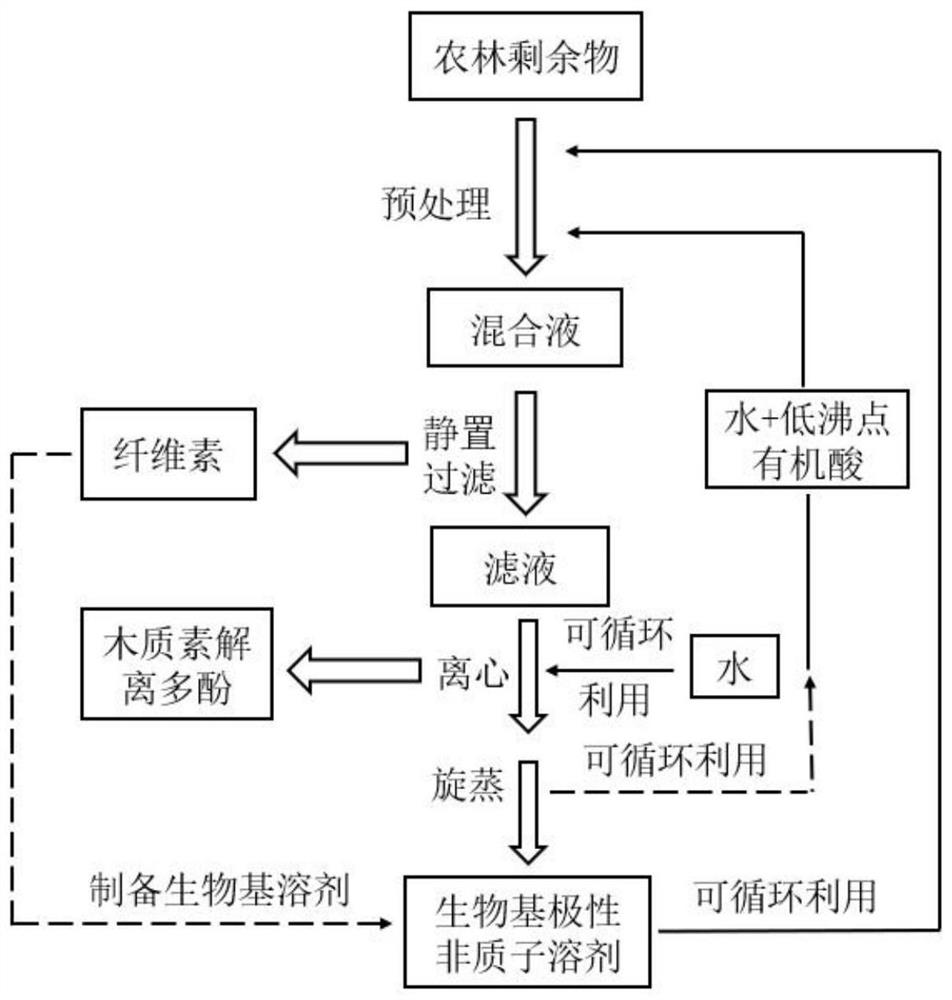
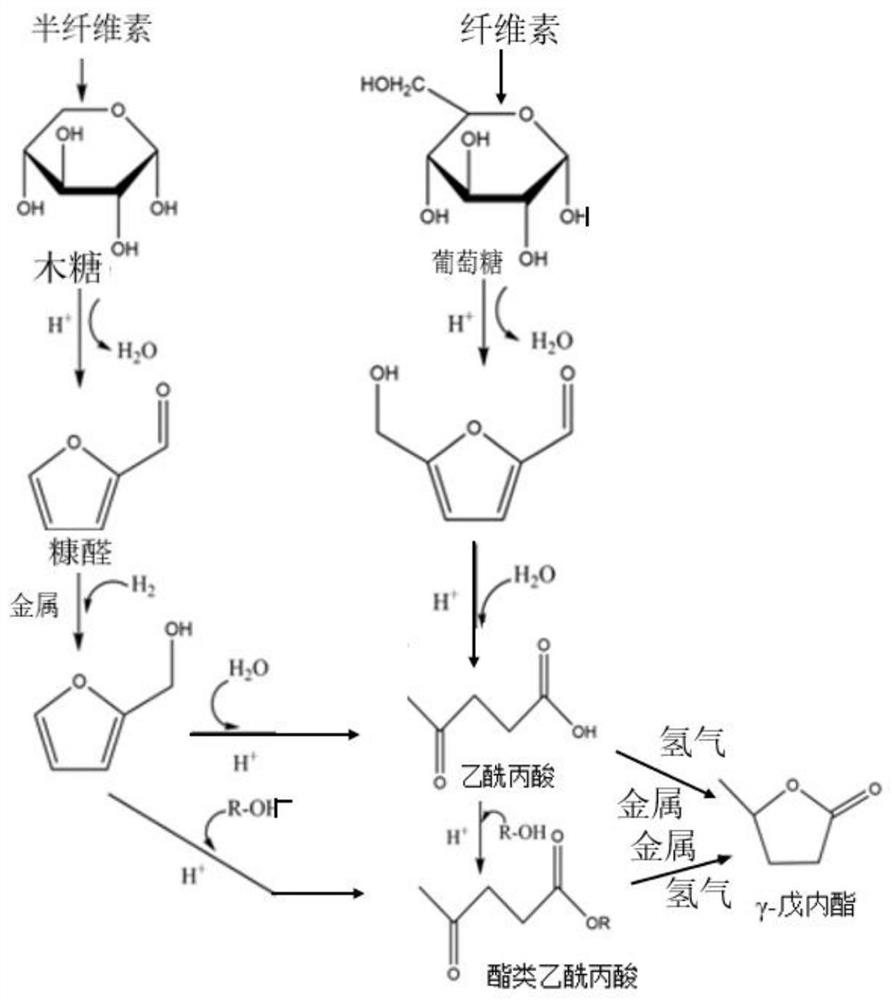
Method for pretreating wood fibers in bio-based polar aprotic solvent system
A polar aprotic, wood fiber technology, used in fiber raw material processing, fiber raw materials, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of complex reactions, complex and diverse products, difficult to separate, and non-renewable solvents.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] The first step: 10g moso bamboo harvesting and processing residues (4.5g of cellulose content, 2.62g of hemicellulose content, 2.28g of lignin content, 0.54g of moisture, 0.06g of ash content) are sieved (120 orders) by ball mill pulverization, The gamma-valerolactone / water composite solvent of gained moso bamboo powder and 100g (raw material and mixed solvent mass ratio 1:10, solvent and water mass ratio are 4:1), 2.0g p-toluenesulfonic acid (raw material and acid mass ratio The ratio is 1:0.2) and then added to the pressurized reactor after mixing.
[0054] Step 2: Raise the temperature of the reactor to 120°C, the reaction time is 60 minutes, then cool down to room temperature, stand and filter, and dry at 105°C to obtain a solid residue and weigh it, which will be used for hydrolysis and hydrogenation to prepare γ - valerolactone bio-based polar aprotic solvent;
[0055] Step 3: Take the filtrate obtained in the previous step, add a certain amount of deionized wate...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The first step: 10g moso bamboo harvesting and processing residues (4.5g of cellulose content, 2.62g of hemicellulose content, 2.28g of lignin content, 0.54g of moisture, 0.06g of ash content) are sieved (120 orders) by ball mill pulverization, The gamma-valerolactone / water composite solvent of gained moso bamboo powder and 100g (raw material and mixed solvent mass ratio 1:10, solvent and water mass ratio are 4:1), 2.0g p-toluenesulfonic acid (raw material and acid mass ratio The ratio is 1:0.2) and then added to the pressurized reactor after mixing.
[0058] Step 2: Stir and raise the temperature of the reactor to 130°C, the reaction time is 60 minutes, then cool down to room temperature, stand and filter, and dry at 105°C to obtain a solid residue and weigh it, to be used for hydrolysis and hydrogenation Preparation of γ-valerolactone bio-based polar aprotic solvent;
[0059] Step 3: Take the filtrate obtained in the previous step, add a certain amount of deionized w...
Embodiment 3
[0061] The first step: 10g moso bamboo harvesting and processing residues (4.5g of cellulose content, 2.62g of hemicellulose content, 2.28g of lignin content, 0.54g of moisture, 0.06g of ash content) are sieved (120 orders) by ball mill pulverization, The gamma-valerolactone / water composite solvent of gained moso bamboo powder and 100g (raw material and mixed solvent mass ratio 1:10, solvent and water mass ratio are 4:1), 2.0g p-toluenesulfonic acid (raw material and acid mass ratio The ratio is 1:0.2) and then added to the pressurized reactor after mixing.
[0062] Step 2: Stir and raise the temperature of the reactor to 140°C, the reaction time is 60min, then cool down to room temperature, stand and filter, and dry at 105°C to obtain a solid residue and weigh it, ready to be used for hydrolysis and hydrogenation Preparation of γ-valerolactone bio-based polar aprotic solvent;
[0063] Step 3: Take the filtrate obtained in the previous step, add a certain amount of deionized ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com