Pseudomonas compound microbial agent and application thereof in disease resistance, yield increase and quality improvement of angelica sinensis
A technology of composite microbial agent and Pseudomonas, which is applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, biocides, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to improve at the same time, and improving disease resistance without angelica growth, so as to achieve the goal of improving resistance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 Composite microbial bacterial agent related enzyme activity detection
[0038] Inoculate the above-mentioned bacteria into 20mL PDB medium respectively, shake culture (30°C, 180r / min) for 24 hours; collect the bacteria by centrifugation at 5000r / min, resuspend the bacteria with sterilized distilled water until the turbidity of the bacteria solution is about 1 , add 1mL of the corresponding enzyme extract in the kit to a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, and add 100μL of the bacteria solution to be tested, break up the bacteria by ultrasonication in an ice bath (power 200W), ultrasonication for 3s, with an interval of 10s, and repeat 30 times; the ultrasonicated bacteria Centrifuge the solution for 10 min (4°C, 9000r / min), draw the supernatant into a new centrifuge tube, and put it on ice for testing; measure the enzyme activity according to the method described in the corresponding assay kit, and divide the calculated results by the corresponding Turbidity of bacterial s...
Embodiment 2
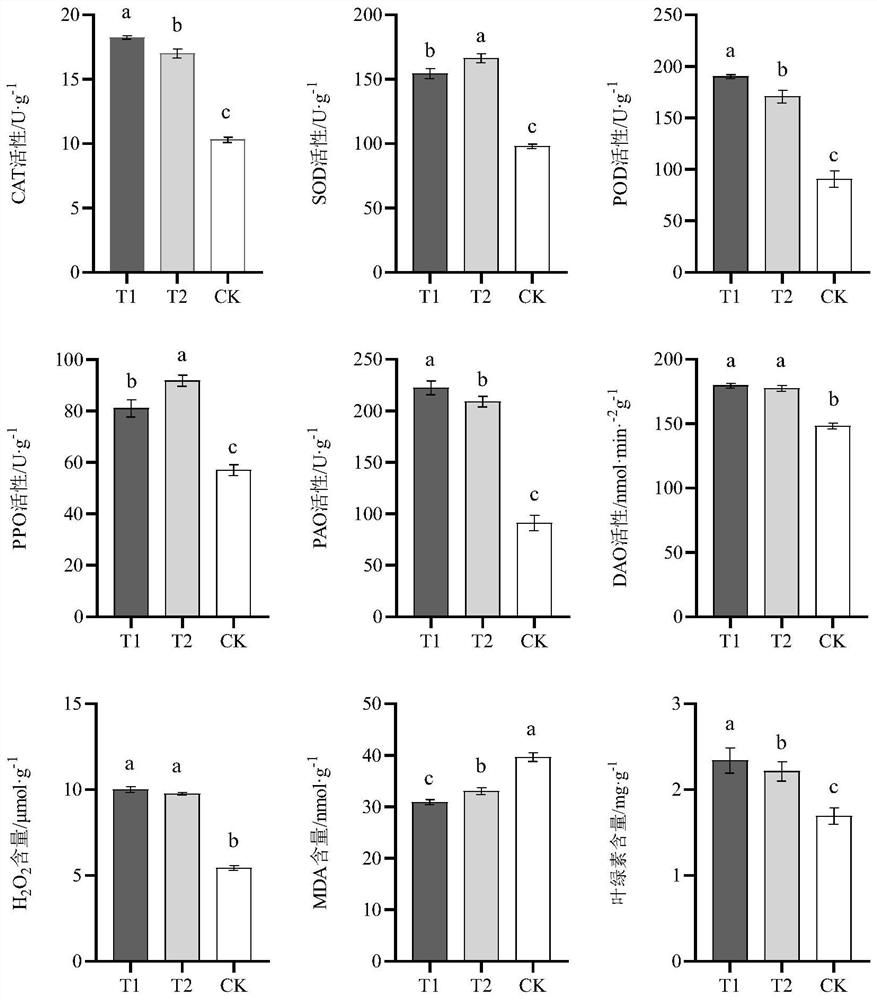
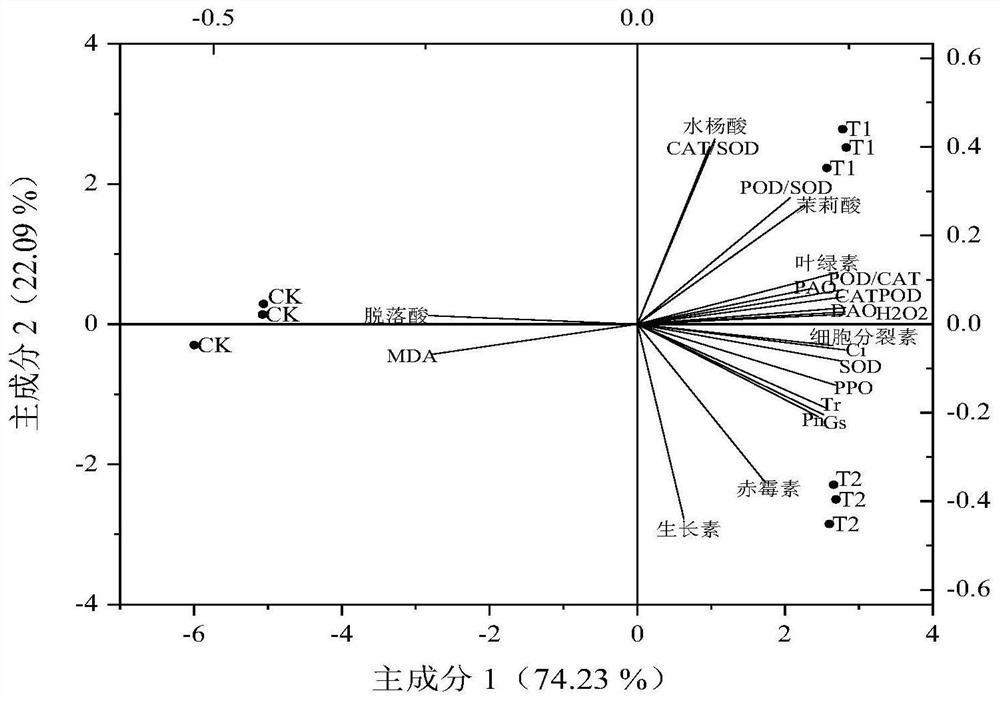
[0042] Example 2 Effects of Different Inoculum Treatment on Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Angelica Sinensis Leaf
[0043] According to the method described in the kit, the chlorophyll, MDA, H 2 o 2 Content, SOD, POD, CAT, PAO, DAO, PPO activity. Each sample was repeated 3 times and the average value was calculated.
[0044] The result is as figure 1 Shown, compound microbial agent T1 of the present invention, positive control group Bacillus compound bacterial agent T2 all significantly improved the activity of CAT, SOD, POD, PAO, DAO, PPO in Angelica blade compared with negative control group CK, and H 2 o 2 , chlorophyll content, significantly reduced the malondialdehyde content (P<0.05) in the leaves, and both treatments have played a better stress protection effect; compared with the positive control group Bacillus composite bacterial agent T2, the present invention After the compound microbial agent T1 treatment, the activities of CAT, POD, PAO and...
Embodiment 3
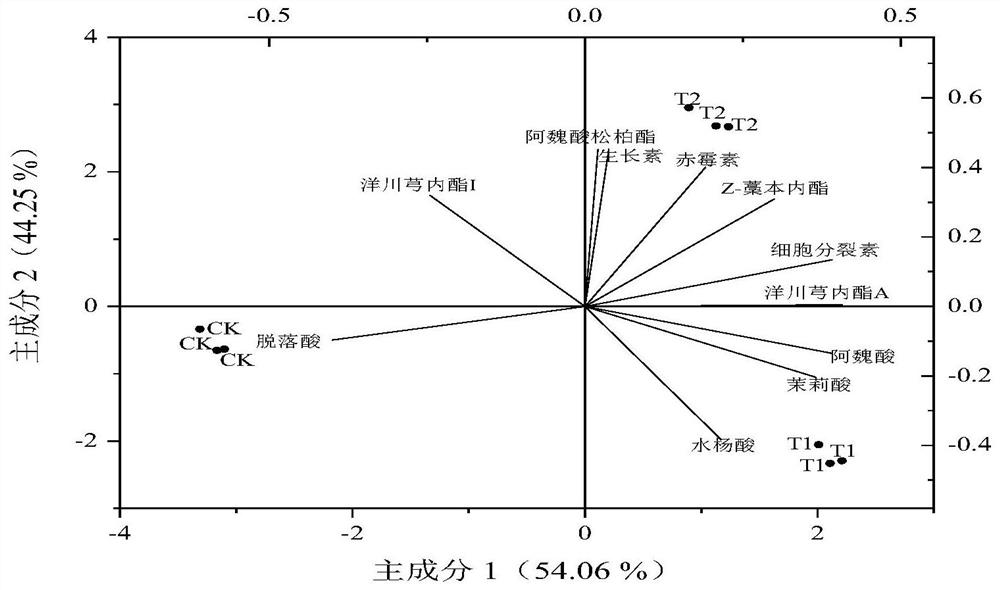
[0045] The influence of embodiment 3 different treatments on Angelica sinensis endogenous hormone
[0046] According to the method reported in the literature "Effects of Nano-iron and Melatonin on the Yield and Quality of Gansu Fritillaria Under Domesticated Cultivation Conditions" (Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulas, 2021), UPLC-MS was used to determine the contents of different endogenous hormones in the leaves of Angelica sinensis, Each sample was repeated 3 times and the average value was calculated.
[0047] The result is as shown in table 2, except salicylic acid, auxin, gibberellin, composite microbial agent T1 of the present invention, positive control group Bacillus composite bacterial agent T2 are more than negative control group CK, other hormone two All showed a consistent trend of change, significantly increasing the content of jasmonic acid, which increased by 257.91% and 99.94% respectively; reducing the content of abscisic acid, which decreased by 64.69% ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com