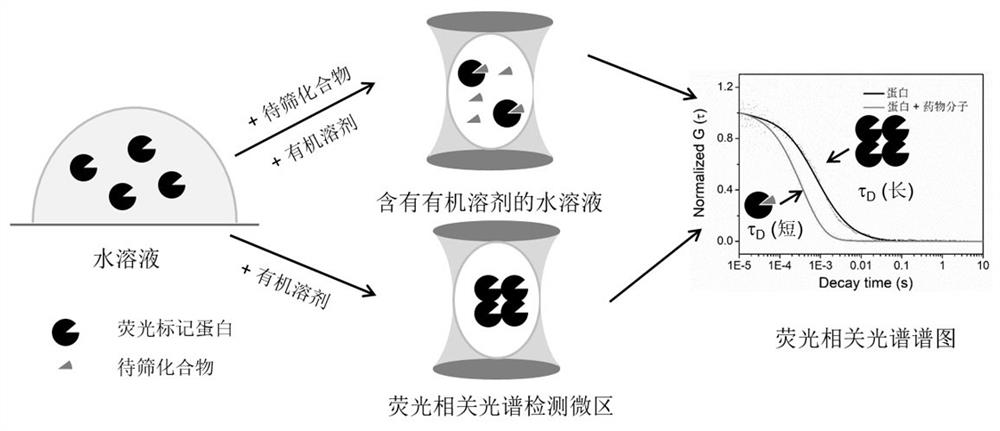
A Drug Screening Method Based on Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy to Detect Protein Aggregation Induced by Organic Solvents
A technology related to organic solvents and fluorescence, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of poor curative effect correlation, complex system, and long time consumption, and achieve the effect of less sample consumption, simplified test steps, and high repetition times
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Aggregation of β-amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE-1) in different organic solvents and drug inhibition of aggregation
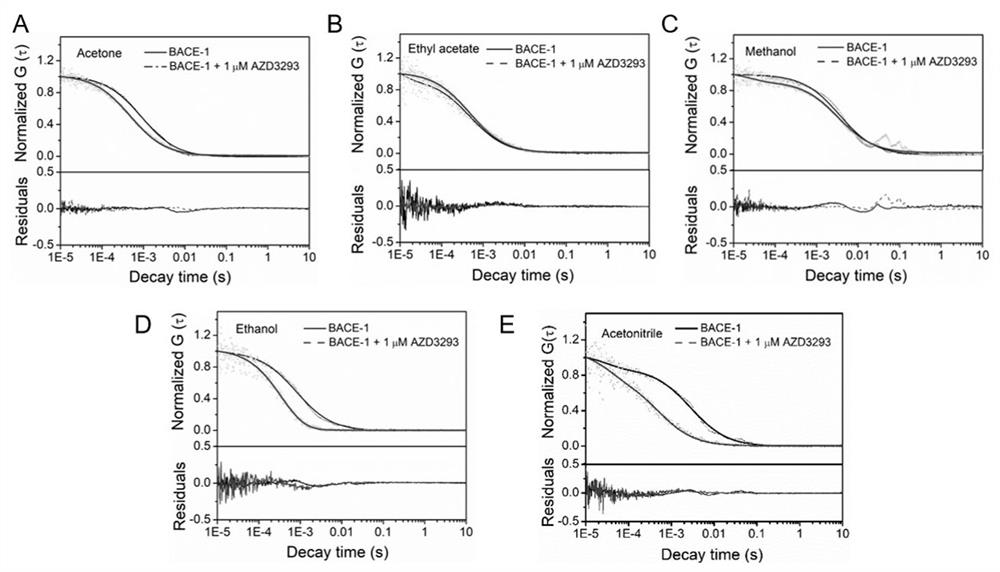
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, when an organic solvent is added to the solution, it will induce aggregation of the fluorescently labeled protein. Add the drug molecule to the fluorescently labeled protein solution, and then add the organic solvent. Due to the interaction between the drug molecule and the protein, the aggregation of the protein will be inhibited. The application of fluorescence correlation spectroscopy can monitor the characteristic diffusion time of proteins in different aggregation states, so as to monitor the strength of interaction between different drug molecules and proteins. Different organic solvents have different effects on protein aggregation. Such as figure 2 As shown, we used five organic solvents methanol, ethanol, acetonitrile, acetone and ethyl acetate, and found that when different or...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: Application of a Drug Screening Model of Beta-Amyloid Precursor Protein Cleaving Enzyme 1 (BACE-1) Inhibitor
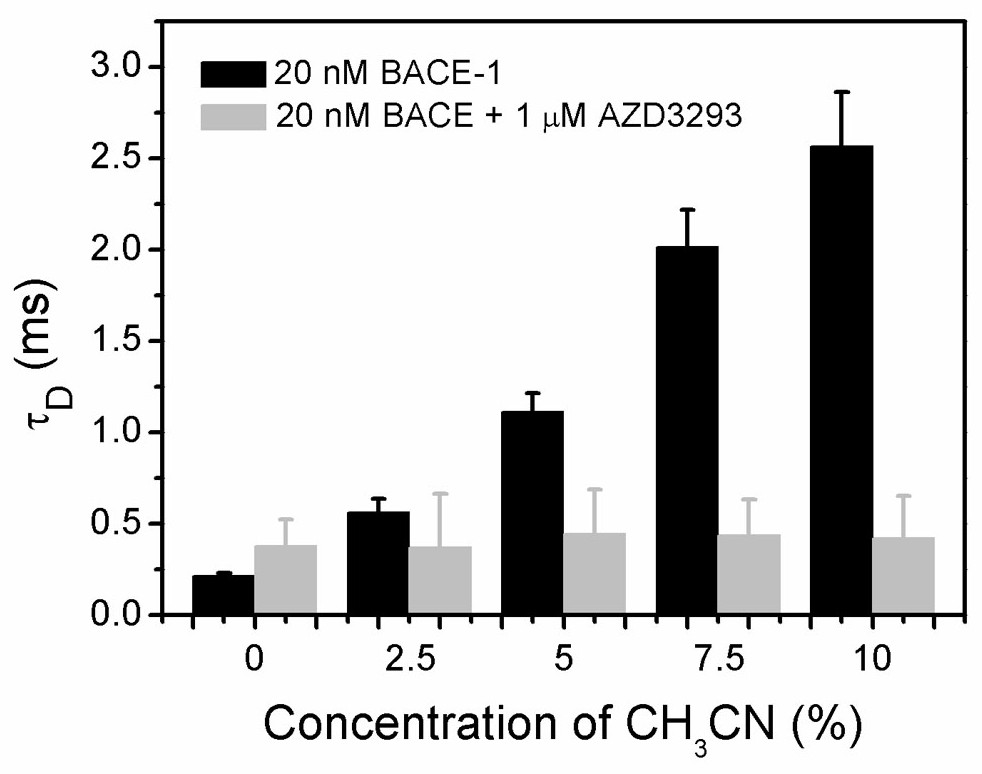
[0037] We used fluorescence correlation spectroscopy to study the inhibitory effect of different concentrations of the drug AZD3293 on the aggregation of BACE-1 protein in organic solvents, so as to evaluate the strength of the interaction between the drug and BACE-1 protein. By monitoring the characteristic diffusion time of protein molecules labeled with fluorescent dyes, information on the strength of interactions between different drug molecules and protein molecules can be obtained. The concentration of BODIPY-labeled BACE-1 was 20 nM, and the concentration of drug AZD3293 increased from 10 -12 increased to 10 -4 mol / L, the characteristic diffusion time of BACE-1 gradually decreased, indicating that the drug AZD3293 had a strong interaction with BACE-1, effectively inhibiting the aggregation of BACE-1 protein in organic solvents. We further st...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: A drug screening model for fluorescent protein EGFR-labeled dihydroreductase
[0039] We studied the inhibitor MTX's inhibitory effect on the aggregation of fluorescent protein EGFR-labeled dihydrofolate reductase in organic solvents by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, so as to evaluate the strength of the drug's interaction with dihydrofolate reductase. We first constructed a plasmid, expressed the fluorescent protein EGFR-tagged dihydrofolate reductase by culturing Escherichia coli, and then purified the protein through a nickel column. We investigated the effect of the concentration of acetonitrile on the aggregation of fluorescent protein EGFR-labeled dihydrofolate reductase with and without drug addition. Such as Figure 6 As shown, when the concentration of acetonitrile is 10%, the characteristic diffusion time difference of the dihydrofolate reductase labeled with fluorescent protein EGFR before and after the action of the drug MTX is the larges...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com