Laccase-producing Coriolopsis gallica NCULAC F1 and method for preparing high-activity laccase liquid
A high-activity, coarse-haired technology, applied in the field of microbial enzymology, can solve the problem of low enzyme activity, and achieve the effect of high extracellular laccase activity, good application value, and high tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
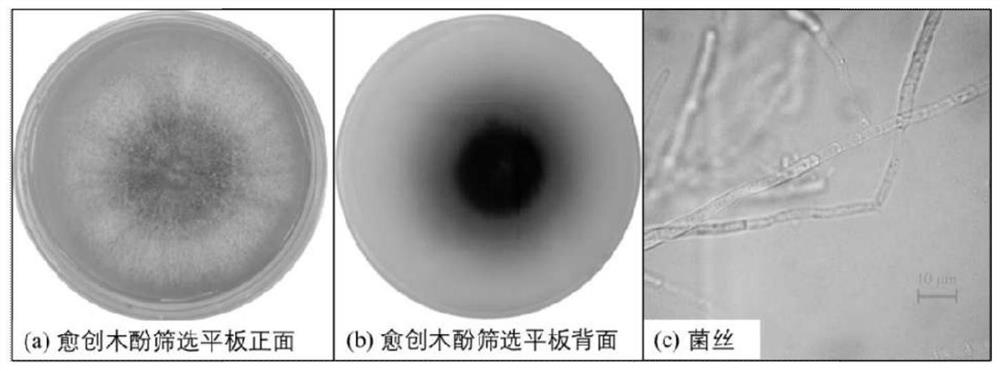
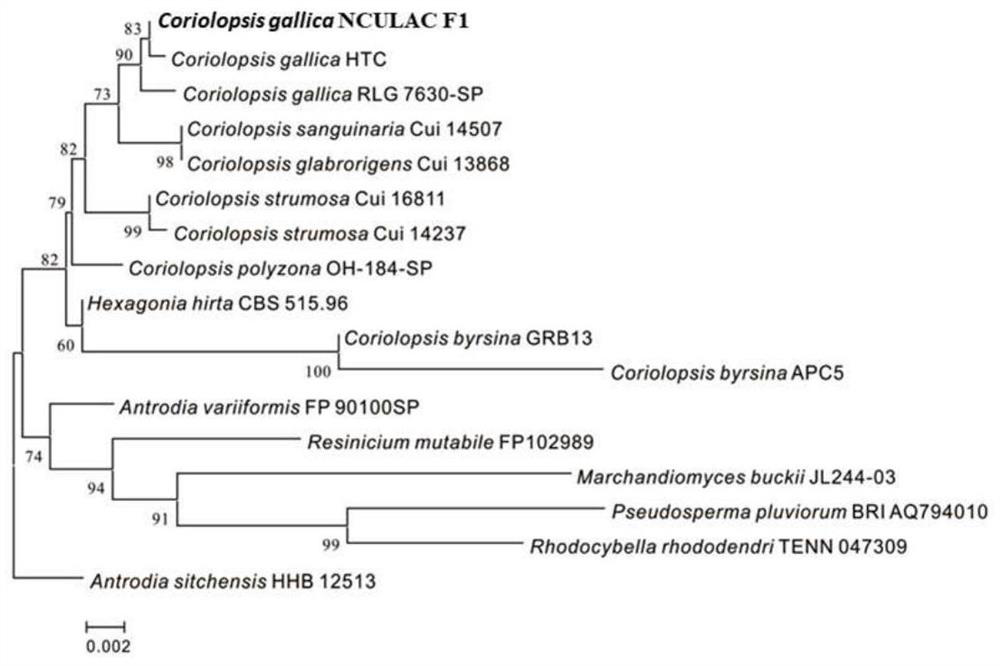
[0019] Example 1 Laccase-producing strain screening and identification
[0020] The decayed wood samples were collected in Nanchang, Jiangxi. Weighed 10g of the decayed wood samples and placed them in 100mL of sterile water containing 5 glass beads, shaken on a shaker for 20min, and diluted 10mL of the sample solution to 10 -1 、10 -2 、10 -3 . Make 5 parallels for each dilution, respectively take 100 μL of the dilution to a PDA solid plate containing 0.04% (v / v) guaiacol, spread it evenly with a coating rod, and place the plate upside down in a 28°C incubator Culture 7d. Pick reddish-brown colonies for plate streaking until pure colonies are obtained.
[0021] According to the size and color depth of the color circle, three strains of laccase-producing fungi were screened out, among which the reddish-brown color around the colony of strain NCULAC F1 was the deepest. It was judged that the strain NCULAC F1 had a strong ability to produce laccase, and it was preserved on the ...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2 Production of high-activity laccase by liquid fermentation of Inonotus roughae NCULAC F1
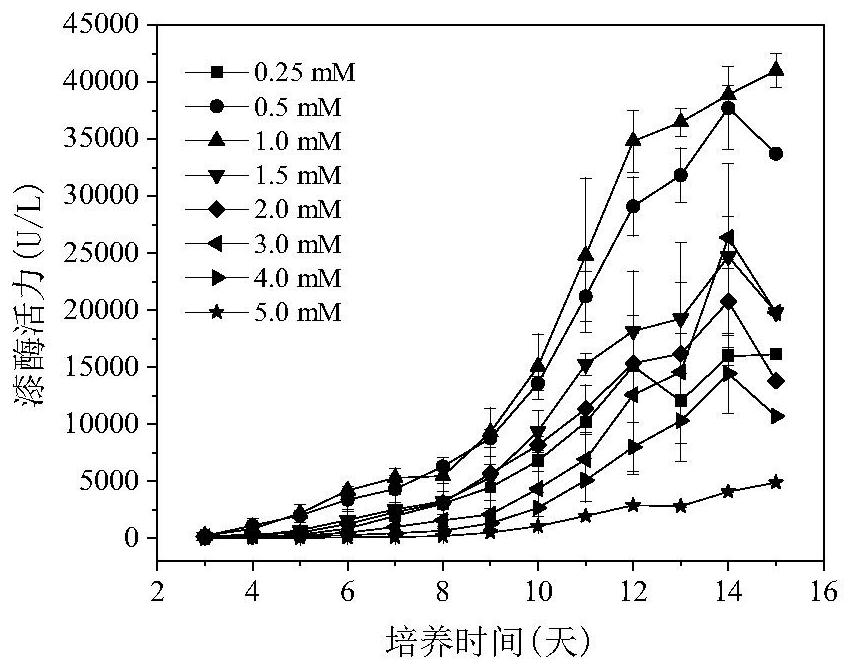
[0023] Prepare PDA liquid medium, add 100mL medium to each 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, add copper sulfate at a final concentration of 0.25-5.0mM, and investigate the effect of copper sulfate addition on the expression of extracellular laccase in Inonotus pilosa NCULAC F1.
[0024] Inoculate the mycelial suspension of Inonotus crescens NCULAC F1 into PDA liquid medium according to the inoculum amount of 5% (v / v), and culture it in shake flask at 30° C. and 120 rpm for 15 days. From the third day of cultivation, 1 mL of fermentation broth was taken every day, centrifuged at 4°C and 6000 rpm for 3 min, and the supernatant was taken to measure laccase activity.
[0025] Laccase activity was determined using ABTS as the catalytic substrate. The 3mL total reaction system consisted of 2mL citric acid-disodium hydrogen phosphate buffer (0.1M, pH 4.5), 0.9mL ABTS (1mM) and 0.1mL enzy...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3 Effects of Temperature and pH on the Activity and Stability of Inonotus pilosa NCULAC F1 Laccase
[0030]1. Effects of temperature on the activity and stability of laccase from Inonotus pilosa NCULAC F1
[0031] Place the laccase solution at 30-80°C for 5 minutes to incubate the activity of the laccase of Inonotus roughans, set the maximum enzyme activity as 100%, and calculate the relative enzyme activities at these temperatures to determine The optimum reaction temperature of laccase. Three parallels were performed in each group, and the average value was taken. Place the laccase solution in water baths at different temperatures (40, 50, 60, 70°C) for 5 hours, measure the remaining laccase activity every 1 hour, set the initial enzyme activity as 100%, and explore the laccase activity at different temperatures. down stability.
[0032] The results of the influence of temperature on the activity of NCULAC F1 laccase from Inonotus roughae are as follows: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com