Active welding flux suitable for ferritic stainless steel argon tungsten-arc welding base metal self-melting welding process
A technology of argon tungsten arc welding and active flux, which is applied in the direction of welding/welding/cutting articles, welding equipment, welding accessories, etc., and can solve problems such as coarse grains, small proportion of equiaxed crystals, and developed columnar crystals in the welding joint area , to achieve the effects of good weld formation, grain refinement, and central equiaxed grain ratio increase
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] This embodiment provides an active flux suitable for the self-melting welding process of ferritic stainless steel tungsten argon arc welding base metal, including the following components by mass percentage:
[0035]
[0036] In this example, a weld bead is formed by self-fluxing welding on the surface of a ferritic stainless steel plate to verify the influence of active flux on the weld formation and microstructure of ferritic stainless steel.
[0037] Before welding, mix and stir it with an appropriate amount of absolute ethanol, prepare a suspension close to the paste shape, apply it to the metal surface to be welded with a brush, and weld after the ethanol is completely volatilized.
[0038] The stainless steel plate used is SUS441 ultra-pure ferritic stainless steel with a thickness of 5 mm. The welding process parameters are shown in Table 1. The shielding gas is 99.99% pure argon, the diameter of the tungsten electrode is 1.6 mm, and the polarity of the power s...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The test conditions in this embodiment are the same as those in Example 1. The stainless steel plate used in the test still uses SUS441 ultra-pure ferritic stainless steel with a thickness of 5 mm. The difference is that the active flux is added with a mass fraction of 33% of the total flux. TiC powder to obtain a finer-grained weld structure.
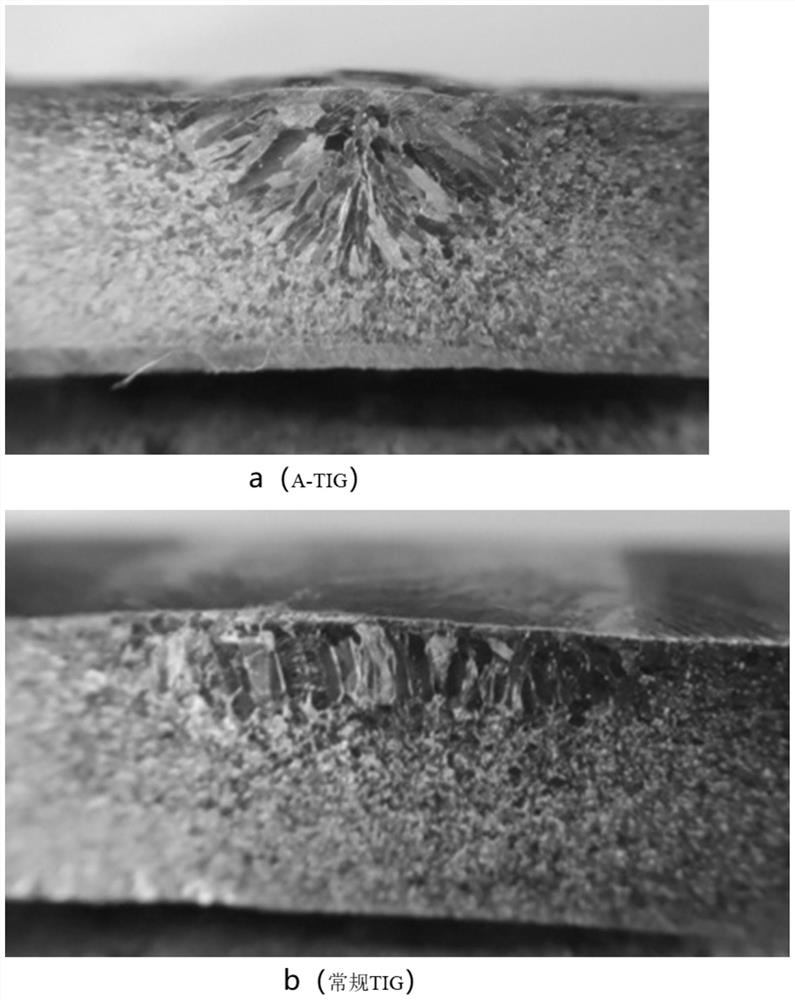
[0047] The shape and low-magnification results of the obtained weld are as follows figure 2 shown, with figure 1 (a) For comparison, the weld penetration and aspect ratio are reduced, but the overall shape is still better than that obtained by ordinary TIG welding.
[0048] This is due to the addition of TiC powder with better electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, the compression effect of the active flux on the arc is weakened, but because the active flux has the effect of increasing the Malagonese flow in the molten pool, it helps to compress the arc. TiC powder is fully dissolved in the molten pool, and these p...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The flux formulation used in this example is the same as that in Example 1, no TiC powder is added, absolute ethanol is also used as a solvent, and the welding process parameters used are also the same as those in Example 1. The difference is that the stainless steel plate used in the test is 409L (00Cr11Ti) ferritic stainless steel with a thickness of 1.5mm, the welding process parameters are welding current 120A, welding speed 400mm / min, and shielding gas flow rate 10L / min. As a comparison, a conventional TIG welding test was carried out using the same process.
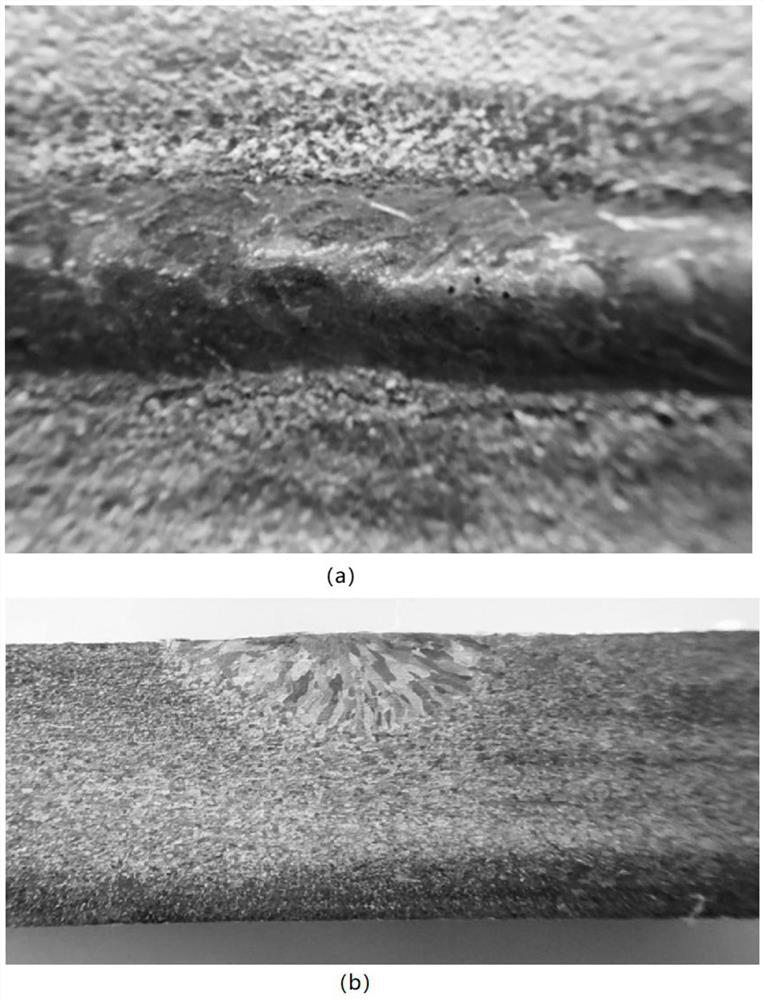
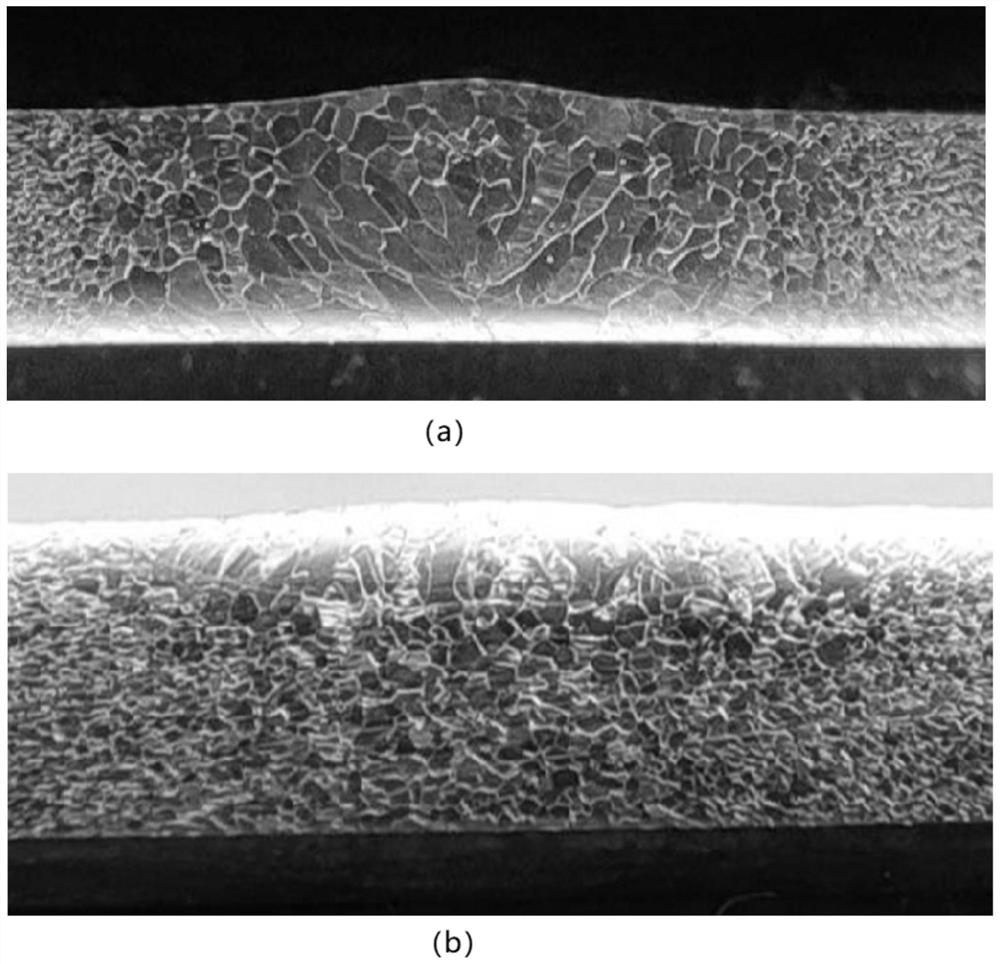
[0052] The low-magnification structure of the obtained welded joint is as follows image 3 As shown, due to the small thickness of the plate, both samples obtained fully penetrated welds.
[0053] The weld obtained by conventional TIG welding has coarse columnar grains, and the width of the weld and HAZ is relatively large; while the grain coarsening of the weld obtained by A-TIG has been significantly suppr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com