Low-temperature preservation diluent for semen of plectropomus leopardus, preservation method and application
A low-temperature preservation technology for leopard echinacea, which is applied in the field of low-temperature preservation diluent for leopard echinacea semen, can solve the problems of reduced viability, easy change of sperm external morphological structure, and impact on storage time, and achieves high-efficiency preservation, Improve the fertilization rate and hatching rate, and the effect of easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
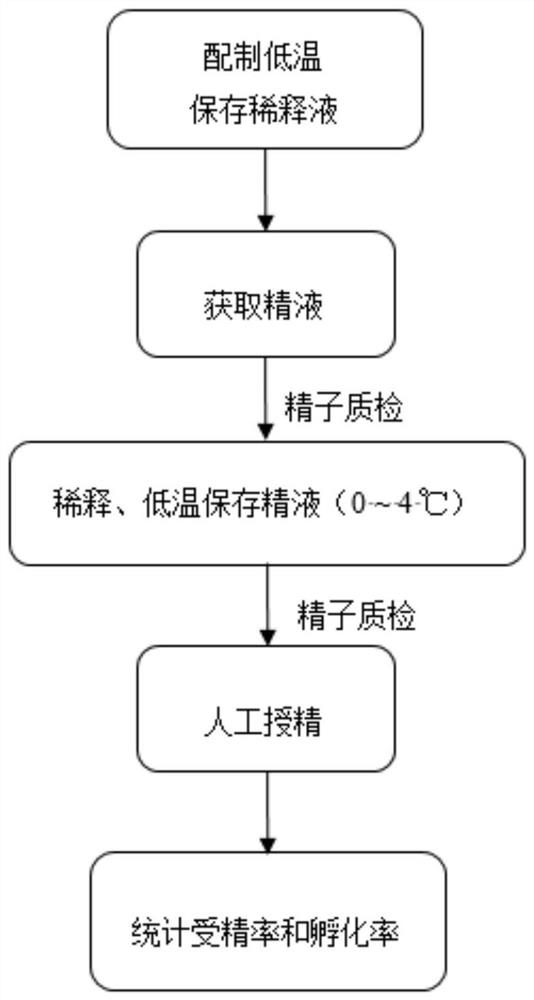
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1 Leopard Gillfish Semen Low Temperature Preservation Diluent Preparation
[0028] 1. Weigh 3.5g of sodium chloride, 1.68g of sodium bicarbonate, 2g of potassium chloride, 2g of reduced glutathione, and 0.44g of glucose with an analytical balance. Dilute to 0.9L in ultrapure water for 30 minutes to obtain a basic dilution, and store at 4°C for later use, preferably no longer than 7 days.
[0029] 2. Before use, take out the fetal bovine serum at -20°C and pipette 0.1L into the basic diluent after it is completely dissolved to obtain a low-temperature preservation diluent.
Embodiment 2
[0030] The collection and dilution of embodiment 2 semen
[0031] 1. During the breeding season, select 20 leopard-print echinacea males that have undergone nutritional fortification, good growth, and mature testes. After eugenol anesthesia, dry the area around the cloaca with a dry towel, and extend the head of the fish to the cloaca. Press the abdomen, and after the milky white, clean and pollution-free semen flows out, use a 200 μL pipette gun to suck it up immediately, and gently inject it into the bottom of a 5mL sterile EP tube without any liquid, and transfer the collected leopard gillfish semen Treatments were pooled to eliminate inter-individual differences.
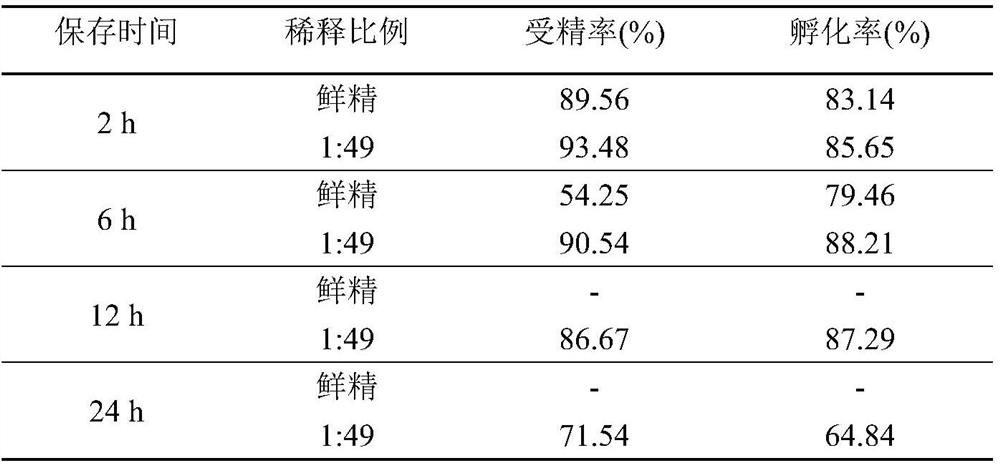
[0032] 2. Dilute the semen and the low-temperature preservation diluent prepared in Example 1 at a ratio of 1:9, 1:29, 1:49, 1:69, and 1:99 and put them into a 5mL sterile EP tube. This is the experimental group. The total volume of each diluted semen was 2.1 mL. The remaining fresh semen without any reagent w...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3 Detection of sperm motility
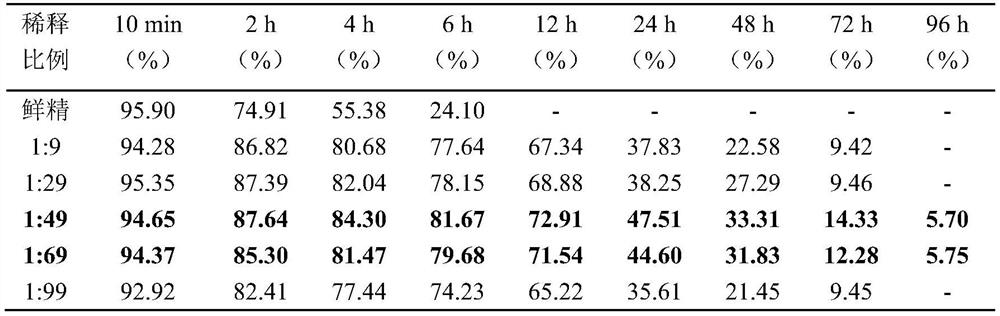
[0035] 1. Vitality detection of fresh semen: According to the fresh semen collected in step 2 in Example 2, 10min, 2h, 4h, 6h, 12h, 24h, 48h, 72h, 96h after taking out the parental male fish, the specific operation for each detection The steps are as follows: Add 99 μL of the diluent for cryopreservation of leopard gillfish semen to the 200 μL EP tube with a 200 μL pipette gun, draw 1 μL of fresh semen with a 2.5 μL pipette gun and gently blow and mix; draw 1 μL of the mixed solution on the Slide, adjust the focus until the image on the display screen is clear, add 2 μL of filtered natural seawater to activate the sperm, that is, after the final semen is diluted 300 times, use the sperm motility detection system (CASA) to detect the motility of the sperm, and mainly record the motility rate.
[0036] 2. Detection of different dilution ratios of semen:
[0037] (1) When the semen with a dilution ratio of 1:9 (diluted 10 times) pre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com