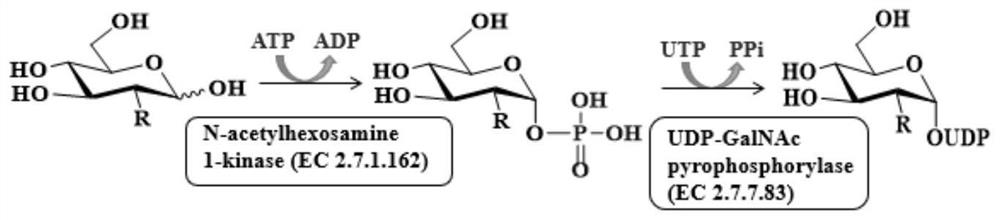
Double-enzyme co-immobilization synthesis method of uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine and derivatives thereof
A technology of glucose derivatives and uridine diphosphate, which is applied in the field of biosynthesis, can solve the problems of inability to reuse enzymes, difficult control of intermediate products, and low yield of products, so as to improve pH tolerance and thermal stability , process environmental protection, the effect of simple steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
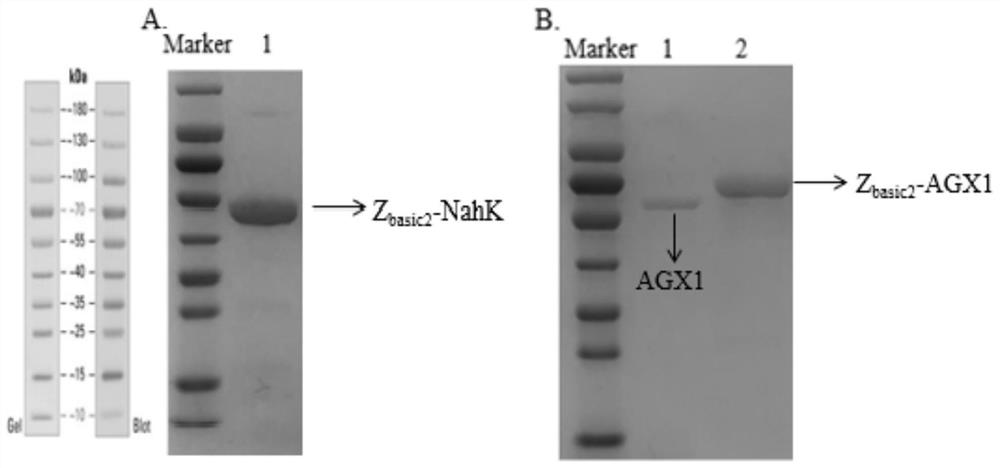
[0102] Example 1. Recombinant E. coli Z basic2 -NahK and Z basic2 -Expression of AGX1 with immobilization alone
[0103] 1. N-acetylhexosamine-1-kinase gene Z basic2 -NahK and UDP-GalNAc pyrophosphorylase gene Z basic2 -AGX1 is the target gene, and pET-21a(+) is used as the vector plasmid to construct the recombinant plasmid Z basic2 -NahK and Z basic2 -AGX1 and then recombinant plasmid Z respectively basic2 -NahK and Z basic2 -AGX1 was transformed into Escherichia coli E.coliBL21(DE3) to obtain the gene Z containing N-acetylhexosamine-1-kinase basic2 -NahK recombinant E. coli and containing UDP-GalNAc pyrophosphorylase gene Z basic2 - AGX1 recombinant E. coli. The construction of the above recombinant bacteria was completed by Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0104] The N-acetylhexosamine-1-kinase gene Z basic2 - The GenBank accession number of NahK is 69578838, and the GenBank accession number of the UDP-GalNAc pyrophosphorylase gene AGX1 is 6675.
[01...
Embodiment 3
[0112] Example 3. Individually immobilized Z basic2 -NahK immobilization preparation and Z basic2 - Catalytic reaction of AGX1 immobilized preparations
[0113] 1) Z basic2 - Determination of catalytic reaction activity of NahK immobilized preparations
[0114] Z prepared in Example 1 basic2 -NahK immobilized preparation was added to the reaction system. The reaction system was shown in Table 3. After reacting at 37°C and 1000 rpm / min for 1 h, the reaction was terminated by boiling for 5 min, and centrifuged at 6000 rpm / min for 2 min at room temperature. After membrane filtration, TLC analysis was performed.
[0115] Table 3 Z basic2 - Catalytic reaction system of NahK immobilized preparation
[0116]
[0117] TLC results such as Figure 4 As shown, compared with the negative control, GlcNAc-1-P was produced in the reaction solution, indicating that Z basic2 -NahK immobilized preparation has the activity of converting N-acetylglucosamine to GlcNAc-1-P.
[0118] 2) ...
Embodiment 4
[0138] Example 4. N-Acetylhexosamine-1-kinase Z basic2 -NahK and UDP-GalNAc pyrophosphorylase Z basic2 -AGX1 co-immobilized enzyme preparation
[0139] 1. Z basic2 -NahK and Z basic2 - Preparation of AGX1 co-immobilized enzyme preparation
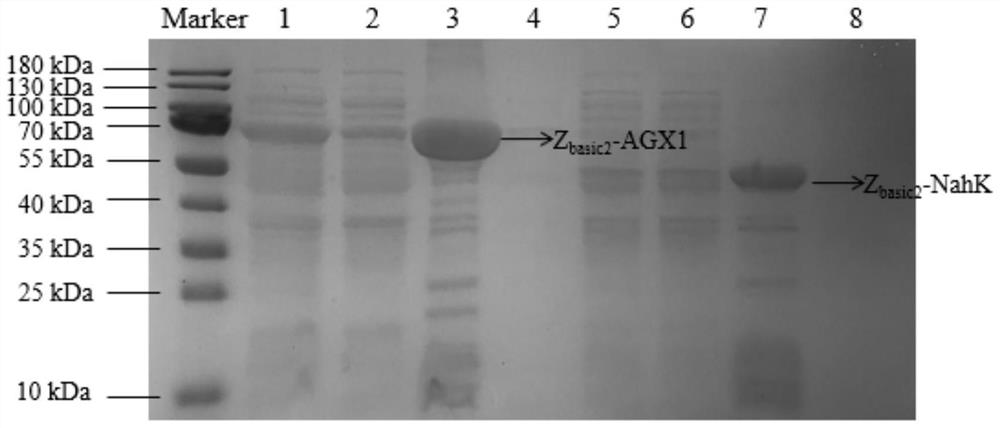
[0140] Take the gene Z containing N-acetylhexosamine-1-kinase in Example 1 basic2 -NahK recombinant E. coli and containing UDP-GalNAc pyrophosphorylase gene Z basic2 -The crushed supernatant of AGX1 recombinant Escherichia coli was mixed and added to the cation exchange resin purolite chromalite MS / C, and incubated at 4°C and 1000rpm / min for 3h for co-immobilization. After the incubation, the supernatant was removed, the resin was washed with Tris-HCl, and the immobilized enzyme was analyzed by SDS-PAGE.
[0141] The result is as Figure 14 As shown, two proteins were bound on the solid support, which were consistent with the molecular weights of the corresponding proteins, indicating that Z basic2 -NahK and Z basic2 -AGX1 was co-i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com