Agaric pilose mixed fungus fermentation culturing method and its culturing medium and product
A technology of mixed bacterial fermentation and culture medium, applied in fermentation, botanical equipment and methods, fungi, etc., can solve problems such as changing the active ingredients of fungi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
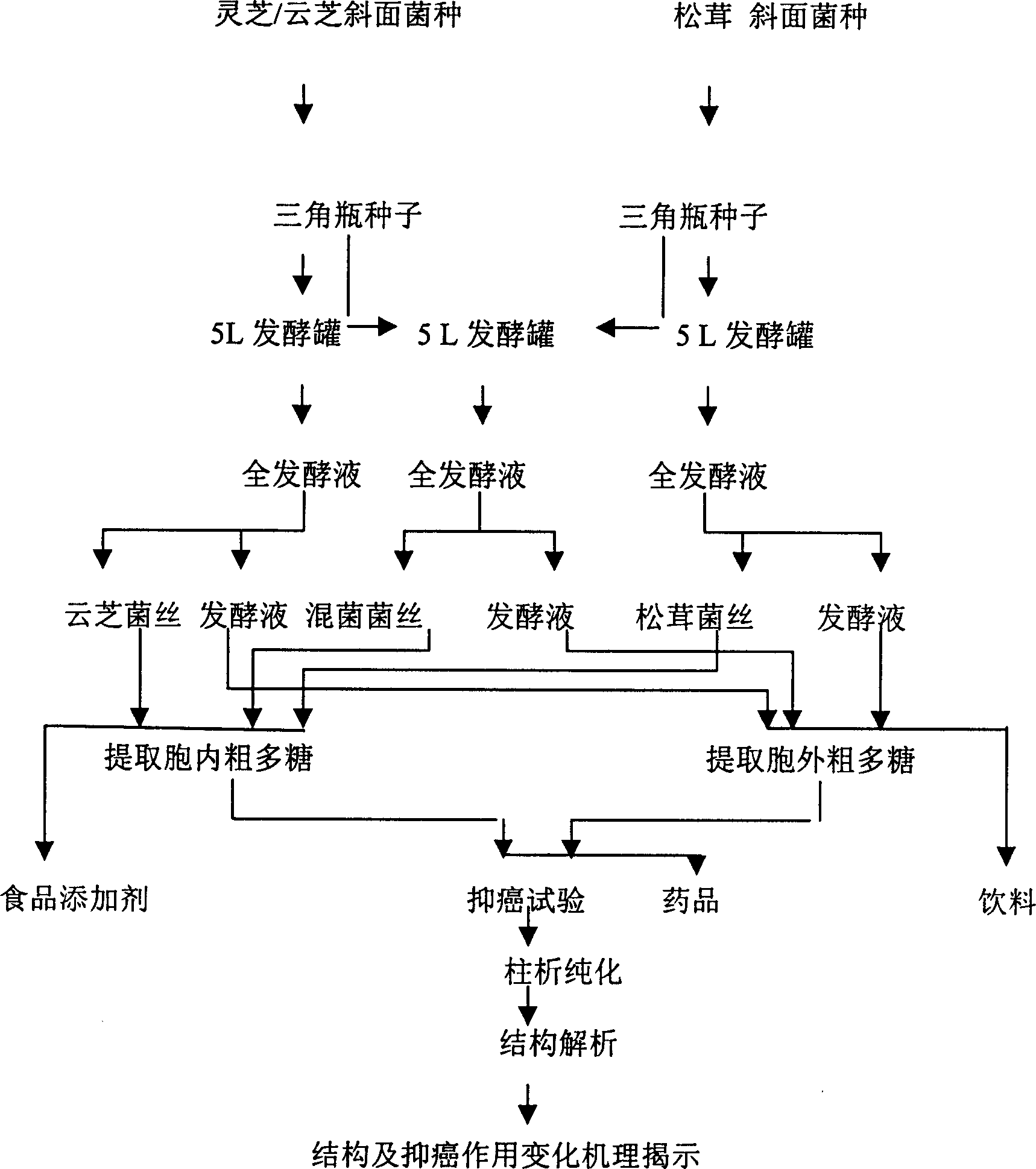
[0048] Mixed fermentation culture of Matsutake, Versicolor versicolor and Ganoderma lucidum
[0049] according to figure 1 Using the same medium and conditions, we used the same medium and conditions to culture matsutake and Yunzhi / Ganoderma lucidum alone, matsutake and Yunzhi / Ganoderma mixed fermentation.
[0050] The mixed bacteria fermentation culture of embodiment 1a Ganoderma lucidum and matsutake CS992 bacterial strain
[0051] 1. Strains:
[0052] (1), Ganoderma lucidum [Ganoderma lucidum (Fr.) Karst]: 60 Co-γ rays and ultraviolet rays alternately accumulate mutagenic strains CJL990 (identified by the Beijing Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences in 1999) to grow 2-4 days faster than the current ganoderma strains.
[0053] (2), Versicolor versicolor [Polyporus versicolor L.: Fr] (purchased from the General Microbiology Center of China Committee for the Collection of Microorganisms)
[0054] (3) Matsutake [Tricholoma matsutake(s Ito.et Imai)sing]: ma...
Embodiment 1b
[0072] The Matsutake strain purchased from the Institute of Edible Fungi, Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences was used to replace the Matsutake CS992 strain, and cultured under the same conditions, the results were as follows:
[0073] Bioaccumulation (36h, dry g / 100ml) (2T fermenter)
[0074] Ganoderma lucidum: 4.3; Matsutake: 6.0; Mixed bacteria: 5.6
[0075] Repeat the above cultivation, the difference is that the Ganoderma lucidum strain is replaced by Yunzhi, the cobalt element concentration of 0, 0.01, 0.5, and 2mg / kg is replaced by the cobalt element concentration of 1.066mg / kg, and the concentration of fumaric acid of 0.01, 0.1, and 0.5wt% is replaced by 0.066wt % fumaric acid.
[0076] The results show that under the above-mentioned cobalt ion concentration, the deep-layer mixed fermentation of matsutake and ganoderma or versicolor can be successfully carried out, but in the absence of cobalt ions, matsutake culture alone can hardly obtain products, and the eff...
Embodiment 2
[0077] The extraction of embodiment 2 fermentation products
[0078] 1. Extraction of Exopolysaccharides
[0079] Filter 100 ml of fermentation broth through gauze, concentrate the filtrate in vacuum at 70°C to 1 / 4 of the original volume, add an equal volume of 95% ethanol, and ethanol analysis for 20 hours. The precipitate is washed 5-6 times with 75% ethanol until there is no reducing sugar, and then washed 5-6 times with absolute ethanol, and vacuum freeze-dried to obtain crude exopolysaccharide. Put it in a test tube, add 5ml of hot water to dissolve, and dilute to 10ml. Take 1 ml in another test tube, add 2N HCl, heat and hydrolyze in a water bath for 5 hours, and obtain extracellular pure polysaccharides.
[0080] 2. Extraction of intracellular polysaccharides:
[0081] Crush the mycelia, sieve (80-90 mesh), boil, extract 3-4 times, combine the extracts, concentrate in vacuum at 70°C to 1 / 4 of the original volume, the following is the same as extracting exopolysacchar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com