Polymer, resist composition and patterning process
a technology of composition and polymer, applied in the field of polymer, resist composition and patterning process, can solve the problems of pattern collapse, difficult use as resist base resin, and the likelihood of polymer swelling during development, and achieve the effect of reducing the influence of swelling due to immersion, low affinity, and high affinity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
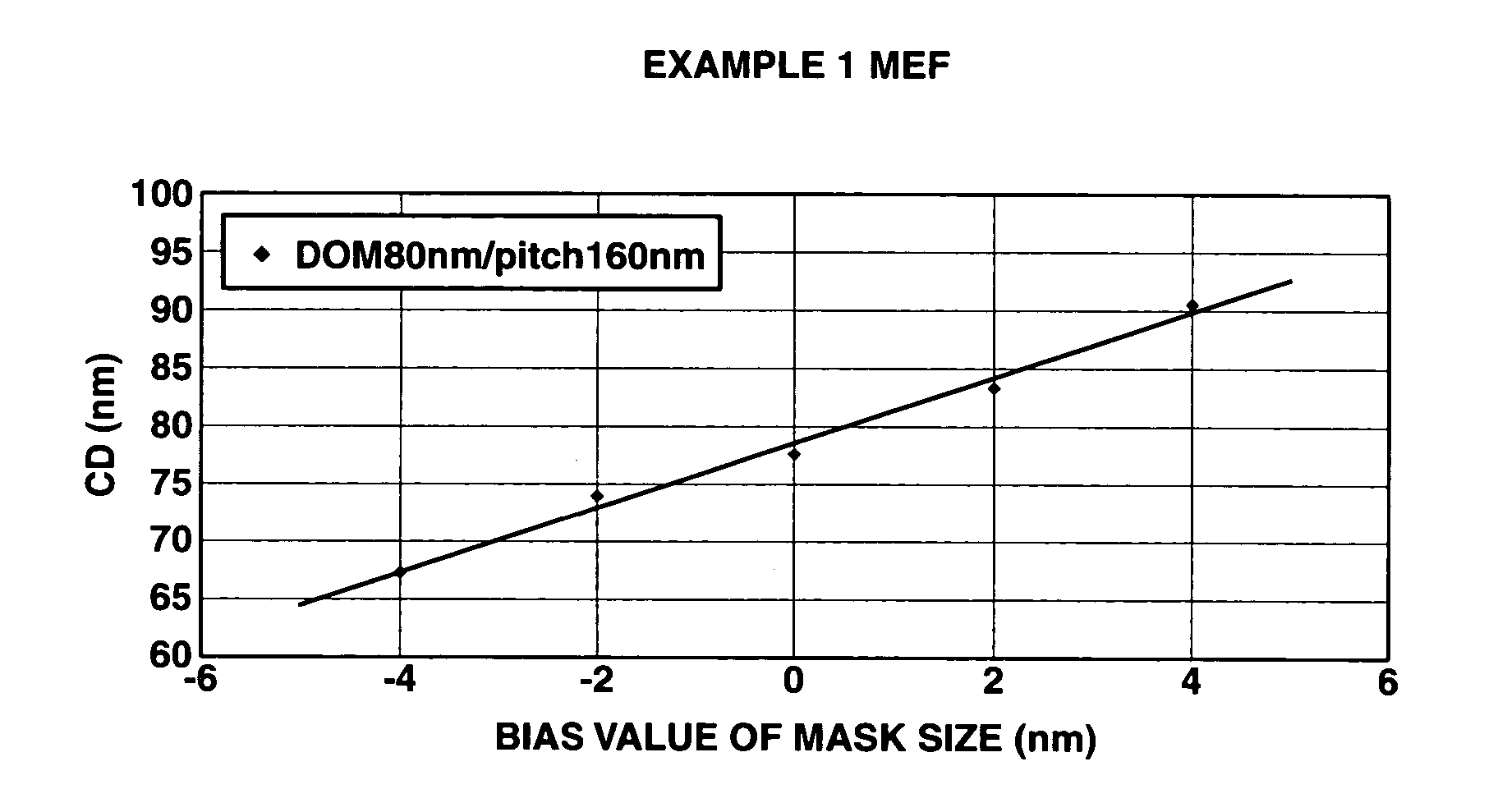
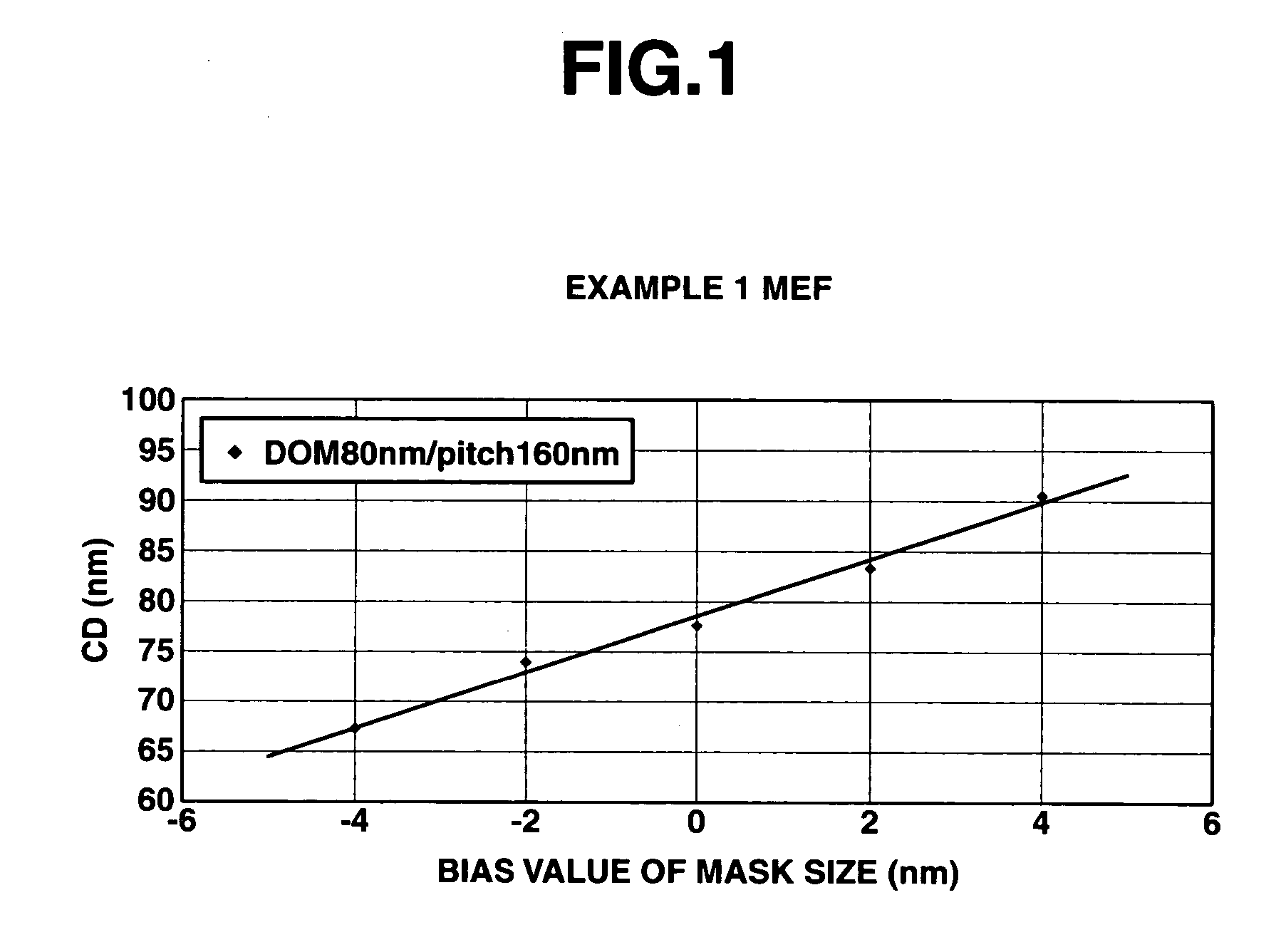
Examples
synthesis example 1
Monomer Synthesis Example 1
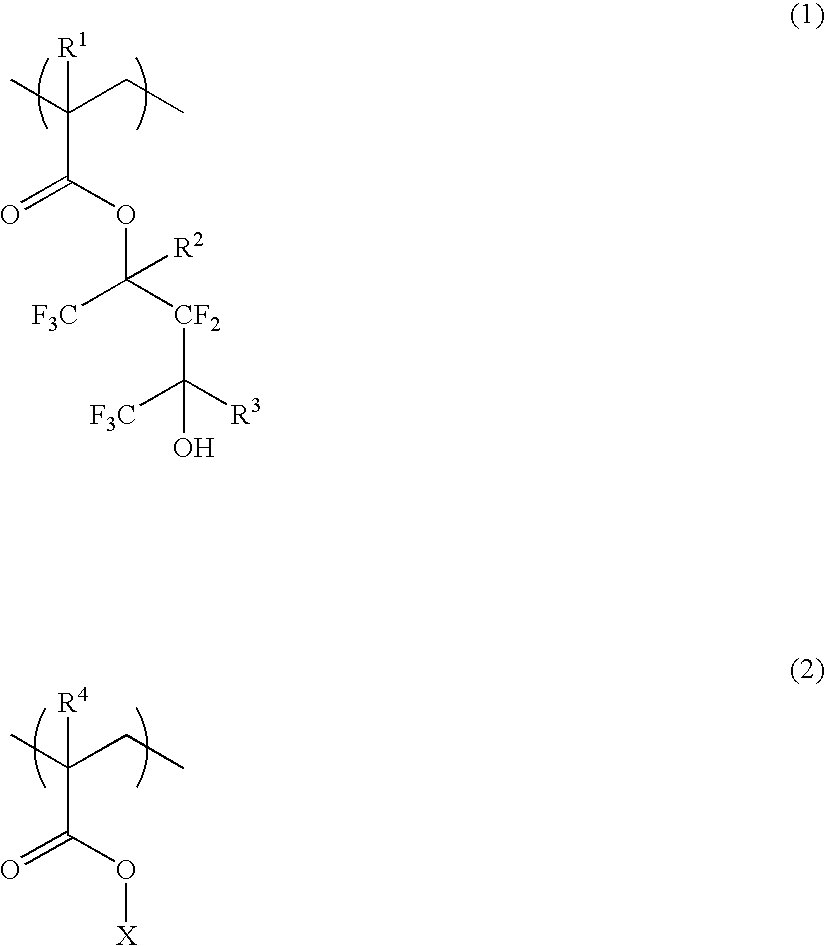
Synthesis of 2,2,4,4,4-pentafluoro-3-hydroxy-1,3-bis(trifluoromethyl)butyl methacrylate
[0395]
[1-1] Synthesis of 1,1,1,3,3,5,5,5-octafluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)pentane-2,4-diol
[0396] With stirring in a nitrogen blanket, a mixture of 109 g of 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol and 500 g of tetrahydrofuran was cooled at 5° C. To the mixture, 500 mL of a solution of 2.71M n-butyllithium in n-hexane was added dropwise, followed by stirring for 2 hours at 5° C. 119 g of hexafluoroacetone was admitted to the reaction solution, which was stirred for 3 hours at 5° C. A mixture of 37.0 g of sodium borohydride and 800 g of water was added dropwise to the reaction mixture, which was stirred for 10 hours at room temperature. 330 g of 20% aqueous hydrochloric acid was added to the reaction mixture to quench the reaction, followed by conventional work-up steps of washing, drying and concentration to give a crude product. It was purified by silica gel column chromatograp...
synthesis example 2
Monomer Synthesis Example 2
Synthesis of 2,2,4,4,4-pentafluoro-3-hydroxy-1,3-bis(trifluoromethyl)butyl acrylate
[0398]
[0399] The procedure of Monomer Synthesis Example 1 was repeated except that acrylic acid chloride was used instead of the methacrylic acid chloride in stage [1-2], yielding 2,2,4,4,4-pentafluoro-3-hydroxy-1,3-bis(trifluoromethyl)butyl acrylate.
synthesis example 3
Monomer Synthesis Example 3
Synthesis of 2,2,4,4,4-pentafluoro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-1,3-bis(trifluoromethyl)butyl methacrylate
[0400]
[0401] The procedure of Monomer Synthesis Example 1 was repeated except that a tetrahydrofuran solution of methylmagnesium chloride was used instead of the mixture of sodium borohydride and water in stage [1-1], yielding 2,2,4,4,4-pentafluoro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-1,3-bis(trifluoromethyl)butyl methacrylate.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dispersity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com