Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiments
(Embodiments)
[Embodiment 1]
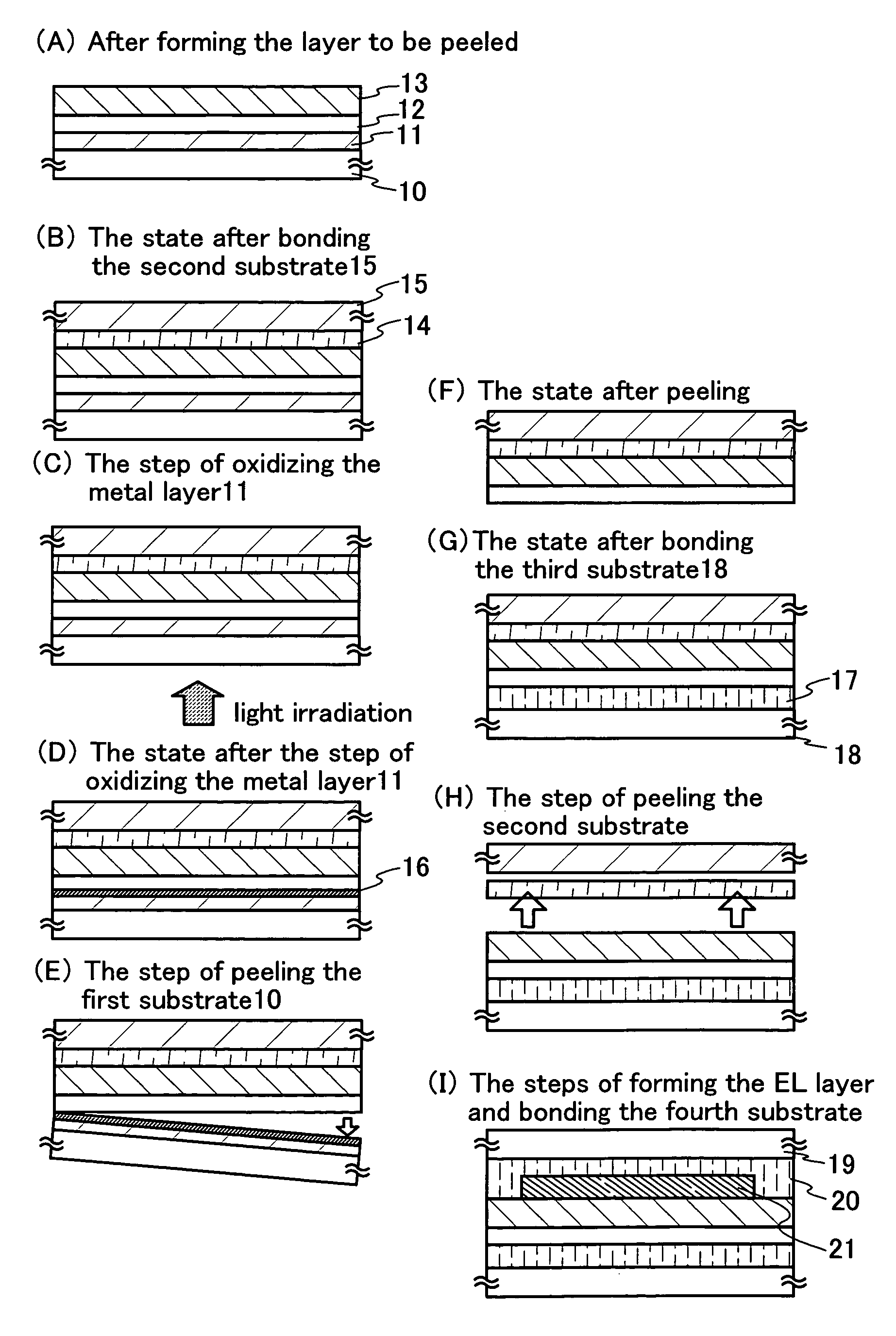
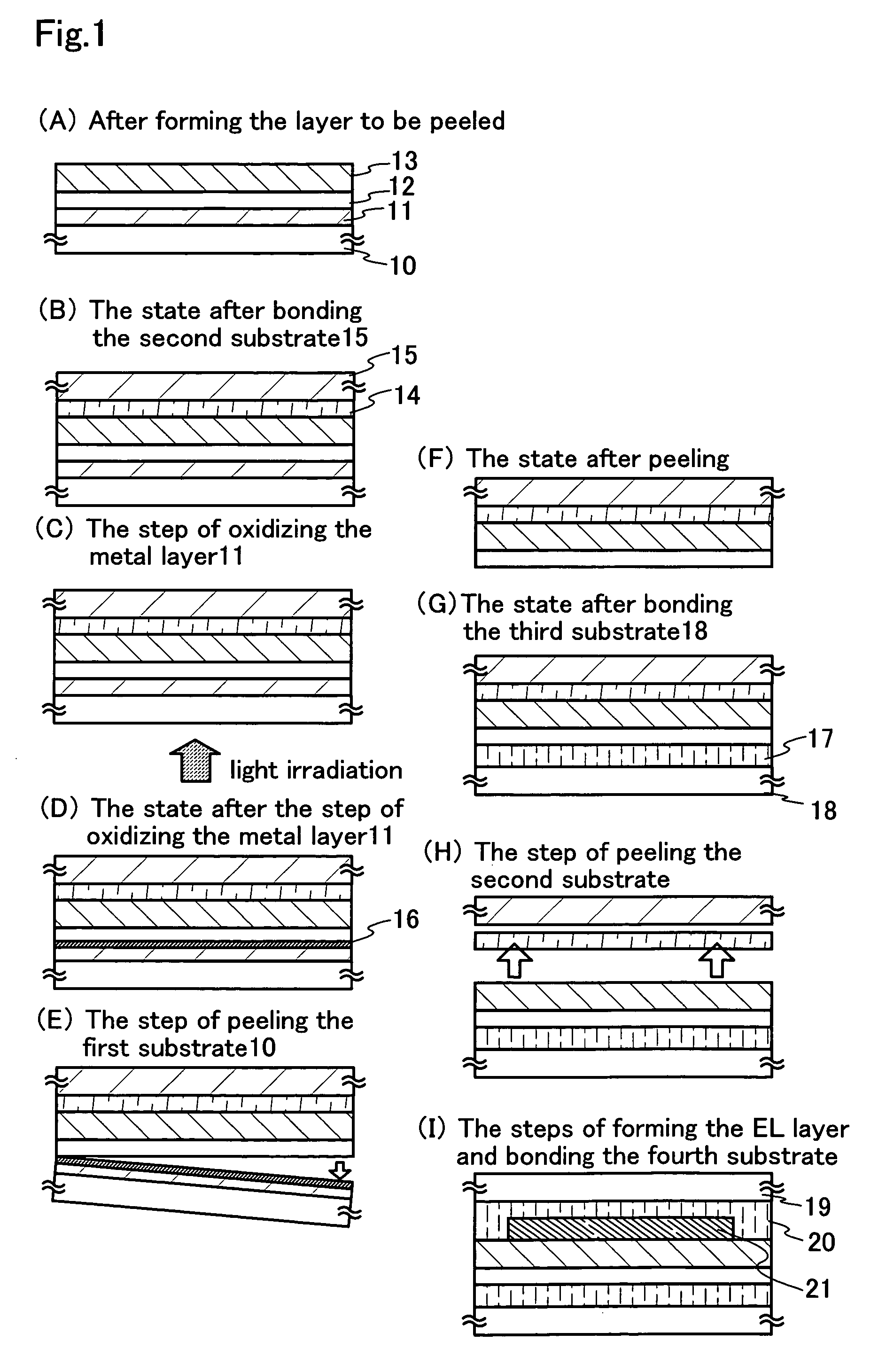
[0080]An embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 3 to 7. Here, a method for manufacturing a pixel portion and TFTs (n-channel TFTs and a p-channel TFT) of a driver circuit provided at the periphery of the pixel portion at the same time on the same substrate will be described in detail. Although an example of manufacturing an active matrix substrate for manufacturing a reflective liquid crystal display device will be shown here, there is no limitation. When an arrangement of TFTs and a material of a pixel electrode are appropriately changed, needless to say, it is also possible to manufacture a transmissive liquid crystal display device and a light-emitting device that has a light-emitting layer including an organic compound.
[0081]A glass substrate (AN100) is used as a substrate 100. First, a silicon oxynitride layer 101 is formed on the substrate with PCVD to be a thickness of 100 nm.
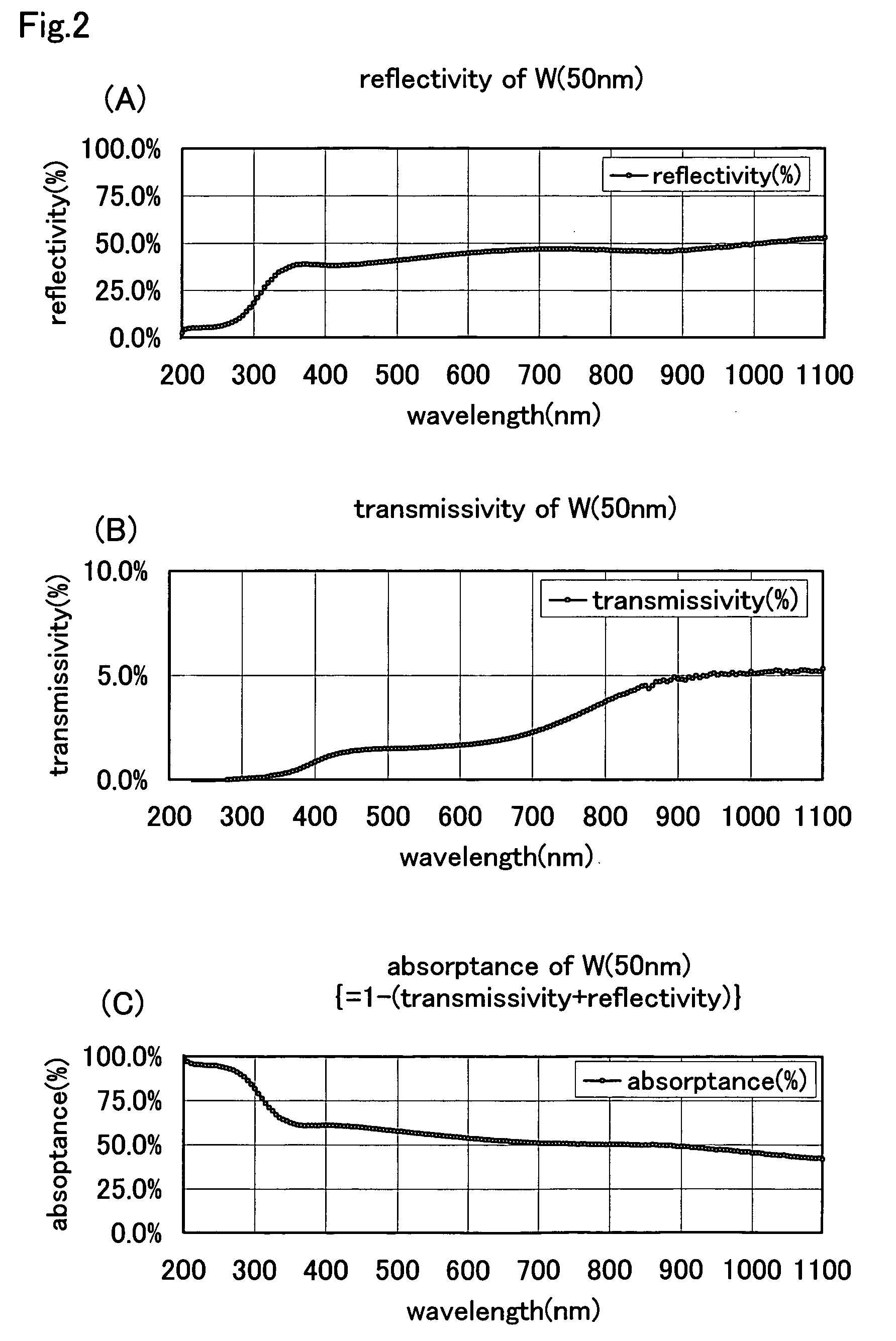
[0082]Subsequently, as a metal laye...
embodiment 2
[Embodiment 2]
[0134]Embodiment 1 shows an example of a reflective display device in which a pixel electrode is formed of a reflective metal material. In the present embodiment, an example of a transmissive display device, in which a pixel electrode is formed of a light-transmitting conductive film, is shown in FIG. 8.
[0135]Since processes up to the step of forming an interlayer insulating film are the same as those of Embodiment 1, the description thereof is omitted here. After forming the interlayer insulating film in accordance with Embodiment 1, a pixel electrode 601 of a light-transmitting conductive film is formed. As the conductive film with transmittance, ITO (indium tin oxide alloy), indium oxide-zinc oxide alloy (In2O3—ZnO), zinc oxide (ZnO) film, and the like may be used.
[0136]Thereafter, contact holes are formed in an interlayer insulating film 600. Then, a connecting electrode 602 overlapping with the pixel electrode is formed. This connecting electrode 602 is connected ...
embodiment 3
[Embodiment 3]
[0139]In the present embodiment, an example for manufacturing a light-emitting device equipped with a light-emitting element that has a light-emitting layer including an organic compound, which formed on a plastic substrate will be described with reference to FIG. 9.
[0140]FIG. 9(A) is a top view that shows a light-emitting device and FIG. 9(B) is a sectional view of FIG. 9(A) taken along A–A′. A dotted line 1101 denotes a source signal line driver circuit, reference numeral 1102 denotes a pixel portion, and reference numeral 1103 denotes a gate signal line driver circuit. Reference numeral 1104 denotes a sealing substrate and reference numeral 1105 is a sealing agent. The inside surrounded by the first sealing agent 1105 is filled with a second transparent sealing material 1107.
[0141]Reference numeral 1108 is a wiring for transmitting signals to be input to the source signal line driver circuit 1101 and the gate signal line driver circuit 1103, and receives a video sig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com