Group VA-doped solution-processed metal chalcogenides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
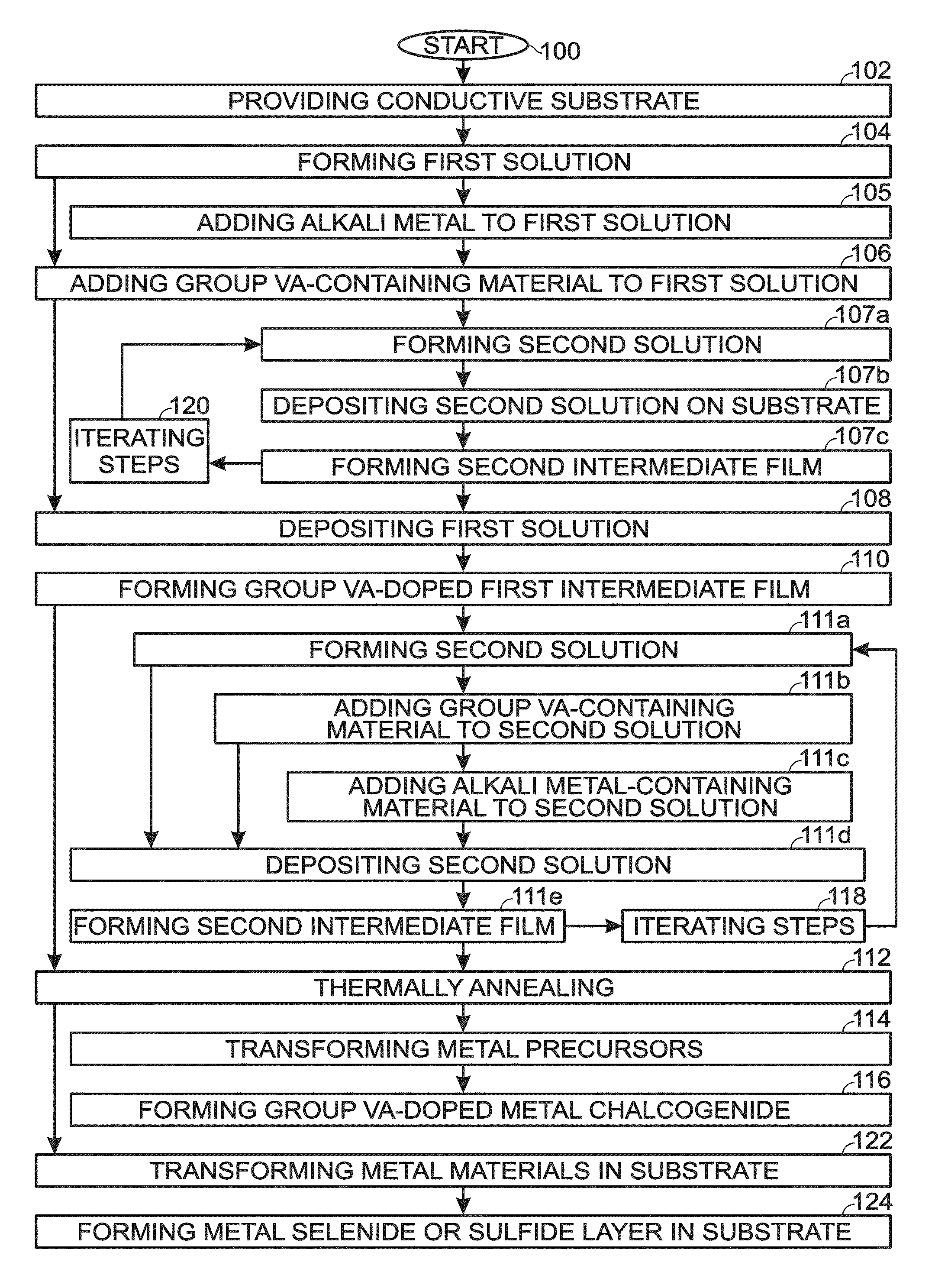
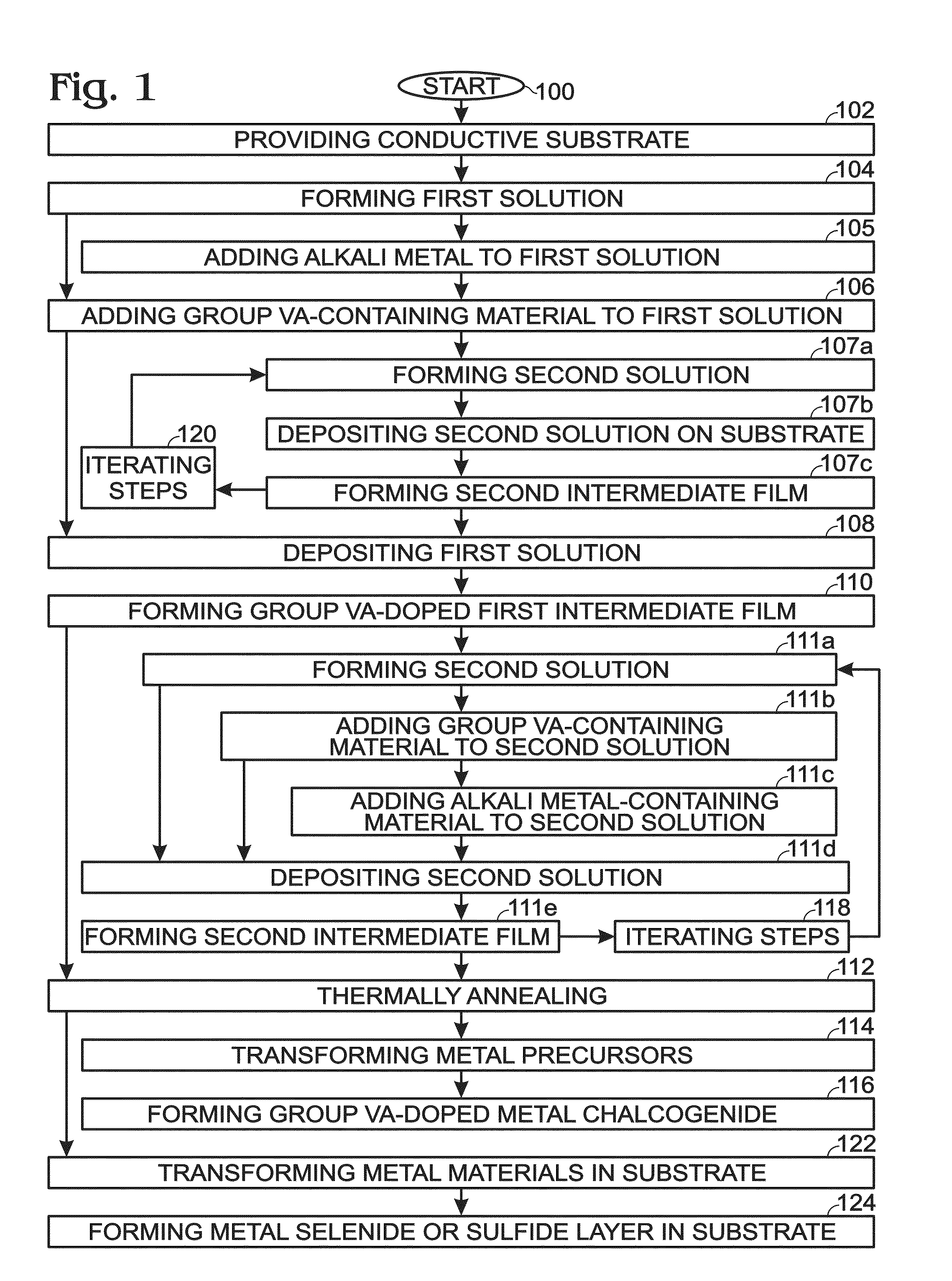
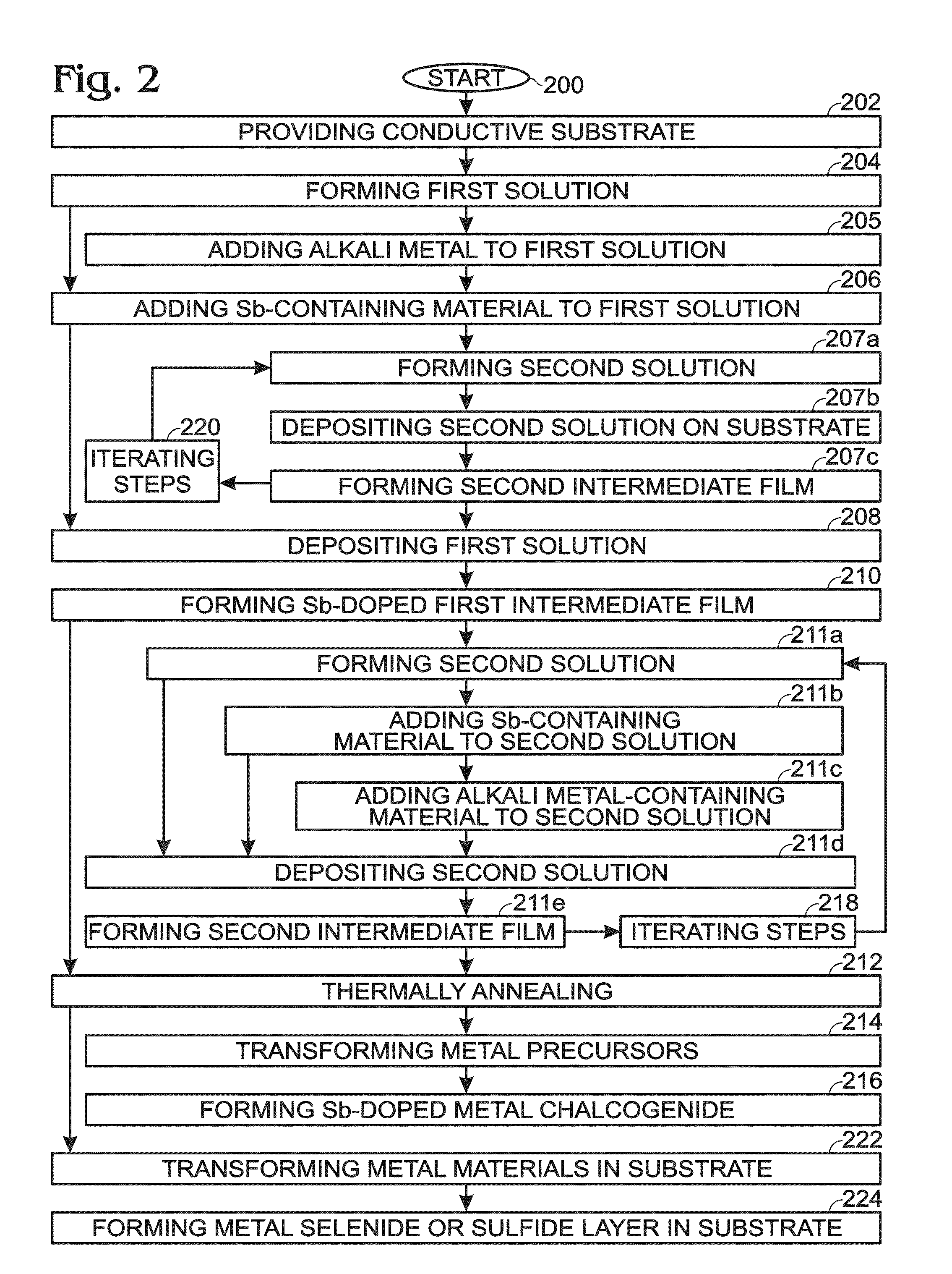
[0040]FIG. 1 is a flowchart illustrating a method for forming a Group VA-doped solution-processed metal chalcogenide. Although the method is depicted as a sequence of numbered steps for clarity, the numbering does not necessarily dictate the order of the steps. It should be understood that some of these steps may be skipped, performed in parallel, or performed without the requirement of maintaining a strict order of sequence. Generally however, the method follows the numeric order of the depicted steps. The method begins at Step 100.
[0041]Step 102 provides a conductive substrate. The conductive substrate may be a metal, metal alloy, metal oxide, mixed metal oxide, or a combination thereof. Some examples of conductive substrate materials include aluminum, chromium, cobalt, copper, gallium, germanium, gold, indium, iron, lead, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, palladium, platinum, silicon, silver, tantalum, tin, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, zinc, zirconium, stainless steel, indium tin oxi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com