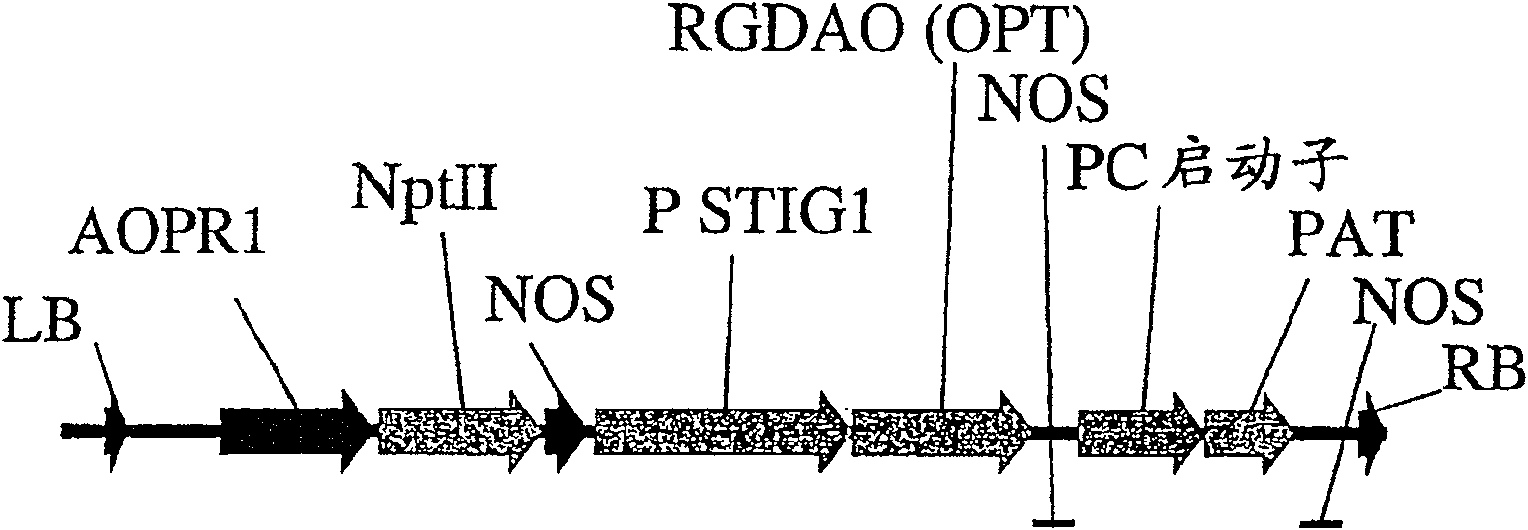
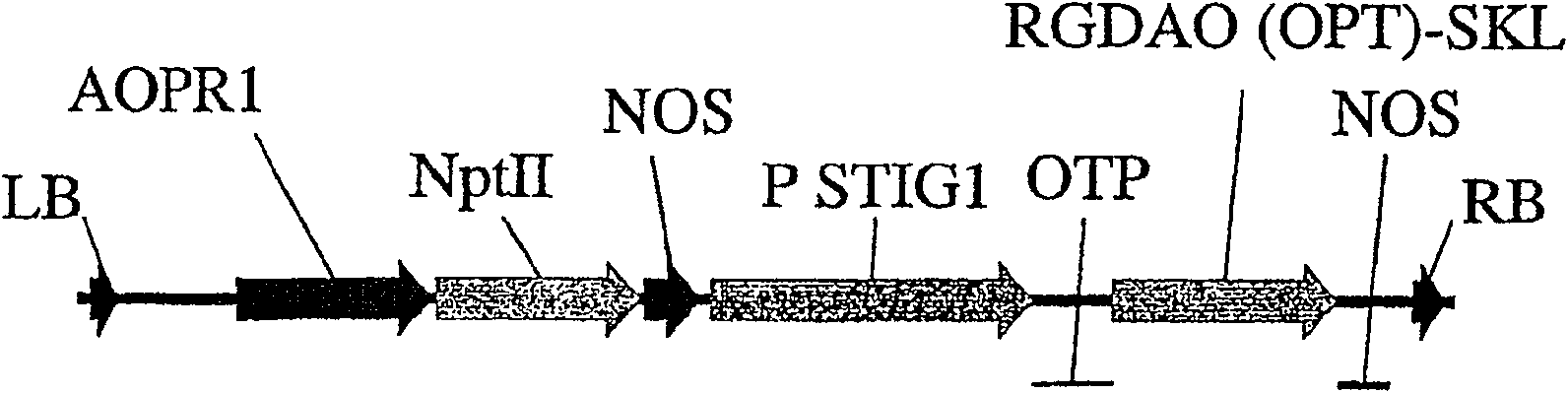
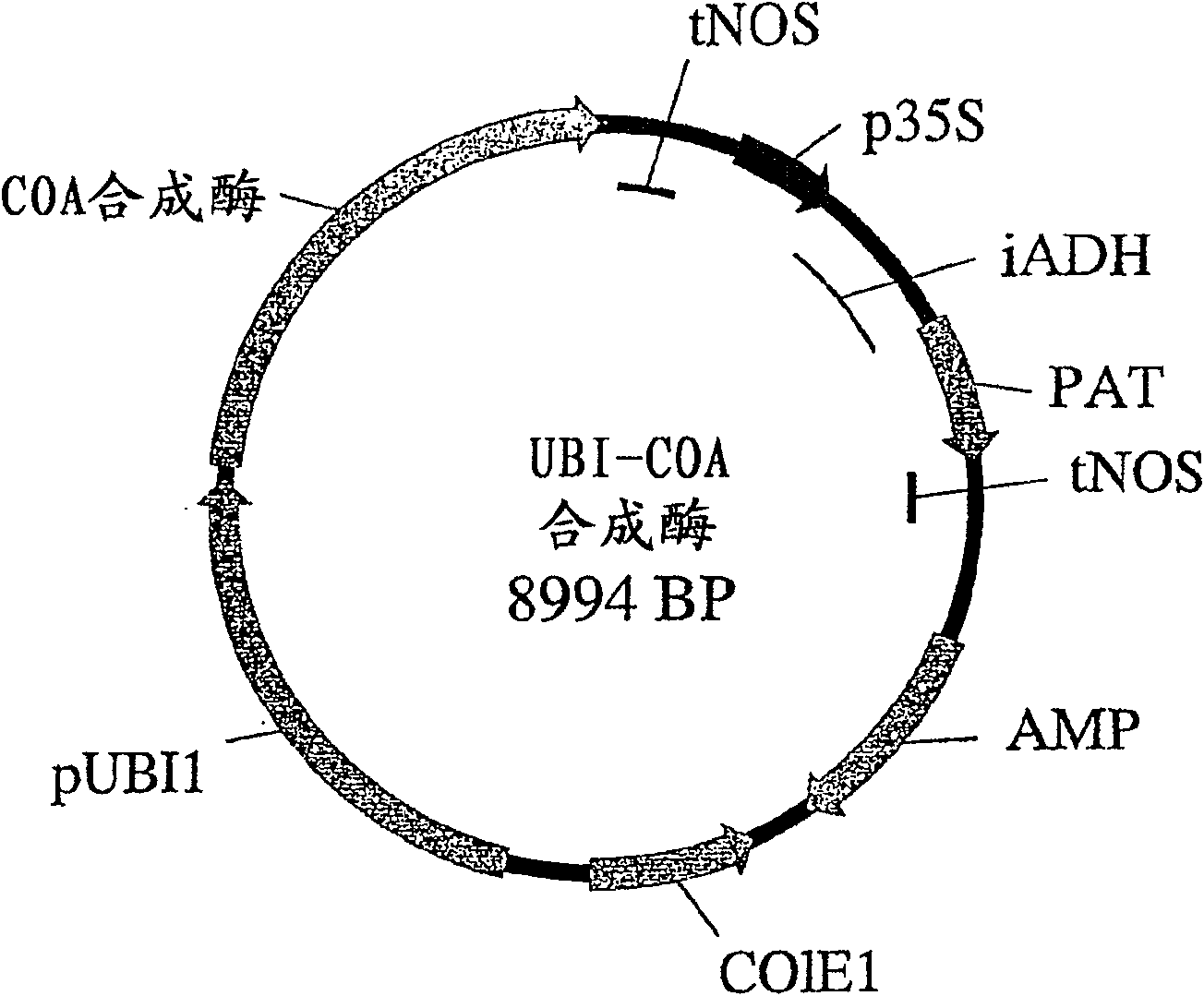
A method of selectively producing male or female sterile plants
A plant and male technology, applied in the field of seeds, can solve the problem of non-routine production of hybrid seeds
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0155] Dependent on exogenous administration of D-phosphinothricin or D-alanine or D-leucine or D-methionine or D-asparagine D-aspartate or D-glutamate Conditionally female sterile tobacco plants
[0156] The DNA sequence encoding the D-amino acid oxidase protein sequence Q99042 (Swissprot) in the EMBL sequence Z50019 was obtained or synthesized from the mRNA of the variant Trigonopsis variabilis by RT-PCR. As an alternative, obtain from yeast-like Rhodosporidium tolruloides (Rhodotorula gracilis) mRNA by RT-PCR or obtain it synthetically (this makes it easier to control the presence of internal restriction enzyme sites and produce Flanking sites to facilitate cloning) the DNA sequence encoding the D-amino acid oxidase protein sequence P80324 (Swissprot) in the EMBL sequence A56901, which can be synthesized, for example, as SEQ ID #7, designed for use in plants (here is wheat) codon usage and used to minimize DNA features potentially detrimental to expression. Alternatively,...
Embodiment 2
[0165] Dependent on exogenous administration of D-phosphinothricin or D-alanine or D-leucine or D-methionine or D-asparagine or D-aspartic acid or D-glutamic acid Conditionally female sterile tobacco plants
[0166] The DNA sequence encoding the D-amino acid oxidase protein sequence Q9HGY3 (Sptrembl) in EMBL sequence AB042032 was obtained by RT-PCR from Candida boidini mRNA or by synthesis. As an alternative, the DNA sequence encoding the D-amino acid oxidase protein sequence P24552 (Swissprot) in EMBL sequence D00809 was obtained by RT-PCR from Fusarium solani mRNA or by synthesis. Design flanking PCR primers or synthesize DNA sequences to place useful single restriction sites. Preferably and in cases where the oxidase coding sequence does not contain confounding internal sites, Nco1 and Nde1 sites are placed at the 5' end to facilitate cloning of in-frame fusions added to the 5' sequence of the ORF. Alternatively, when placing a restriction site upstream of the ATG transla...
Embodiment 3
[0176] A chimera that preferentially expresses and encodes enzymes capable of hydrolyzing imazamox or flamprop M methyl or flamprop M isopropyl into their respective carboxylic acids in male reproductive structures Gene
[0177] The DNA sequence encoding the carboxylesterase protein sequence Q01470 (Swissprot) in EMBL sequence M94965 was obtained by PCR from Arthrobacter oxydans genomic DNA or by synthesis. As an alternative, the DNA sequence encoding the carboxylesterase protein sequence P37967 (Swissprot) in the EMBL sequence BS06089 was obtained by PCR from Bacillus subtilis genomic DNA or synthesized. Alternatively, the DNA sequence encoding the carboxylesterase protein sequence P40363 (Swissprot) in EMBL sequence Z34288 was obtained from Saccharomyces cervisiae mRNA by RT-PCR or synthesized. Flanking PCR primers or synthetic DNA sequences are designed to place useful single restriction sites for cloning. Preferably and in cases where the carboxylesterase coding sequence...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com