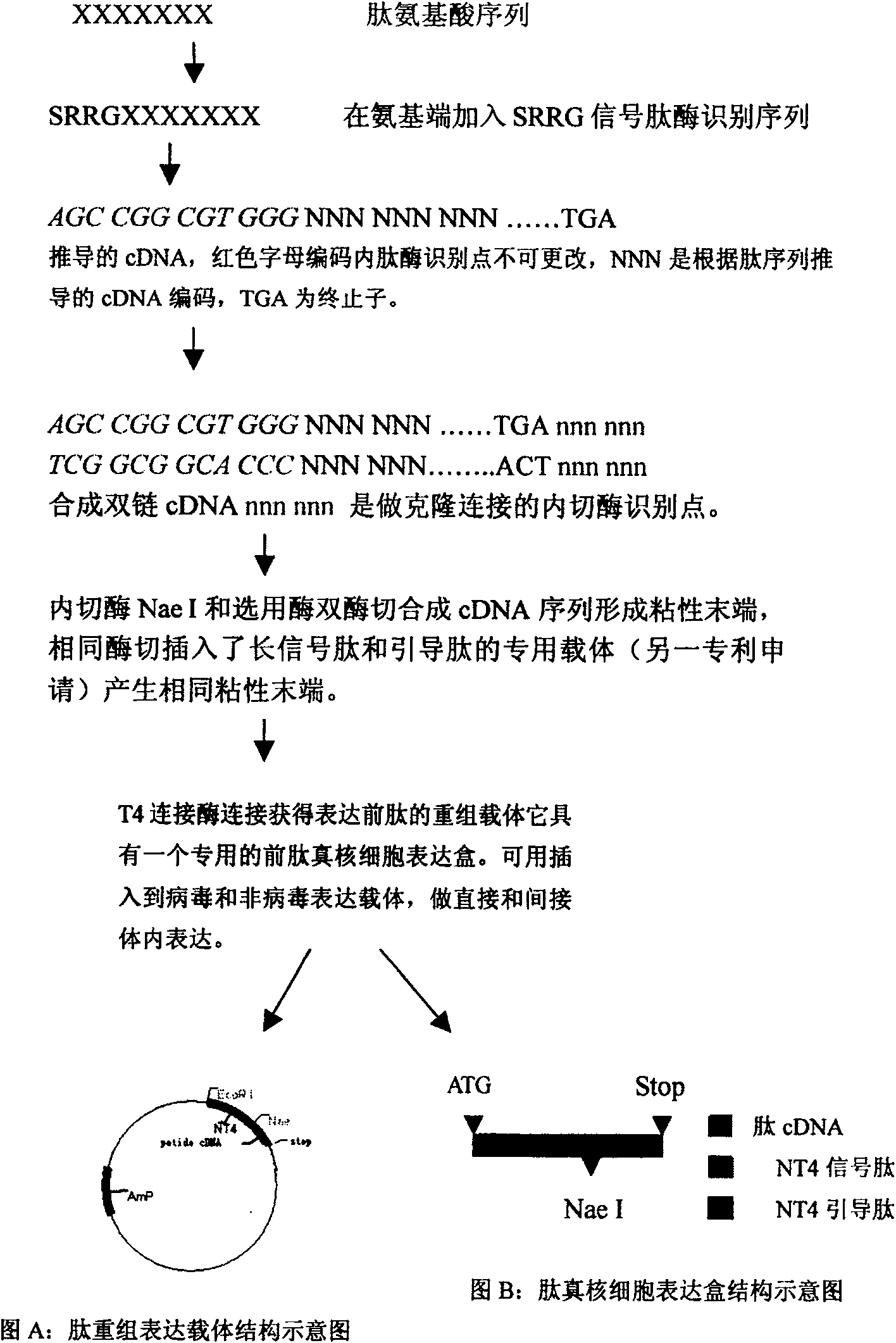
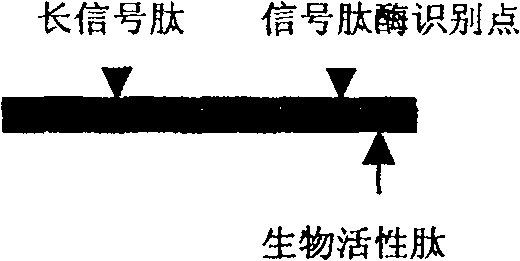
Boactivity peptide gene therapy method realized by propeptide recombination
A technology of bioactive peptides and expression methods, which is applied to peptide preparation methods, chemical instruments and methods, peptides, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, failure to meet industrial production requirements, and inability to realize the prevention and treatment of bioactive peptides. Prevent degradation, ensure recognition and effective cutting effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: Construction of recombinant propeptide of anti-tumor angiogenesis peptide Anginex and its gene therapy
[0031] (1) Determining the sequence of the biologically active peptide: XXXXXX in the figure represents the amino acid sequence of the selected biologically active peptide, and each X represents an amino acid residue. According to the desired biological effect, users have selected peptides with specific biological activities from published literature or through their own previous research findings, such as promoting apoptosis and inhibiting tumor angiogenesis. Peptides, antiviral infection peptides that antagonize HIV or HCV invading target cell receptors, aptamer peptides that truncate intracellular signal transduction, and nutritional peptides that activate cellular functions to treat senile degenerative diseases. The mechanisms and principles of action of these bioactive peptides vary widely, and the subcellular locations where they act are also diverse...
Embodiment 2
[0106] Example 2, Construction of TAT-VHL β structural propeptide and anti-renal cancer effect:
[0107] Step 1: Determine the sequence of bioactive peptides: Renal cell carcinoma is a common malignant tumor, recurrence and metastasis after surgery are common, and the tumor is not sensitive to radiation and chemical anticancer drug treatment, so the prognosis of the patient Difference. Recent biological studies of renal cancer cells revealed that the proliferation and metastasis of these cells depend on insulin-like growth factor 1 (insulin-like growth factor 1, ILGF1) receptor signaling. Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) is a tumor suppressor gene. Its expression product inhibits the ILGF1 receptor signaling through binding with protein kinase Cδ to induce apoptosis of renal cancer cells, and has a therapeutic effect on renal cancer. However, there are technical difficulties in the use of VHL protein in the treatment of renal cancer solid tumors. One is that the protein molecules with...
Embodiment 3
[0133] Example 3, Construction of recombinant adeno-associated virus expressing humanin propeptide against senile dementia and its protective effect on neurons.
[0134] Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a common degenerative disease of the central nervous system in the elderly. The etiology is currently unknown, but the pathology is characterized by neuronal loss, senile plaque formation, and neurofibrillary tangles. Using molecular biology screening technology, a 24 amino acid residue polypeptide-Humanin was found to antagonize AD pathological changes caused by various known genetic causes, especially neural apoptosis. We used this patented technology to construct a recombinant propeptide expressing Humanin, express the propeptide using an adeno-associated virus vector, and transduce rat cortical nerve cells, successfully preventing amyloid peptide (the most important pro-neuron apoptosis in AD occurrence). apoptosis induced by apoptosis.
[0135] Step 1: Determine the sequence ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com