Synthetic method of astaxanthin
A technology of astaxanthin and a new method, applied in the field of preparation of carotenoid products, can solve the problems of large molecular weight of triphenylphosphine, troublesome post-processing and high production cost, and achieve high product quality, convenient post-processing and high production cost. low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Synthesis of bis(N, N-methyl, methoxy) 3-hexenediamide
[0037] Mix 15g of trans-3-hexene-1,6-dioic acid and 50mL of dichloromethane, add dropwise 30g of oxalyl chloride under ice bath, control the temperature below 20°C, add DMF1ml dropwise after the dropwise addition, and put the above mixture at room temperature The reaction was carried out at low temperature for half an hour, and then at about 40°C for two hours. The solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure to obtain a tan oil. Dilute with 30 mL of chloroform. Another 50 mL of chloroform, 50 mL of pyridine, and 25 g of N, O-dimethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride were mixed, and the chloroform solution of the acid chloride prepared above was added dropwise under ice cooling. Control the temperature below 20°C for 24 hours. After the reaction is complete, add 100 mL of water, separate the layers, wash the layers with 100 mL of water, dry the organic layer with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filter, evaporate the...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Synthesis of 4-octene-2,7-dione
[0040] Cool the Grignard reagent prepared by 18 g of iodomethane, 3.5 g of magnesium, and 100 mL of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran to below -10°C, and add 11.5 g of bis(N,N-methyl, methoxy) 3-hexenediamide compound to dissolve A solution in 50 mL of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran. Add 100mL of saturated ammonium chloride aqueous solution and 100mL of ethyl acetate to separate layers, then wash the layers with 100mL saturated sodium chloride aqueous solution, and wash the organic layer with anhydrous magnesium sulfate Dry, filter, and evaporate the solvent under normal pressure to obtain 4.7 g of 4-octene-2,7-dione with a yield of 66%.
Embodiment 3
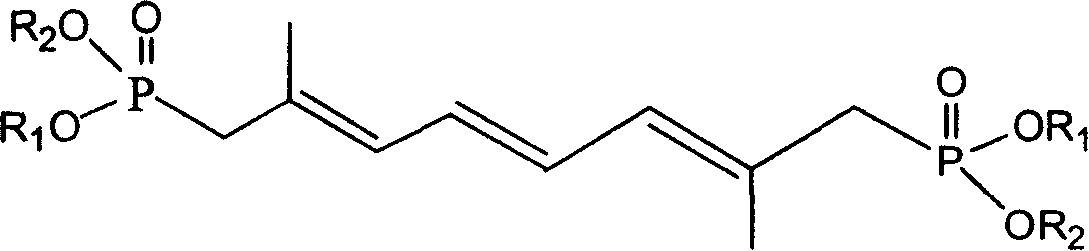
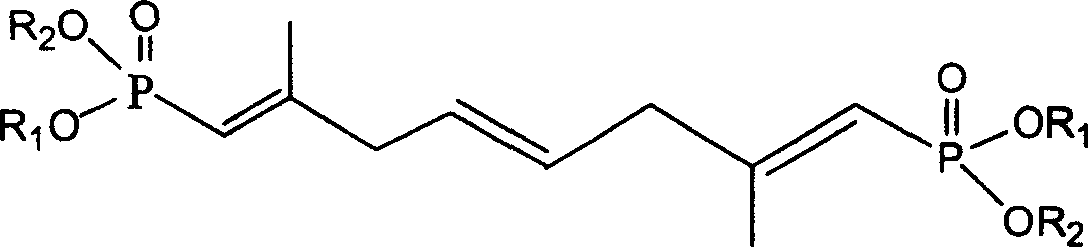
[0042] Synthesis of Diethyl 2,7-Dimethyl-1,4,7-octatriene-1,8-diphosphonate
[0043]Weigh 2.9g of 60% sodium hydride, wash with n-hexane, add 50mL of anhydrous toluene, add dropwise a solution of 26g of diethyl methylene bisphosphonate dissolved in 20mL of anhydrous toluene under nitrogen protection, and control the temperature at 25°C After the dropwise addition, react for another half an hour, then add 4.2 g of 4-octene-2,7-dione in 20 mL of anhydrous toluene dropwise at a controlled temperature below 25°C, and react for another hour after the dropwise addition, and the reaction is complete Add 100mL of water to wash and separate the layers, dry the organic layer with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filter, and evaporate the solvent under reduced pressure to obtain 2,7-dimethyl-1,4,7-octatriene-1,8-bisphosphonic acid diethyl Esters 12g.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com