Method for extracting tea-polyphenol and separating monomer EGCG from tea
A technology of tea polyphenols and tea leaves, which is applied in the field of extracting tea polyphenols and separating monomer EGCG, which can solve the problems of complex operation process, difficult control of conditions, and easy pollution of chromatographic columns, and achieve simple process, low cost, and avoid extraction process Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The mass ratio of feeding is tea powder: solid-phase alkaline reagent is 1:0.1, wherein the solid-phase alkaline reagent is sodium bicarbonate.
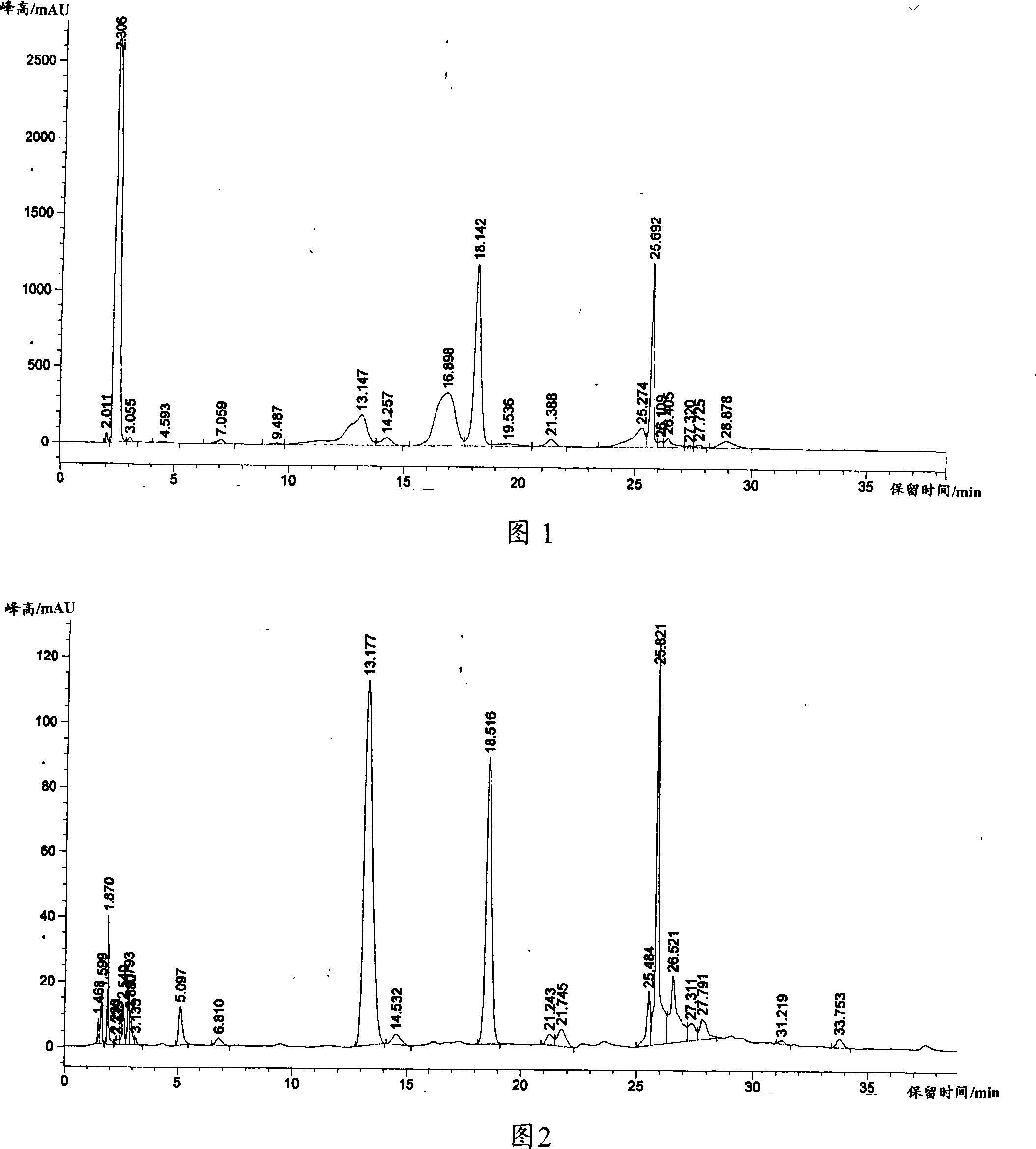
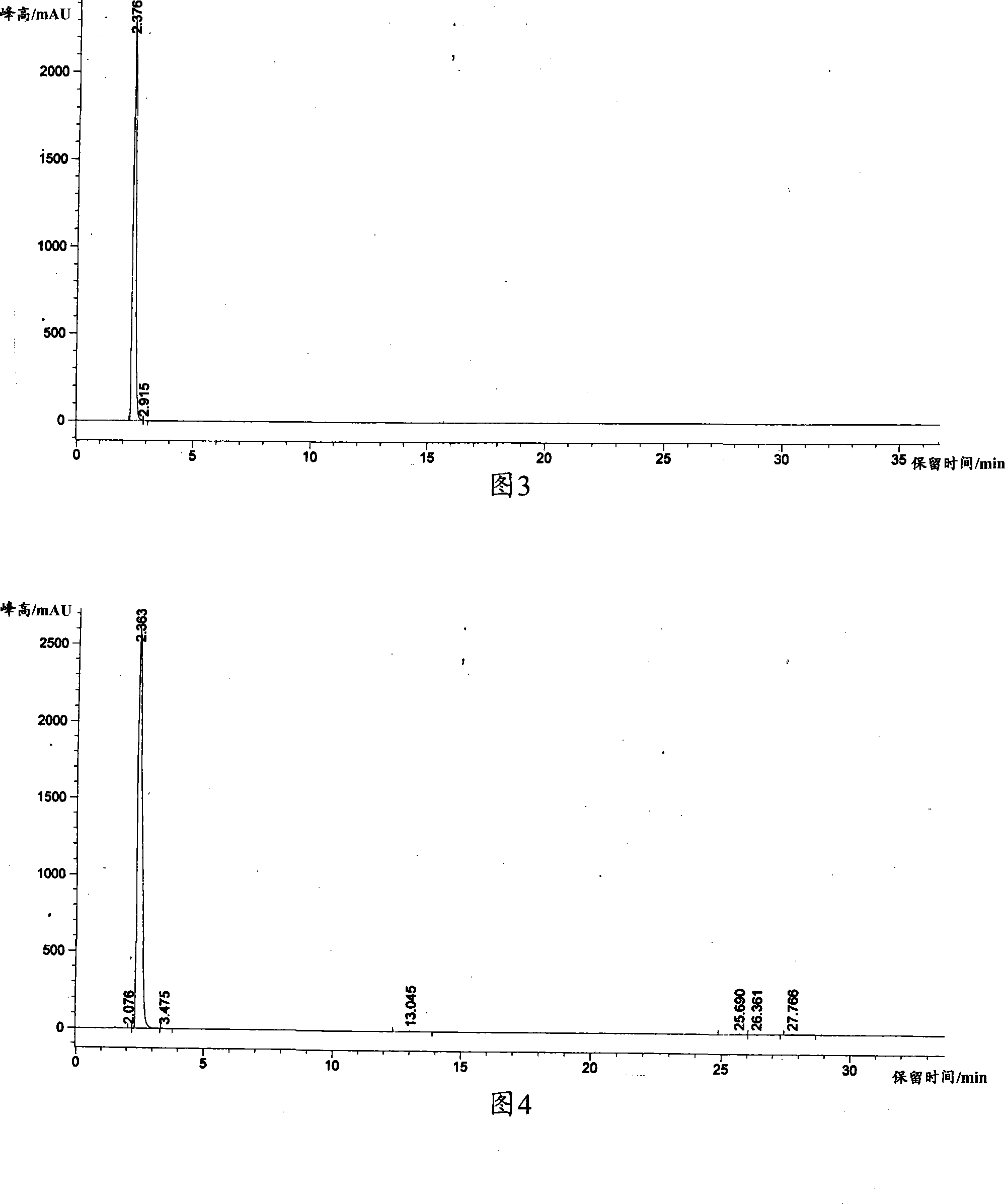
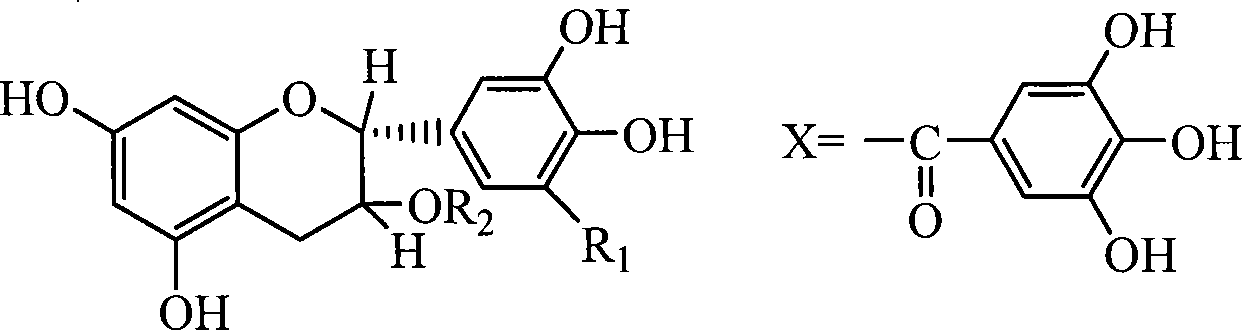
[0036] At room temperature, first pulverize the tea leaves with a universal grinder, the particle size is less than 1mm, and add 0.5g (about 2.5mmol) of tea powder calculated according to the average molecular weight of 400 (estimated value) to the mortar, and 0.05g of sodium bicarbonate (0.6mmol), mechanical grinding, the grinding time is 30min, add 20ml of water, stir for 30min, centrifuge, take the supernatant, add phosphoric acid to adjust the pH value to 1~2, produce gray precipitate, filter to obtain gray solid 0.006g, get The yield was 1.2%, and the content was 95%. After the filtrate was dried, 0.085g of tea polyphenol crude product was obtained. The yield of tea polyphenol was 17%, and the content was 75%.
[0037] Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the product: using commercially available tea polyphenols as a ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The feeding mass ratio is tea powder: solid-phase alkali reagent is 1:0.1, wherein the solid-phase alkali reagent is sodium bicarbonate. The added quality of tea powder is 0.5g.
[0040] Grinding time was 15min, other operations were the same as in Example 1, and 0.005g of gray solid was obtained with a yield of 1.0% and a content of 93%. After the filtrate was dried, 0.0825g of tea polyphenol crude product was obtained with a yield of 16.5%. was 73%. Product identification and content determination are the same as those described in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0042] The feeding mass ratio is tea powder: solid-phase alkali reagent is 1:0.1, wherein the solid-phase alkali reagent is sodium bicarbonate. The added quality of tea powder is 0.5g.
[0043] Grinding time is 5min, and other operations are the same as in Example 1 to obtain 0.004g of gray solid with a yield of 0.8% and a content of 95%. After the filtrate is dried, 0.0775g of tea polyphenol crude product is obtained with a yield of 15.5%. 70%. Product identification and content determination are the same as those described in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com