Purified high-specific-activity recombinant batroxobin
A batroxobin, specific activity technology, applied in the field of high specific activity recombinant batroxobin, can solve the problems of high disulfide bond pairing error rate, low specific activity, poor reproducibility, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] Preparation Example
[0088] One, obtain the fermented liquid containing batroxobin protein
[0089] Fermentation of rBAT engineering bacteria in 30L tank:
[0090] Insert the inoculation ratio of 1:10 into a 30L fermenter that has been pre-sterilized and equipped with 15L batch fermentation medium, and carry out fed-batch culture (use ammonia water to control the pH at 4.0, and the temperature is controlled at 30°C). After the carbon source is exhausted (DO rises sharply, within 1 minute), glycerol is added in a stream (the flow rate maintains dissolved oxygen greater than 20%). When the wet weight of the bacteria is about 200 g / L, stop feeding, and after the glycerin is exhausted, add methanol to induce expression (control the pH at 5.8 with ammonia water, and control the temperature at 20°C), by adjusting the rotation speed, tank pressure, air flow and The feeding rate was such that the dissolved oxygen was greater than 20%, and the induction time was 60 hours. At...
Embodiment 2
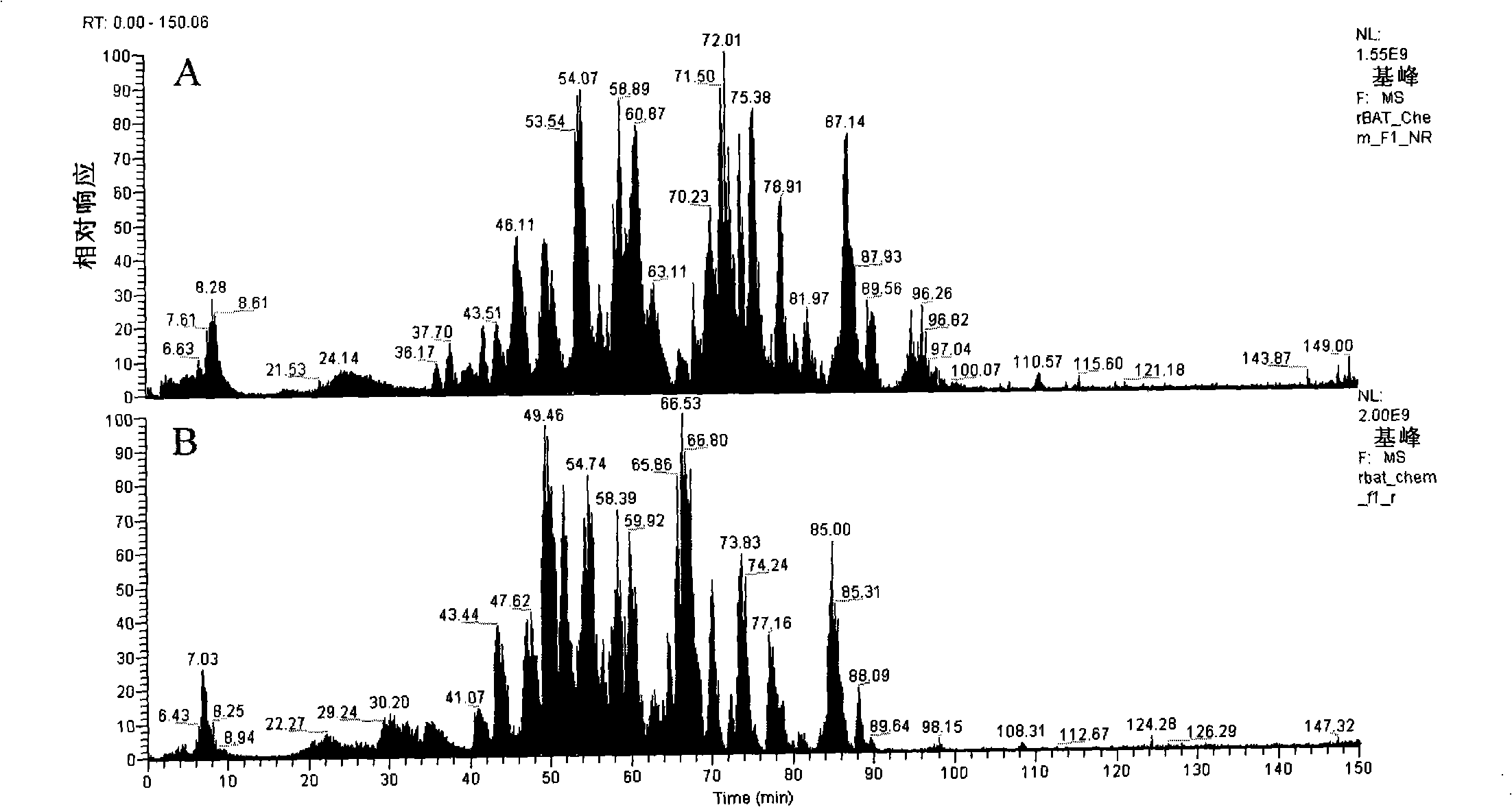
[0097] performance example
[0098] Detect the rBAT stock solution I prepared in Example 1:
[0099] 1. The main parameters of the experiment:
[0100] Detection instrument model: LCQ DECA XP plus Sampling method: Microspray
[0101] Capillary temperature: 170°C Column: 0.15MM*150MM (RP-C18)
[0102] Instrument company: FINNIGAN Detection method: Positive ion
[0103] 2. Experimental method:
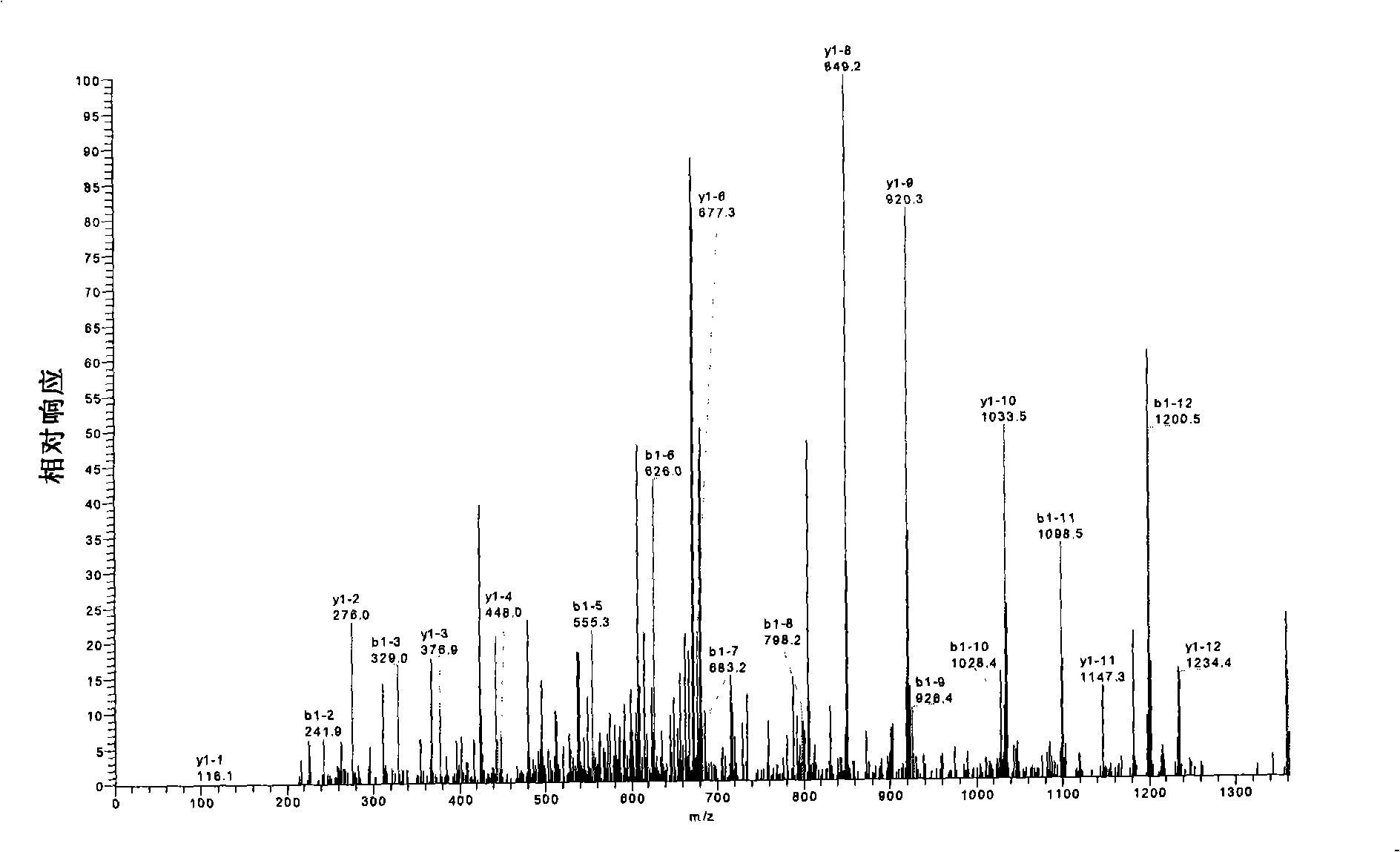
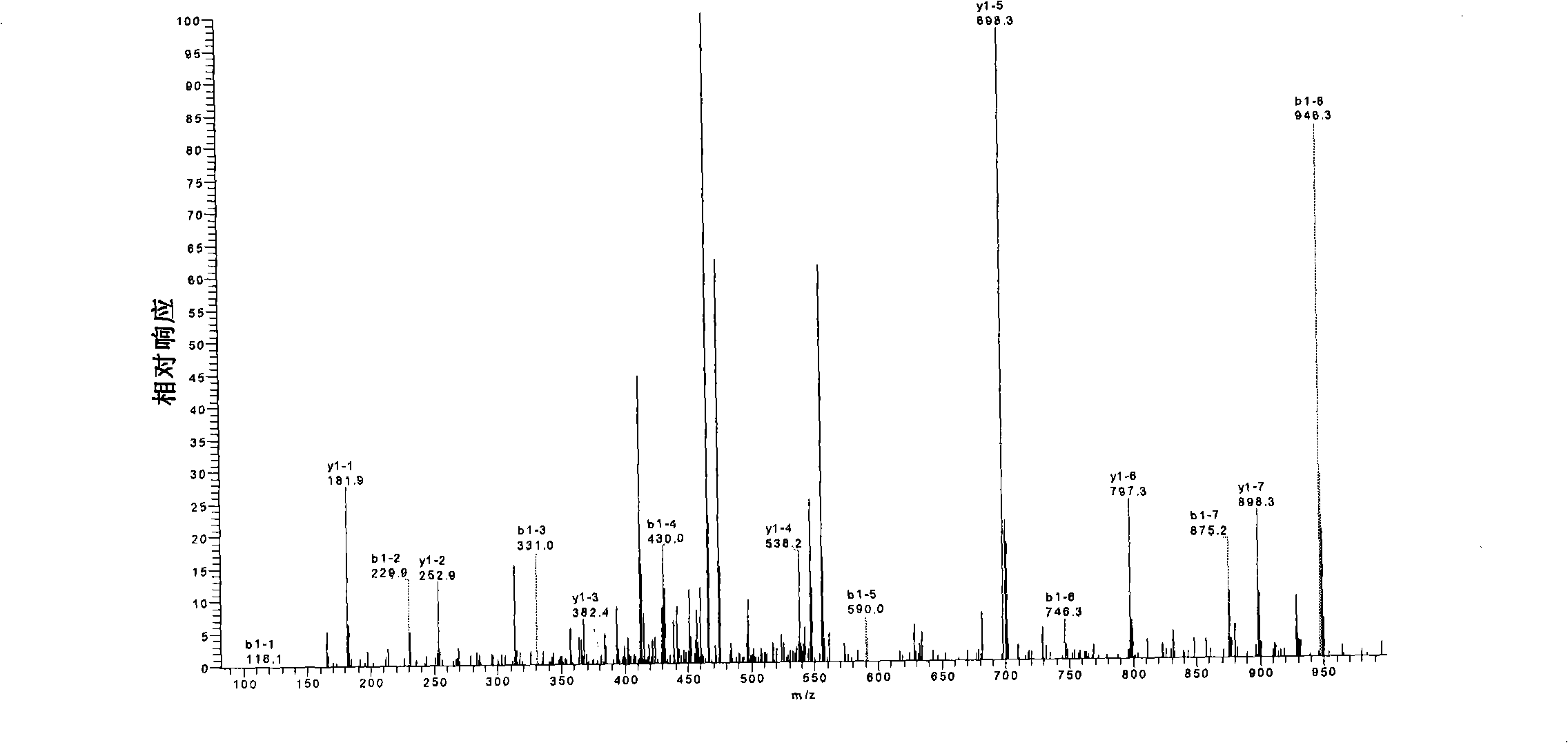
[0104] Sample rBAT was desalted by ultrafiltration, modified with iodoacetamide (IAA) → enzymatic hydrolysis with trypsin and chymotrypsin → enzymatic hydrolysis with N-glycosidase F and F1 → 1 / 2 enzymatic hydrolysis product dithiothreo Sugar alcohol (DTT) reduction, IAA modification→mass spectrometry analysis→data analysis, determine the C-terminal sequence, glycosylation site and disulfide bond pairing mode of rBAT protein.
[0105] 3. Experimental results and analysis:
[0106] 3.1 C-terminal sequence analysis
[0107] The principle of protein C-terminal sequence mass spectrome...
Embodiment 3
[0123] Purification process research example
[0124] 1. Study on hydrophobic chromatography conditions
[0125] Since the fermentation uses an inorganic salt medium (pH value around 6.0), the fermentation supernatant contains higher salt and higher conductivity, so it is desired to use hydrophobic chromatography as the first step of purification to obtain crude and pure rBAT.
[0126] 1.1 Study on Hydrophobic Chromatography Conditions at pH6.0
[0127] Take 100ml of the fermentation supernatant respectively, and proceed as follows:
[0128] Fermentation supernatant volume
(ml)
(ml)
Volume of water for injection
(ml)
total capacity
(ml)
Ammonium sulfate final concentration
(M)
Group A
100
150
50
300
1.5
Group B
100
100
100
300
1.0
Group C
100
50
150
300
0.5
[0129] For group...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com