Application of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) as biological dosemeter of ionizing radiation
A high mobility, biological dose technology, applied in dosimeters and other directions, can solve the problems of time-consuming, expensive and laborious
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
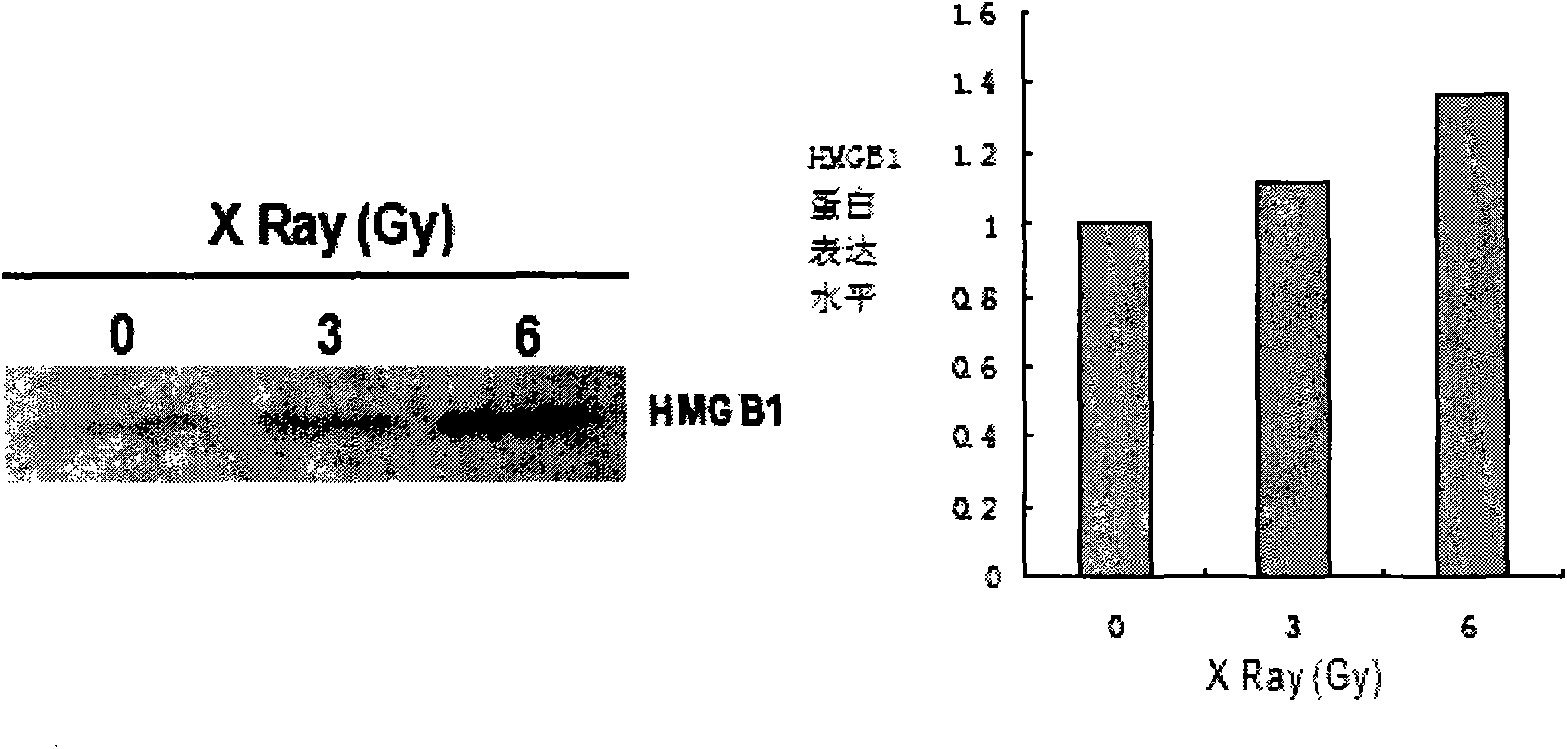
[0019] Dose-effect relationship of HMGB1 protein release in culture medium of mouse fibroblasts cultured in vitro with different doses of ionizing radiation
[0020] (1) Materials: mouse fibroblast cell line L929 was purchased from the American Cell Collection Center (ATCC), and was preserved and cultured by our laboratory; RPMI 1640 medium dry powder, calf serum, and trypsin were purchased from Gibco; amicon ultrafiltration Centrifuge tubes were purchased from Millipore, USA. Standard protein molecular weight, SDS-PAGE loading buffer, RIPA protein lysate, TE electrophoresis buffer, 10× transfer solution, 30% Acry-Bis, Tris-Hcl, ammonium persulfate (AP), SDS, tetramethyl Ethylenediamine (TEMED) was purchased from Jiangsu Beyantian Biotechnology Research Institute; dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), agarose and Tween-20 were purchased from Shanghai Hi-Tech Bioengineering Co., Ltd.; anti-HMGB1 and other antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruzs Biotechnology, USA technology company. ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Dose-effect relationship of HMGB1 protein release in human peripheral anticoagulated whole blood with different doses of ionizing radiation
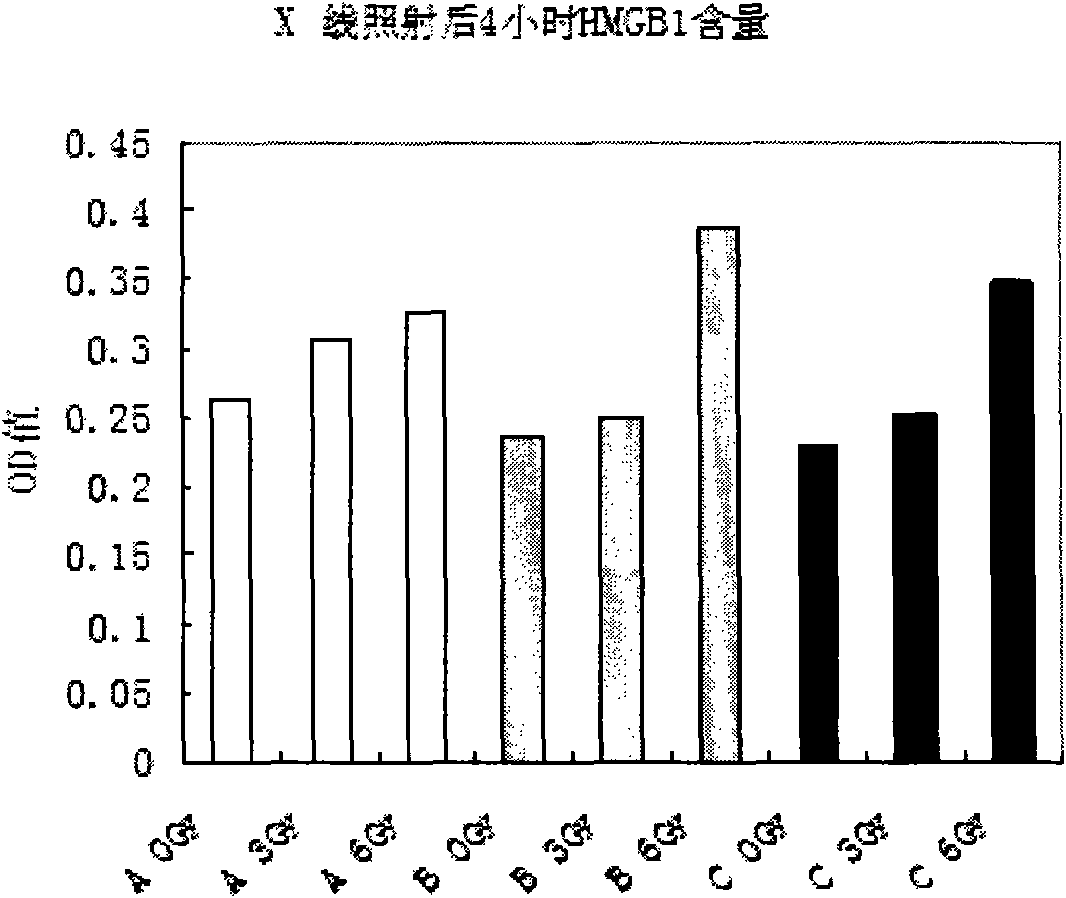
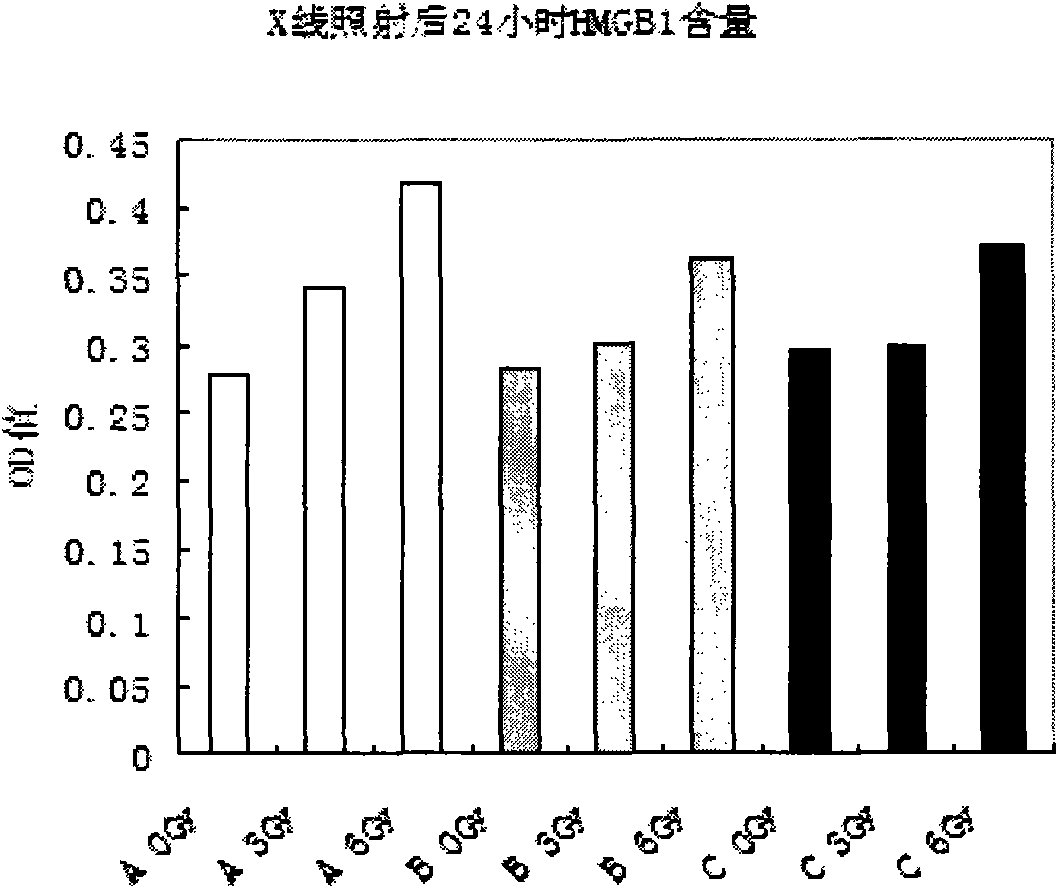
[0027] (1) Human peripheral blood collection, human anticoagulant peripheral venous blood used in the experiment came from 3 healthy blood donors, 1 male and 2 female, aged about 30 years old, requirements: no smoking, no drinking, good health, no history of chronic diseases, within half a year Free from irradiated and inflammatory diseases. 20ml of blood was collected from each person, divided into 6 vials, and subjected to 0, 3, and 6Gy of x-rays at room temperature, and then left to stand at 37°C for 4h and 24h to collect plasma samples.
[0028] (2) ELISA method to determine the amount of HMGB1 protein in the human peripheral anticoagulated whole blood sample obtained in step (1): For the operation steps, refer to the kit instruction manual. Afterwards, it was reacted at 37°C for 2 hours, the sample solution was discarded, an...
Embodiment 3
[0033] (1) GM cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% calf serum, glutamine and 1 million U / L penicillin and streptomycin.
[0034] (2) using different dosage levels 60 Co gamma ray irradiation step (1) obtained GM cell culture fluid, according to the method of embodiment two, adopts ELISA method to detect the change of HMGB1 protein content in the cell culture fluid after irradiation: 24h directly collects the supernatant of cell culture fluid after irradiation, according to the implementation The method of Example 2, using ELISA method to detect the content of HMGB1 wherein, the results are shown in Table 1, Figure 4 shown.
[0035] As shown in Table 1, the content of HMGB1 in the culture medium gradually increased with the increase of irradiation dose: compared with the unirradiated control group, the content of HMGB1 in each irradiation dose group increased significantly (0.5Gy, 1Gy, 2Gy and 4Gy irradiation groups P <0.05, P<0.01 in the 8Gy irradiation gr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com