Biomass liquefaction method in presence of coupling action of subcritical/supercritical cyclohexane and molecular sieve
A supercritical and biomass technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biofuels, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve the problems of corrosion, harsh reaction conditions, and poor thermal stability of bio-oil, etc. The effect of mild reaction conditions and low critical pressure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Take 20 g of dried corn stalk powder with a particle size of 40-60 mesh, 1 g of molecular sieve catalyst (this example uses a commercially available molecular sieve mainly containing REUSY-type zeolite, and the product number provided by the manufacturer is BCR-2), 20 ml Pure cyclohexane was added into a batch-type autoclave with a volume of 1 L and equipped with a magnetic stirrer, sealed and heated to 310 °C, and kept at this temperature for 0.5-80 min. Cool to room temperature and collect the product. Products that are gaseous at normal temperature and pressure are gas phase products. Wash the inner wall of the reactor with absolute ethanol to obtain a solid-liquid product, place it at room temperature and wait for the ethanol to dry up, add distilled water to extract water-soluble organic matter, that is, light oil, use a vacuum pump to filter, and use a rotary evaporator to evaporate the filtrate to remove water. The remaining substances are water-soluble organic ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Using the same method and steps as in Example 1, the difference is that no molecular sieve catalyst is added.
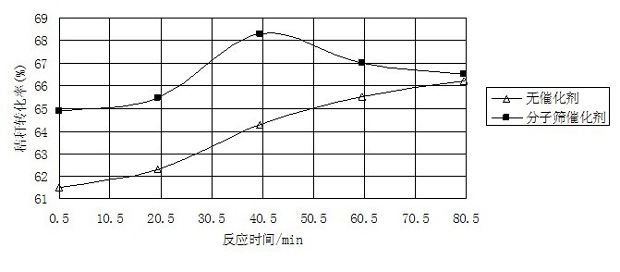
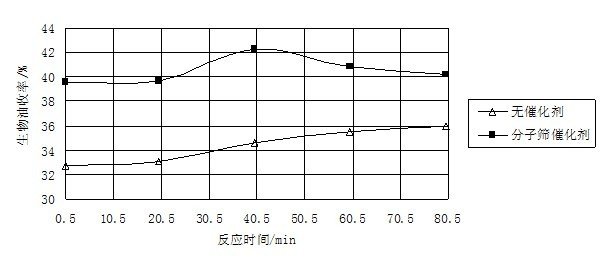
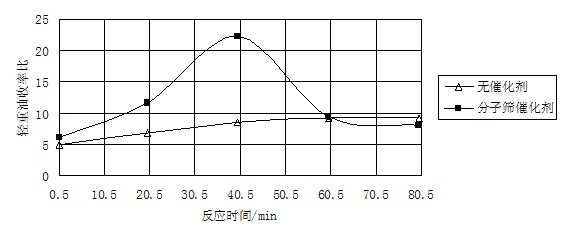
[0039] The experimental results are shown in Table 4 and attached figure 1 As shown, the data in Table 4 show that in the cyclohexane medium under sub / supercritical conditions, with the increase of the reaction time, the yield of bio-oil, light oil yield and conversion rate of corn stalks obtained after the conversion of corn stalks were all the same. Gradually increase. When the reaction time is 80 min, the conversion rate of straw can reach 66.22%, the yield of bio-oil is 35.92%, and the yield ratio of light and heavy oil is 9.26.
[0040] Table 4 Liquefaction results of corn stover under the action of sub / supercritical cyclohexane
[0041]
[0042] attached figure 1 It shows that in the sub / supercritical cyclohexane medium, without the presence of molecular sieve catalyst, the conversion rate of corn stover increases with the reaction time; under the ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Table 5 Liquefaction results of corn stover under the coupling action of sub / supercritical cyclohexane and molecular sieve
[0048]
[0049] The data in Table 5 shows that under the coupling action of cyclohexane and molecular sieve catalyst under sub / supercritical conditions, the yield of bio-oil obtained after conversion of corn stover is higher with the increase of reaction temperature within 285-310 °C. , light oil yield and conversion all increase with the increase of reaction temperature. When the reaction temperature was 310 ℃, the straw conversion rate, bio-oil yield and light-to-heavy oil yield ratio all reached the highest values, which were 65.45%, 39.64% and 22.21, respectively.
[0050] Example 4
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com