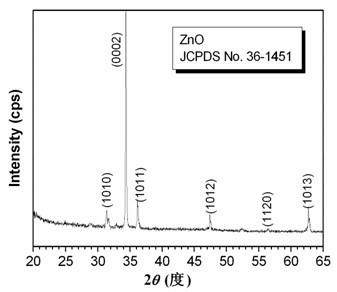
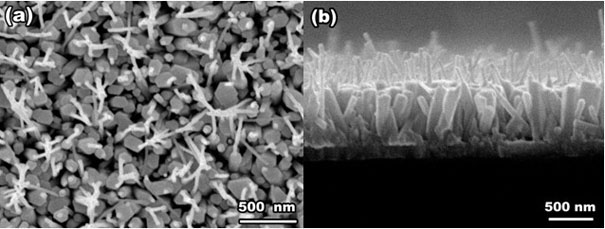
Preparation method of injector-shaped ZnO nanostructural array for field emission
A nanostructure and nanopillar array technology is applied in the field of preparation of a syringe-like ZnO nanostructure array for field emission, which can solve the problem that the aspect ratio of the tip portion of the one-dimensional ZnO nanostructure is difficult to implement effectively control, difficult to scale industrial production, High reaction temperature and other problems, to achieve the effect of easy industrial-scale implementation, improved electrical conductivity, and simple and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] (1) Dissolve analytically pure zinc nitrate hexahydrate in distilled water and keep stirring to prepare Zn 2+ A clear solution with a concentration of 0.005 mol / L, and the pH of the solution is controlled at 5.0±0.1 with NaOH or HCl, and the resulting solution is recorded as A;
[0025] (2) Using the A solution prepared above as the electrolyte, a three-electrode electrochemical deposition system (conductive glass as the working electrode, a platinum electrode as the counter electrode, and a saturated calomel electrode as the reference electrode) was used to directly grow ZnO on the conductive glass substrate. Nanopillar array; the deposition potential used is -0.5 V, the electrolyte temperature is 50 °C, and the deposition time is 30 min;
[0026] (3) Dissolve analytically pure zinc nitrate hexahydrate, hexamethylenetetramine and sodium fluoride in turn in a beaker containing distilled water, and keep stirring. The molar concentration ratio of the three is 1:1:1, wh...
Embodiment 2
[0031] (1) Dissolve analytically pure zinc nitrate hexahydrate in distilled water and keep stirring to prepare Zn 2+ A clear solution with a concentration of 0.005 mol / L, and the pH of the solution is controlled at 5.0±0.1 with NaOH or HCl, and the resulting solution is recorded as A;
[0032] (2) Using the A solution prepared above as the electrolyte, a three-electrode electrochemical deposition system (conductive glass as the working electrode, a platinum electrode as the counter electrode, and a saturated calomel electrode as the reference electrode) was used to directly grow ZnO on the conductive glass substrate. Nanopillar array; the deposition potential used was -1.1 V, the electrolyte temperature was 50 °C, and the deposition time was 30 min;
[0033] (3) Dissolve analytically pure zinc nitrate hexahydrate, hexamethylenetetramine and sodium fluoride in turn in a beaker containing distilled water, and keep stirring. The molar concentration ratio of the three is 1:1:2,...
Embodiment 3
[0038] (1) Dissolve analytically pure zinc nitrate hexahydrate in distilled water and keep stirring to prepare Zn 2+ A clear solution with a concentration of 0.005 mol / L, and the pH of the solution is controlled at 5.0±0.1 with NaOH or HCl, and the resulting solution is recorded as A;
[0039] (2) Using the A solution prepared above as the electrolyte, a three-electrode electrochemical deposition system (conductive glass as the working electrode, a platinum electrode as the counter electrode, and a saturated calomel electrode as the reference electrode) was used to directly grow ZnO on the conductive glass substrate. Nanopillar array; the deposition potential used was -1.5 V, the electrolyte temperature was 50 °C, and the deposition time was 30 min;
[0040] (3) Dissolve analytically pure zinc nitrate hexahydrate, hexamethylenetetramine and sodium fluoride in turn in a beaker containing distilled water, and keep stirring. The molar concentration ratio of the three is 1:1:2,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com