Method for production of polyester copolymer using genetically modified microorganism
A technology of a recombinant microorganism and a manufacturing method, applied in the field of manufacturing copolyester, can solve the problems of unfavorable raw material cost, low yield of productive carbon source and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0193] use LA high accumulation Escherichia coli to produce copolyester
[0194] (1) Production of recombinant microorganisms
[0195] Genomic DNA was extracted from M. elsdenii (ATCC17753) using the DNeasy Tissue Kit (Qiagen), and a nucleic acid encoding propionyl-CoA transferase (Accession No. J04987) was synthesized by PCR to include an EcoRI recognition sequence. The primer DNA of the forward primer and the reverse primer containing the PstI recognition sequence. Using the above-mentioned genomic DNA as a template, use iCycler (BioRad), in the environment containing KOD-Plus-DNA polymerase (1U), PCR buffer, 1mM MgSO 4 , 15 pmol of each primer, and 0.2 mM dNTPs (all manufactured by Toyobo Co., Ltd.), one cycle was performed at 94°C for 2 minutes, followed by 1 cycle at 94°C for 15 seconds, 55°C for 30 seconds, and 68°C for 2 minutes. One cycle of PCR reaction was carried out for 30 cycles, and then the amplified fragment of about 1,500 bp was recovered and digested with ...
Embodiment 2
[0242] Production using highly LA-accumulating microorganisms
[0243] (1) Production of polymers
[0244] The pTV118NPCTC1(ST / QK)AB1 prepared in (1) of Example 1 was used to transform Escherichia coli Jw2293 strain, Jw0885 strain, and Jw0886 strain with high accumulation of lactic acid.
[0245] The obtained transformant was inoculated into 1000 ml of LB medium containing 100 μg / ml ampicillin, 2% glucose, and 10 mM pantothenic acid, and cultured at 37° C. for 72 hours. After culturing, the cells were collected by centrifugation at 4°C, 3,100 rpm, and 15 minutes, suspended in 10 mM Tris-hydrochloric acid buffer (pH 7.5), centrifuged again under the same conditions, and then freeze-dried for 2 sky.
[0246] Move the dried bacteria to a glass pressure-resistant reaction tube, add 40ml of chloroform to make a suspension, then keep it in a micro-thermostat at 100°C for 3 hours, then cool it to room temperature, and filter it with a 0.2μm PTFE filter (ADVANTEC) , to separate the ...
Embodiment 3
[0280] Manufacture of copolyester by culturing under anaerobic conditions
[0281] (1) Construction of the carrier
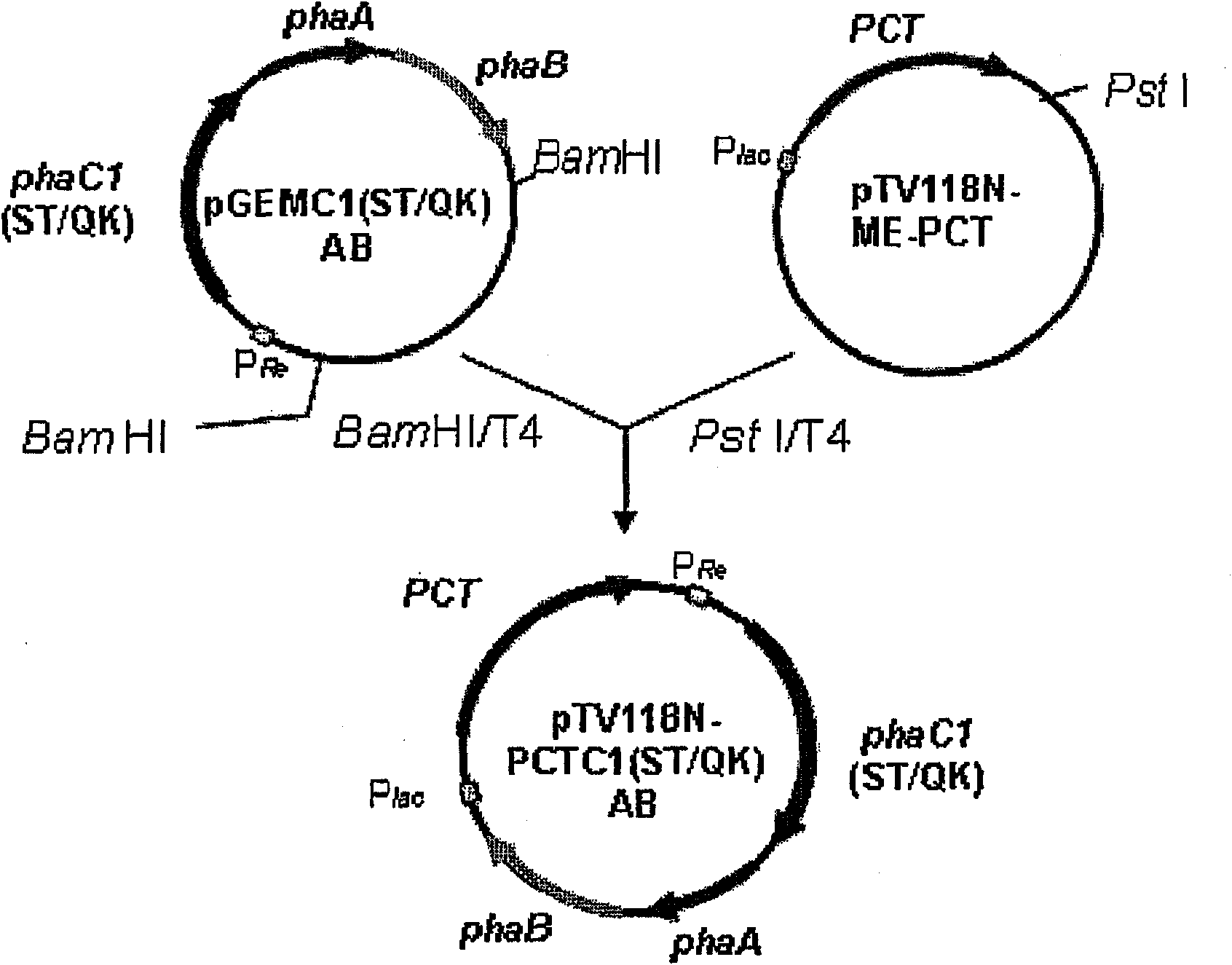
[0282] Using the pTV118NPCTC1(ST / QK)AB produced in (1) of Example 1 as a template, PCR was performed to obtain a linear plasmid in which the gene encoding βKT and the gene encoding AACoA-R were removed, so that the obtained amplified fragment Circularization, thereby making the plasmid pTV118NpctC1(ST / QK) having the gene encoding Pct and the gene encoding PhaCm in pTV118N ( Figure 16 Left).
[0283] The pGEMC1AB prepared in (1) of Example 1 was digested with the restriction enzyme BamHI, and the obtained DNA fragment of about 3,200 base pairs was digested with the linear chain obtained by digesting the pACYC177 DNA, which is a low-copy plasmid, with the restriction enzyme BamHI. Like vector plasmid connection, thereby obtains the plasmid pACYC177AB that the gene encoding βKT and the gene encoding AACoA-R have been introduced into the BamHI site of pACYC177DN...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystallinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com