Screening of high-yield glycine strains and application thereof in nitrile compound conversion
A glycine and compound technology, applied in fungi, fermentation and other directions, can solve the problem of no mold and other problems, and achieve the effects of environmental friendliness, mild reaction conditions, convenient and fast product separation and application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 Isolation and Identification of Fusarium oxysporum H3 and Preservation of the Strain
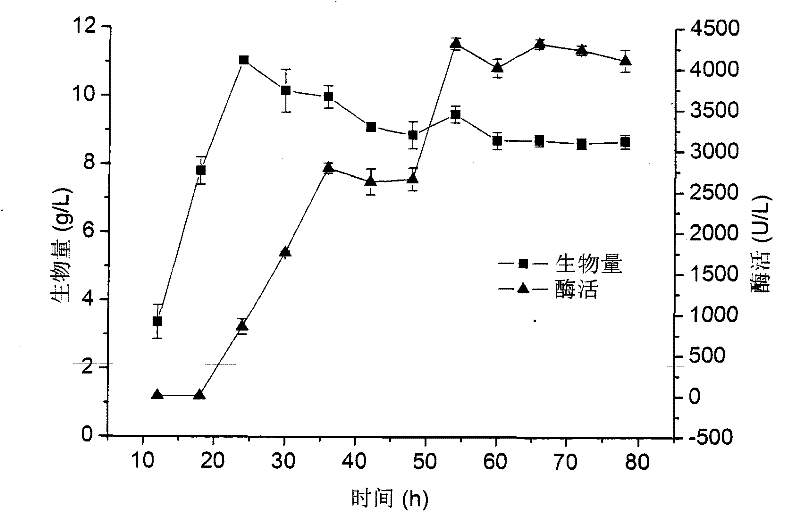
[0036] (1) Enrichment screening process of Fusarium oxysporum H3.
[0037] Collect soil samples around the nitrile compound production plant. When sampling, first remove the top soil with a small shovel, and collect soil samples at 5-15cm. Take 1g of soil sample, put it into an Erlenmeyer flask (20mL / 250mL) containing physiological saline, shake it vigorously for 10min, and let it stand still. Take 1mL of soil suspension, inject it on a sterile plate, and pour 25mL of sterilized and cooled to 40-50°C solid screening medium into the plate. After the culture medium was completely cooled and solidified, the plate was placed in a constant temperature incubator and cultured upside down at 30°C for 3 days. The composition of solid screening medium is: glucose 5.0g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.0g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.1g / L, ferrous sulfate 0.02g / L, calcium chloride 0.02g / ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2 Fusarium oxysporum (Fusarium oxysporum H3) fermentation method for producing glycine
[0056] This example illustrates the method of culturing Fusarium oxysporum H3 into a nutrient-rich medium to obtain bacteria with high activity and high biomass, and the method of biotransforming glycylnitrile to produce glycine.
[0057] The composition of the medium: glycerol 10.0g / L, yeast extract 1.0g / L, peptone 1.0g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.1g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.0g / L, sodium chloride 0.5g / L, sulfite Iron 0.01g / L, caprolactam 0.5g / L, pH 7.5;
[0058] Insert Fusarium oxysporum H3 into the culture medium with 1% inoculum amount, and cultivate it for 3 days at 30°C and 120rpm. After the cultivation is over, collect the cultured cells by centrifuging at 12000rpm for 10min, and wash them with 0.5M phosphoric acid. The bacteria were washed twice with the buffer, and the bacteria were resuspended in the buffer to prepare the bacteria suspension.
[0059] Pre...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3 Change of fermentation conditions, Fusarium oxysporum (Fusarium oxysporum H3) fermentation to produce glycine
[0061] This embodiment adopts the same method as in embodiment 2, changing the reaction time.
[0062] The bacteria were collected from the culture medium by centrifugation, washed twice with 0.5M phosphate buffer, resuspended to make a bacterial suspension, mixed with 7.8g / L glycyl nitrile solution, at 30°C, 120rpm After 12 hours of reaction, the concentration of glycine in the reaction liquid was 8.5 g / L, and the yield reached 80%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com