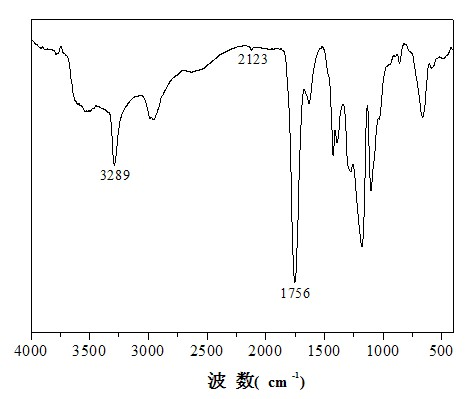
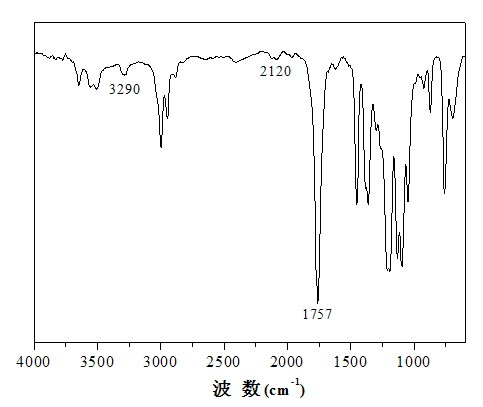
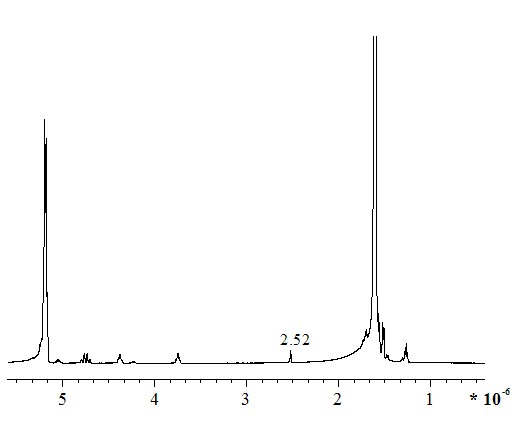
Biological functionalization degradable polyester and preparation method thereof
A technology for biological functionalization and degradation of polyester, applied in organic chemistry, bulk chemical production, etc., can solve problems such as difficult high-density biological modification and unsatisfactory biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Step (1): Add ethyl glyoxylate, bromobutyne and magnesium in toluene solvent at a molar ratio of 1:1:0.8, stir and react at 25°C for 32 hours, filter with a sand core funnel after the reaction is completed, and the organic layer Wash and extract with dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, and dilute hydrochloric acid solution in sequence, and dry the organic layer with anhydrous magnesium sulfate until it is washed with ethyl acetate / n-hexane=60 / 40 ( v / v ) as a developing agent for thin-layer chromatography separation, until the iodine gas chromogenic method shows that the reaction is complete, it is separated by silica gel chromatography column, and the organic solvent is removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a light yellow liquid.
[0053] Step (2): After the reaction in step (1) is completed, add the light yellow product obtained in step (1) in diethyl ether at a molar ratio of 1.1:1.0:0.8, 2- Bromopropionyl chloride and triethylamine were stirred at 40°C for 8 hours. ...
Embodiment 2
[0059]Step (1): Add butyl glyoxylate, propyne bromide and sodium in chloroform at a molar ratio of 1.1:1.1:0.8, stir and react at 25°C for 18 hours, filter with a sand core funnel after the reaction is complete, organic layer was extracted with toluene, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate until ethyl acetate / n-hexane = 70 / 30 ( v / v ) as a developing agent for thin-layer chromatography separation, until the iodine gas chromogenic method shows that the reaction is complete, it is separated by silica gel chromatography column, and the organic solvent is removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a light yellow liquid.
[0060] Step (2): After the reaction in step (1) is completed, add the light yellow product obtained in step (1), bromoacetyl chloride and pyridine in dimethylformamide at a molar ratio of 1.1:1.2:1.1, and stir at 40°C for 8h After the reaction is completed, filter with a sand core funnel, distill off the organic solvent under reduced pressure, extract with tolue...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Step (1): Add ethyl glyoxylate, chloropropane azide and Grignard reagent in chloroform at a molar ratio of 1:1.2:1.1, stir and react at 25°C for 24 hours, and use a sand core after the reaction is completed Filter through a funnel, extract the organic layer with ether, and dry over anhydrous magnesium sulfate until ethyl acetate / n-hexane = 50 / 50 ( v / v ) as a developer for thin-layer chromatography separation, until the 1,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine chromogenic method shows that the reaction is complete, it is separated by silica gel chromatography column, and the organic solvent is removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a light brown liquid.
[0067] Step (2): After the reaction in step (1) is completed, add the light brown product obtained in (1) to dimethylformamide at a molar ratio of 1.0:1.3:1.5, 2- Bromoacetyl chloride and sodium bicarbonate were stirred at 20°C for 36 hours. After the reaction was completed, filter with a sand core funnel, wash with distilled hyd...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com