Non-refrigeration infrared detector
An uncooled infrared and detector technology, applied in the direction of electric radiation detectors, manufacturing microstructure devices, piezoelectric devices/electrostrictive devices, etc., can solve the problem of pixel failure, large difference in thermal insulation performance, and influence on correction effects, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
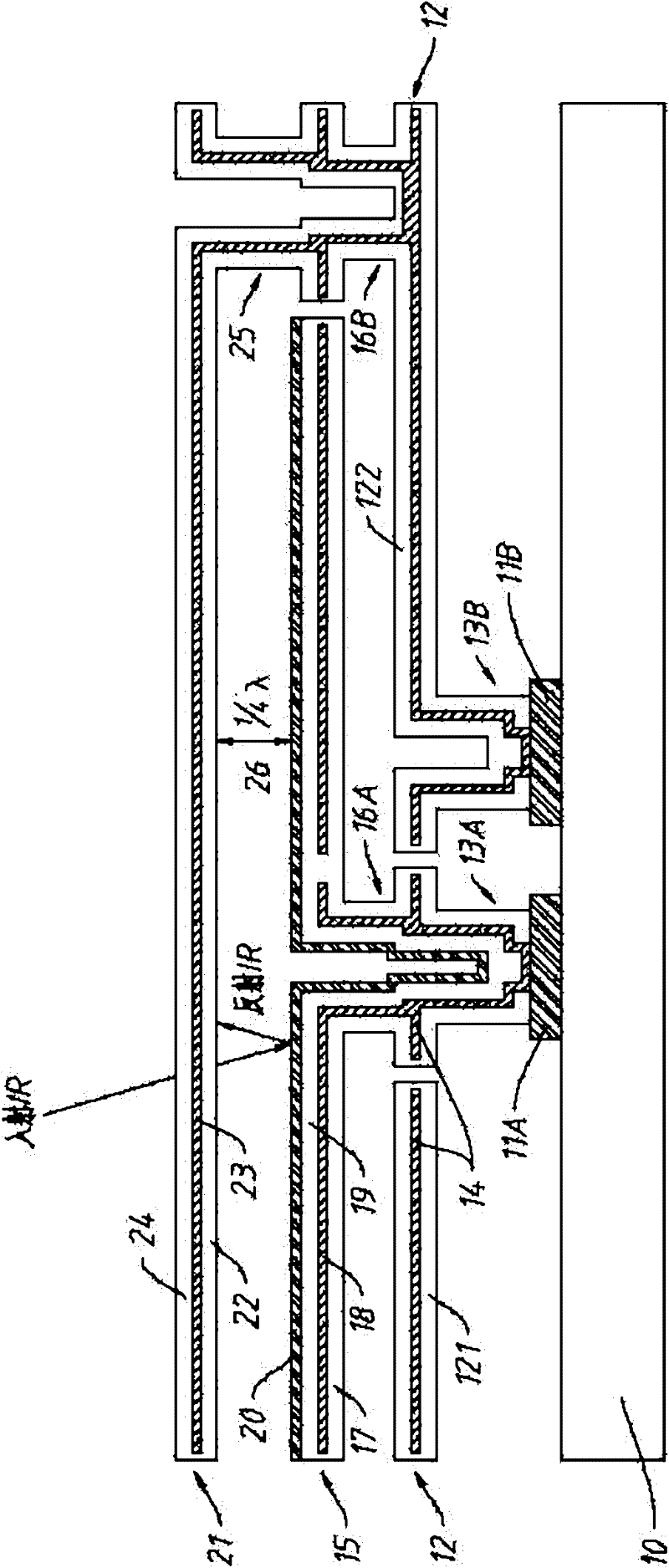
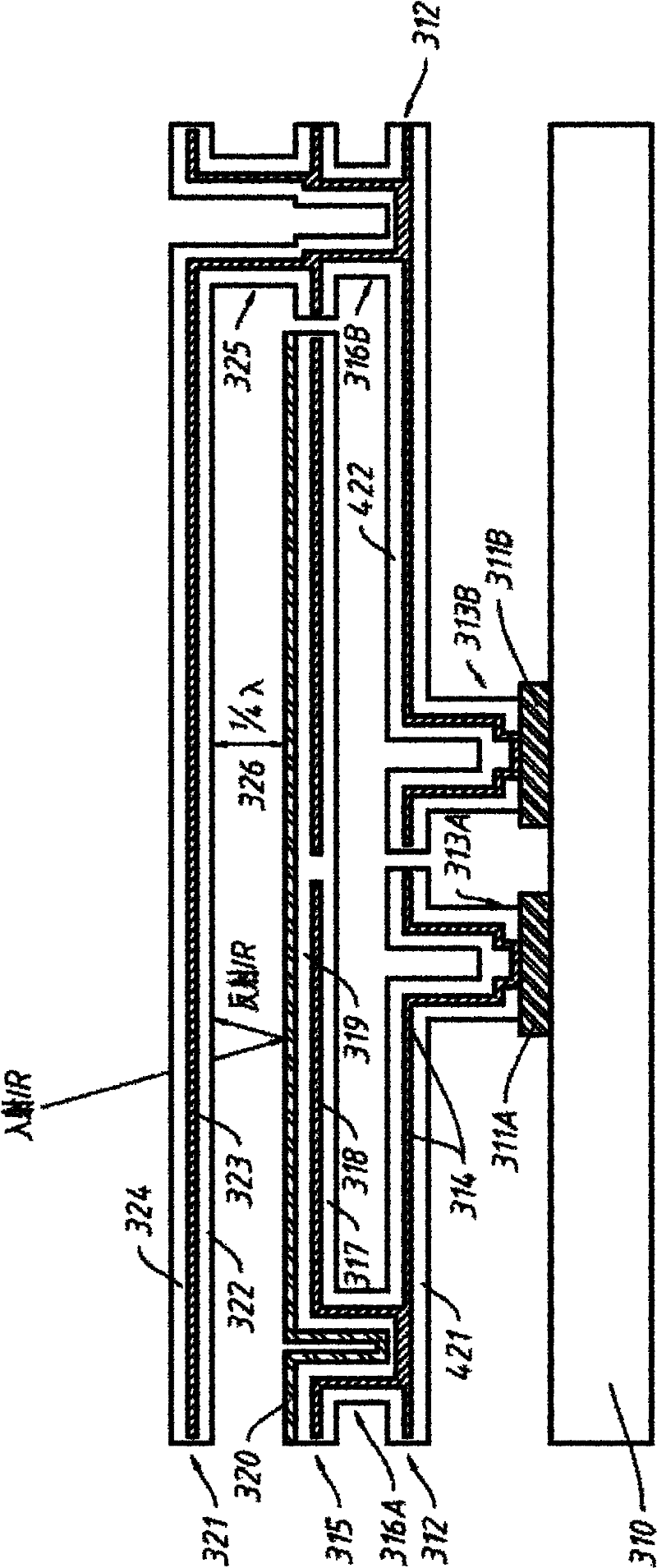
[0092] attached figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view of the first detector microbridge structure provided by the present invention, including:
[0093] The semiconductor substrate 10 is characterized by including various circuits (not explicitly shown in the figure) for signal detection of the uncooled detector, commonly referred to in the industry as a readout circuit (ROIC). The substrate 10 is generally made of single crystal silicon, but other semiconductor materials can also be used. The readout circuit is generally fabricated by a CMOS process.
[0094] The metal plates 11A and 11B for the electrical connection between the micro-bridge structure and the ROIC are generally made of CMOS materials such as aluminum or aluminum alloys, copper, and tungsten. The metal discs 11A and 11B can be completed together with the ROIC through a CMOS process, or can be implemented during the detector processing process. in the attached figure 1 Four metal discs are set up in total, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com